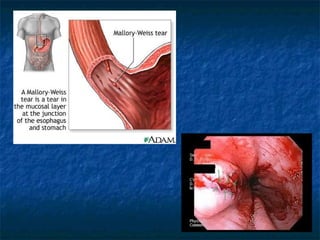
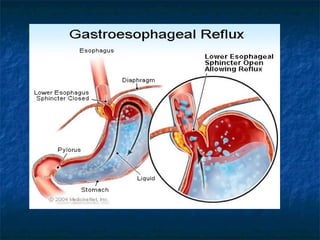
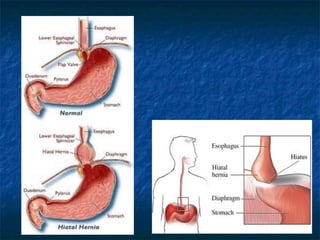
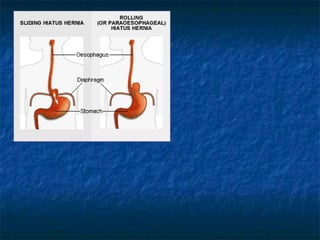
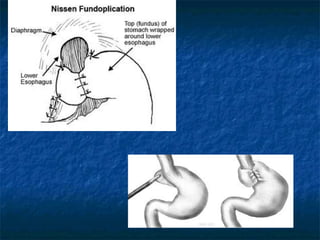
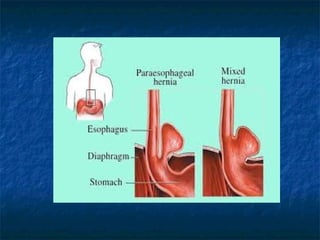
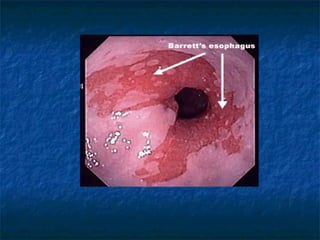
Mallory-Weiss syndrome and corrosive injury are caused by vomiting and corrosive ingestion respectively, leading to tears in the gastric mucosa or esophagus. GERD is caused by reflux of gastric acid into the esophagus due to incompetence of the lower esophageal sphincter, resulting in inflammation and ulcers. Hiatal hernia is a protrusion of the stomach through the esophageal hiatus that can cause reflux. Barret's esophagus is a complication of longstanding GERD where the esophageal mucosa is replaced by intestinal metaplasia, increasing the risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma.