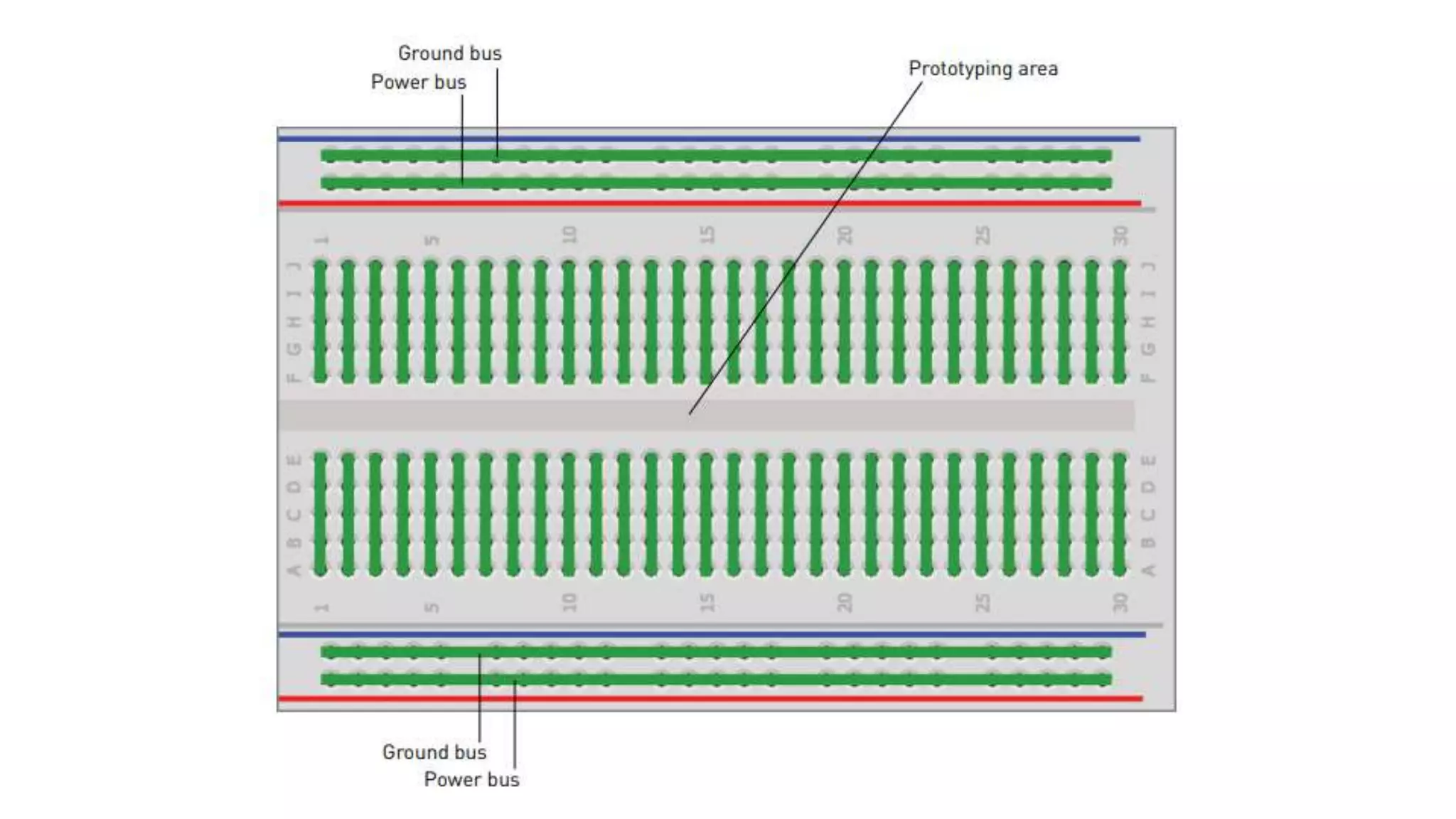
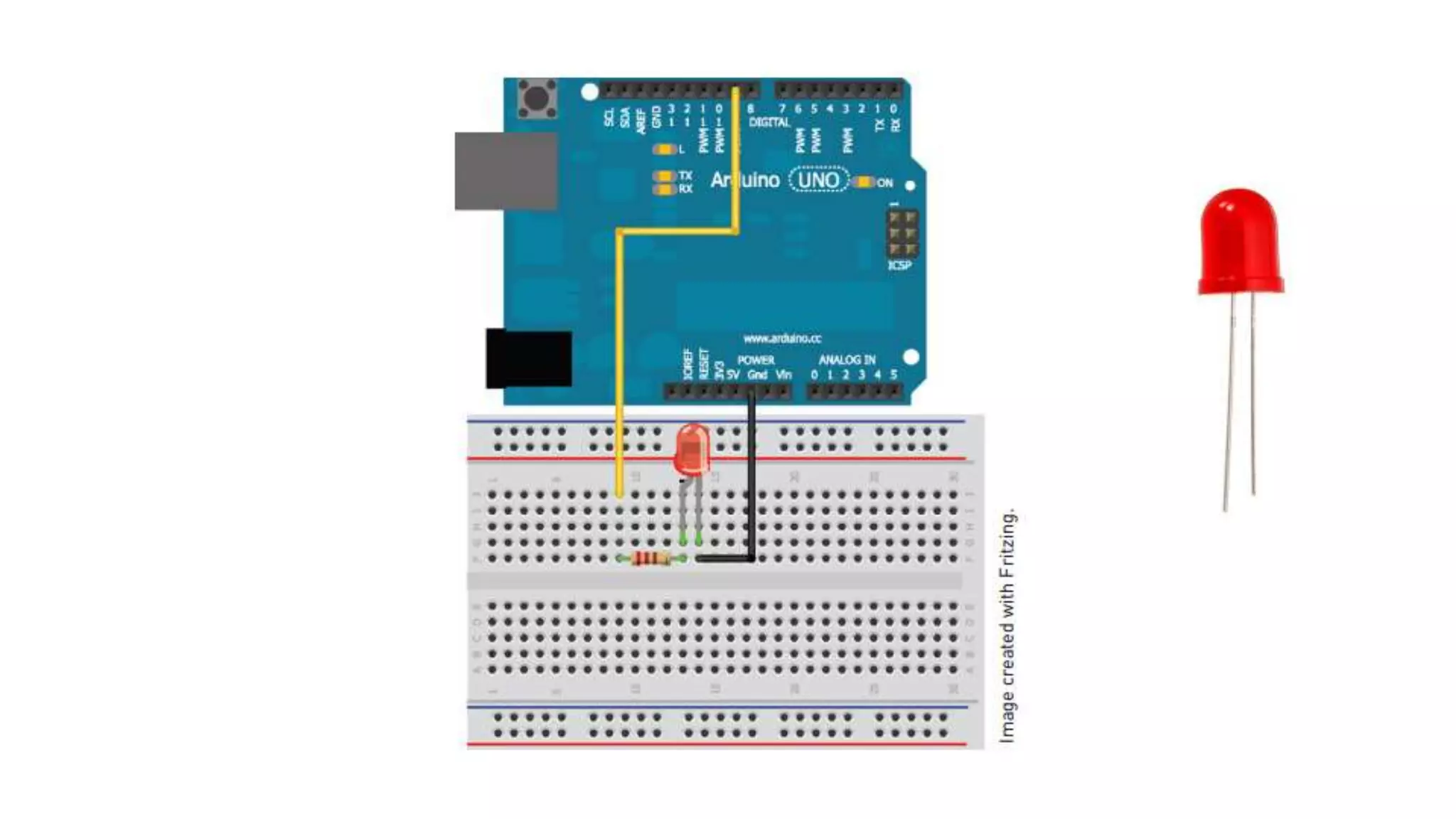
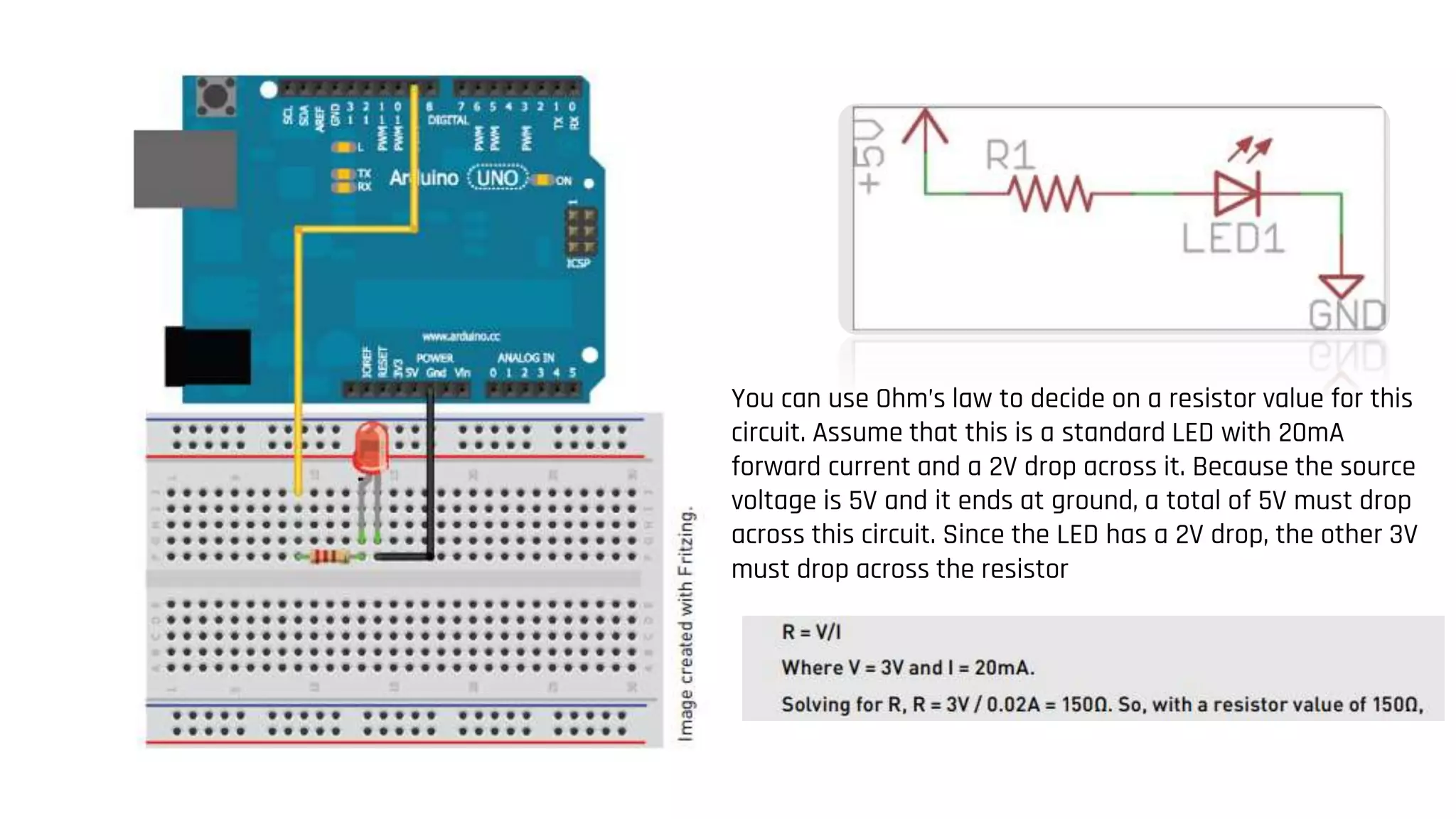
The document provides an overview of the Arduino prototyping platform. It discusses the main components of Arduino including the Arduino board itself, external hardware like sensors and actuators, and the Arduino IDE. It describes the key capabilities of Arduino boards like the ATmel microcontroller, I/O pins, and programming interfaces. The Arduino can be used to build all kinds of projects from automatic plant watering systems to quadcopter autopilots by connecting various external hardware and programming it using the Arduino IDE.