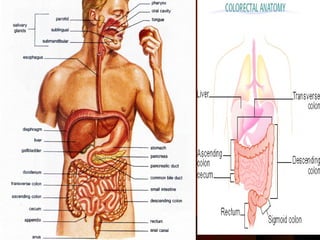
1oesophagus
- 1. 11
- 2. NORMAL ESOPHAGUSNORMAL ESOPHAGUS The normal esophagus is a hollow, highly distensible muscular tubeThe normal esophagus is a hollow, highly distensible muscular tube that extends from the pharynx to the gastroesophageal junction at thethat extends from the pharynx to the gastroesophageal junction at the level of the T11level of the T11 Length of about - 25 cmLength of about - 25 cm 22
- 3. A 3-cm segment in the proximal esophagus at the level of theA 3-cm segment in the proximal esophagus at the level of the cricopharyngeus muscle is referred to as the upper esophagealcricopharyngeus muscle is referred to as the upper esophageal sphincter.sphincter. The 2- to 4-cm segment just proximal to the anatomic esophagogastricThe 2- to 4-cm segment just proximal to the anatomic esophagogastric junction, at the level of the diaphragm, is referred to as the lowerjunction, at the level of the diaphragm, is referred to as the lower esophageal sphincter (LES).esophageal sphincter (LES). Wall of the esophagus -mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria, andWall of the esophagus -mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria, and adventitiaadventitia Mucosa - nonkeratinizing stratified squamous epithelialMucosa - nonkeratinizing stratified squamous epithelial 33
- 4. DysphagiaDysphagia (subjective difficulty in swallowing)(subjective difficulty in swallowing) Is encountered both with deranged esophageal motor function andIs encountered both with deranged esophageal motor function and with diseases that narrow or obstruct the lumen.with diseases that narrow or obstruct the lumen. HeartburnHeartburn (retrosternal burning pain)(retrosternal burning pain) Usually reflects regurgitation of gastric contents into the lowerUsually reflects regurgitation of gastric contents into the lower esophagus.esophagus. 44
- 5. EsophagitisEsophagitis Inflammation of the esophagusInflammation of the esophagus CausesCauses Heavy smoking & ingestion of hot tea, alcohol, corrosive acid orHeavy smoking & ingestion of hot tea, alcohol, corrosive acid or alkaliesalkalies Reflux of gastric contents (reflux esophagitis) - commonestReflux of gastric contents (reflux esophagitis) - commonest Bacterial, viral, fungalBacterial, viral, fungal UraemiaUraemia MicroscopicMicroscopic Hyperemia, edema, polymorphonuclear(immune cells that hasHyperemia, edema, polymorphonuclear(immune cells that has granules with enzyme) infiltrategranules with enzyme) infiltrate Stratified squamous epithelium may be thinned, necrosed or ulceratedStratified squamous epithelium may be thinned, necrosed or ulcerated 55
- 6. GASTRO-ESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)GASTRO-ESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD) is defined as chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by theis defined as chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by the abnormal reflux in the esophagusabnormal reflux in the esophagus PathophysiologyPathophysiology Occasional episodes of GE reflux are common in health.Occasional episodes of GE reflux are common in health. Normally Esophageal peristaltic waves clear the esophagus, alkalineNormally Esophageal peristaltic waves clear the esophagus, alkaline saliva neutralises residual acid, and symptoms do not occur.saliva neutralises residual acid, and symptoms do not occur. GE reflux disease develops when the oesophageal mucosa isGE reflux disease develops when the oesophageal mucosa is exposed to gastric contents for prolonged periods of time, resulting inexposed to gastric contents for prolonged periods of time, resulting in symptoms and in a proportion of cases, oesophagitis.symptoms and in a proportion of cases, oesophagitis. 66
- 7. Several factors are known to be involved .Several factors are known to be involved . Esophgeal antireflux mechanism is decreased (reduced lowerEsophgeal antireflux mechanism is decreased (reduced lower oesophageal sphincter tone)oesophageal sphincter tone) Presense of hiatus herniaPresense of hiatus hernia Increased gastric contents (intra-abdominal pressure rises.)Increased gastric contents (intra-abdominal pressure rises.) 77
- 8. 88
- 9. Congenital Anomalies –Atresia & fistulaCongenital Anomalies –Atresia & fistula AtresiaAtresia Congenital anomaly in which the esophagus ends in a blind pouchCongenital anomaly in which the esophagus ends in a blind pouch rather than connecting normally to the stomachrather than connecting normally to the stomach The esophagus is divided into two pouch blind, an upper and lower,The esophagus is divided into two pouch blind, an upper and lower, which may or may not communicate with the tracheobronchial tree,which may or may not communicate with the tracheobronchial tree, through fistulous tract called Tracheoesophageal Fistula (TEF).through fistulous tract called Tracheoesophageal Fistula (TEF). 99
- 10. ACHALASIAACHALASIA Motility disorder characterised by lose of normal peristalsis & failure toMotility disorder characterised by lose of normal peristalsis & failure to relax properly LES due to absence or reduction of ganglion cells ofrelax properly LES due to absence or reduction of ganglion cells of auerbach’s plexusauerbach’s plexus This produces functional obstruction of the esophagus, withThis produces functional obstruction of the esophagus, with consequent dilation of the more proximal esophagusconsequent dilation of the more proximal esophagus Achalasia is characterized by three major abnormalities:Achalasia is characterized by three major abnormalities: (1) aperistalsis,(1) aperistalsis, (2) partial or incomplete relaxation of the LES with swallowing, and(2) partial or incomplete relaxation of the LES with swallowing, and (3) increased resting tone of the LES.(3) increased resting tone of the LES. 1010
- 11. PathogenesisPathogenesis The pathogenesis of primary achalasia is poorly understood but isThe pathogenesis of primary achalasia is poorly understood but is thought to involve degenerative changes in neural innervation,thought to involve degenerative changes in neural innervation, either intrinsic to the esophagus or in the extraesophageal vaguseither intrinsic to the esophagus or in the extraesophageal vagus nerves and the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus.nerves and the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus. Secondary achalasia may arise in Chagas disease, in whichSecondary achalasia may arise in Chagas disease, in which Trypanosoma cruzi causes destruction of the myenteric plexus(majorTrypanosoma cruzi causes destruction of the myenteric plexus(major nerve supply to GIT) of the esophagus, duodenum, colon, and ureter,nerve supply to GIT) of the esophagus, duodenum, colon, and ureter, Most instances, achalasia occurs as primary disorder of uncertainMost instances, achalasia occurs as primary disorder of uncertain cause.cause. 1111
- 12. MorphologyMorphology Dilation of the esophagus above the level of obstructionDilation of the esophagus above the level of obstruction Muscle hypertrophy or markedly thinned by dilationMuscle hypertrophy or markedly thinned by dilation Mucosa may be ulceratedMucosa may be ulcerated Narrowing occurs at its lower endNarrowing occurs at its lower end 1212
- 13. Achalasia is characterized by the following symptoms and signs:Achalasia is characterized by the following symptoms and signs: Dysphagia (most common),Dysphagia (most common), RegurgitationRegurgitation Chest painChest pain HeartburnHeartburn Weight lossWeight loss 1313
- 14. HIATUS HERNIAHIATUS HERNIA Herniation of the stomach through the diaphragm into the chestHerniation of the stomach through the diaphragm into the chest Occurs in 30% of the population over the age of 50 yearsOccurs in 30% of the population over the age of 50 years Often asymptomaticOften asymptomatic Heartburn and regurgitation can occurHeartburn and regurgitation can occur 1414
- 15. TypesTypes Sliding types –Sliding types – Most common (95%)Most common (95%) Where the gastroesophageal junction moves above the diaphragmWhere the gastroesophageal junction moves above the diaphragm together with some of the stomachtogether with some of the stomach Rolling / (or paraesophageal) hiatus hernia,Rolling / (or paraesophageal) hiatus hernia, When a part of the stomach herniates through the esophageal hiatus andWhen a part of the stomach herniates through the esophageal hiatus and lies beside the esophagus, without movement of the gastroesophageallies beside the esophagus, without movement of the gastroesophageal junction.junction. 1515
- 16. Barrett's oesophagusBarrett's oesophagus Metaplasia of distal squamous epithelium to columnar epithelium, dueMetaplasia of distal squamous epithelium to columnar epithelium, due to long-standing gastroesophageal refluxto long-standing gastroesophageal reflux There may be ulceration with Bleeding.There may be ulceration with Bleeding. There may be associated dysplasia(enlargement of organs)There may be associated dysplasia(enlargement of organs) A precancerous lesion – adenocarcinoma(tumour) may ariseA precancerous lesion – adenocarcinoma(tumour) may arise 1616
- 17. LACERATIONS (MALLORY-WEISS SYNDROME)LACERATIONS (MALLORY-WEISS SYNDROME) Longitudinal tears in the esophagus at the esophagogastric junctionLongitudinal tears in the esophagus at the esophagogastric junction and are believed to be the consequence of severe retching.and are believed to be the consequence of severe retching. They are encountered most commonly in alcoholics, attributed toThey are encountered most commonly in alcoholics, attributed to episodes of excessive vomiting and refluxing of gastric contents inepisodes of excessive vomiting and refluxing of gastric contents in the setting of an alcoholic stupor.the setting of an alcoholic stupor. 1717
- 18. ESOPHAGEAL VARICESESOPHAGEAL VARICES Varices are tortuous dilated veins at the distal esophagus andVarices are tortuous dilated veins at the distal esophagus and proximal stomachproximal stomach Caused by increased portal pressure (most often due to cirrhosis),Caused by increased portal pressure (most often due to cirrhosis), (portal hypertension)(portal hypertension) Leading to increased pressure in the esophageal venous plexus;Leading to increased pressure in the esophageal venous plexus; may cause severe bleeding.may cause severe bleeding. 1818
- 19. MorphologyMorphology Varices-is dilated sub-mucosal veinVarices-is dilated sub-mucosal vein Varices appear as tortuous dilated veins lying primarily within theVarices appear as tortuous dilated veins lying primarily within the submucosa of the distal esophagus and proximal stomachsubmucosa of the distal esophagus and proximal stomach The net effect is irregular protrusion of the overlying mucosa into theThe net effect is irregular protrusion of the overlying mucosa into the lumen.lumen. When the varix is unruptured, the mucosa may be normal, but oftenWhen the varix is unruptured, the mucosa may be normal, but often it is eroded and inflamed because of its exposed position, furtherit is eroded and inflamed because of its exposed position, further weakening the tissue support of the dilated veins.weakening the tissue support of the dilated veins. Variceal rupture produces massive hemorrhage into the lumen, asVariceal rupture produces massive hemorrhage into the lumen, as well as suffusion of blood into the esophageal wall.well as suffusion of blood into the esophageal wall. 1919
- 20. Tumours of esophagusTumours of esophagus Benign – very rare & are almost always of connective tissue origin &Benign – very rare & are almost always of connective tissue origin & forms polyps around the lumen causing obstructionforms polyps around the lumen causing obstruction LeiomyomasLeiomyomas FibromasFibromas NeurofibromasNeurofibromas LipomasLipomas HaemangiomasHaemangiomas LymphangiomasLymphangiomas Squamous papillomasSquamous papillomas 2020
- 21. MALIGNANT TUMORSMALIGNANT TUMORS Malignant esophageal tumors arise from the epithelial layer.Malignant esophageal tumors arise from the epithelial layer. Most commonMost common Squamous cell carcinomaSquamous cell carcinoma Adeno carcinomaAdeno carcinoma For many years, most esophageal cancers were of squamous cellFor many years, most esophageal cancers were of squamous cell origin, but there has been a declining incidence of these tumorsorigin, but there has been a declining incidence of these tumors coupled with a steadily increasing incidence of adenocarcinomas.coupled with a steadily increasing incidence of adenocarcinomas. Upper third (10% of esophageal cancers)Upper third (10% of esophageal cancers) Middle third (40%)Middle third (40%) Lower third (50%)Lower third (50%) 2121
- 22. Squamous Cell CarcinomaSquamous Cell Carcinoma Most squamous cell carcinomas occur in adults over age 50.Most squamous cell carcinomas occur in adults over age 50. The incident is higher in male than female.The incident is higher in male than female. 2222
- 23. Aetiopathogenesis –Aetiopathogenesis – MultifactoralMultifactoral Esophageal DisordersEsophageal Disorders - Long-standing esophagitis- Long-standing esophagitis - Achalasia- Achalasia - Plummer-Vinson syndrome (, ID anemia, glossitis)- Plummer-Vinson syndrome (, ID anemia, glossitis) Life-styleLife-style - Alcohol consumption, Tobacco abuse- Alcohol consumption, Tobacco abuse DietaryDietary - Deficiency of vitamins (A, C, riboflavin, thiamine, pyridoxine)- Deficiency of vitamins (A, C, riboflavin, thiamine, pyridoxine) - Deficiency of trace metals (zinc, molybdenum)- Deficiency of trace metals (zinc, molybdenum) - Fungal contamination of foodstuffs (Aspergillus flavus – aflatoxin)- Fungal contamination of foodstuffs (Aspergillus flavus – aflatoxin) - High content of nitrites/nitrosamines- High content of nitrites/nitrosamines Genetic PredispositionGenetic Predisposition 2323
- 24. MorphologyMorphology Starts as carinoma in situ - small, gray-white, plaque like thickenings orStarts as carinoma in situ - small, gray-white, plaque like thickenings or elevations of the mucosa.elevations of the mucosa. When invasive one of three forms:When invasive one of three forms: (1)(1) polypoid exophytic massespolypoid exophytic masses that protrude into the lumen;that protrude into the lumen; (2) necrotizing cancerous(2) necrotizing cancerous ulcerationsulcerations that extend deeply andthat extend deeply and sometimes erode into the respiratory tree, aorta, or elsewhere; andsometimes erode into the respiratory tree, aorta, or elsewhere; and (3)(3) diffuse infiltrative neoplasmsdiffuse infiltrative neoplasms that cause thickening and rigiditythat cause thickening and rigidity of the wall and narrowing of the lumen.of the wall and narrowing of the lumen. Whichever the pattern, about 20% arise in the cervical and upper thoracicWhichever the pattern, about 20% arise in the cervical and upper thoracic esophagus, 50% in the middle third, and 30% in the lower third.esophagus, 50% in the middle third, and 30% in the lower third. 2424
- 25. HistologyHistology Shows different degrees of differentiations – most are wellShows different degrees of differentiations – most are well differentiateddifferentiated 2525 Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus showing invasion into the submucosa
- 26. AdenocarcinomaAdenocarcinoma The great majority of esophageal adenocarcinoma arise in the lowerThe great majority of esophageal adenocarcinoma arise in the lower third of the esophagus in the setting of pre-existant Barrett'sthird of the esophagus in the setting of pre-existant Barrett's esophagusesophagusPathogenesisPathogenesis The evolution of esophageal adenocarcinoma follows the followingThe evolution of esophageal adenocarcinoma follows the following path:path: reflux esophagitis - metaplastic Barrett's esophageal mucosareflux esophagitis - metaplastic Barrett's esophageal mucosa -glandular epithelial dysplasia - adenocarcinoma-glandular epithelial dysplasia - adenocarcinoma 2626
- 27. MorphologyMorphology They are usually in the distal one-third of the esophagus and mayThey are usually in the distal one-third of the esophagus and may invade the subjacent gastric cardia.invade the subjacent gastric cardia. Initially appearing as flat or raised patches on an otherwise intactInitially appearing as flat or raised patches on an otherwise intact mucosa, they may develop intomucosa, they may develop into large nodular masseslarge nodular masses or showor show deeplydeeply ulcerativeulcerative oror diffusely infiltrativediffusely infiltrative features.features. 2727
- 28. Microscopically,Microscopically, Mucous-producing glandular tumors showing gastric or intestinal-Mucous-producing glandular tumors showing gastric or intestinal- type of glandstype of glands 2828 Esophageal Dysplasia Barrett's Esophagus. Esophageal Adenocarcino
- 29. SpreadSpread Local spreadLocal spread Into adjacent mediastinal structuresInto adjacent mediastinal structures Distant spread / MetastasisDistant spread / Metastasis Upper 3Upper 3rdrd – cervical lymph nodes– cervical lymph nodes Middle 3Middle 3rdrd - mediastinal & tracheo bronchial nodes- mediastinal & tracheo bronchial nodes Lower 3Lower 3rdrd – gastric group of nodes– gastric group of nodes 2929
- 30. Clinical FeaturesClinical Features Esophageal carcinoma is insidious in onset and producesEsophageal carcinoma is insidious in onset and produces dysphagia and obstruction gradually and late.dysphagia and obstruction gradually and late. Weight loss, anorexia, fatigue, and weakness appear, followed byWeight loss, anorexia, fatigue, and weakness appear, followed by pain, usually related to swallowing.pain, usually related to swallowing. Diagnosis is usually made by imaging techniques and endoscopicDiagnosis is usually made by imaging techniques and endoscopic biopsy.biopsy. Because these cancers extensively invade the rich esophagealBecause these cancers extensively invade the rich esophageal lymphatic network and adjacent structures relatively early in theirlymphatic network and adjacent structures relatively early in their development, surgical excision is rarely curative.development, surgical excision is rarely curative. Esophageal cancer confined to the mucosa or submucosa isEsophageal cancer confined to the mucosa or submucosa is amenable to surgical treatment.amenable to surgical treatment. 3030
