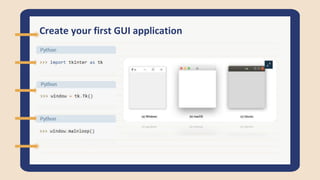
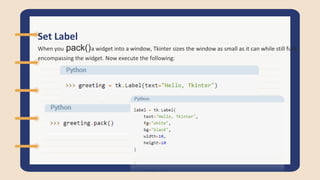
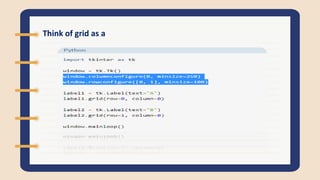
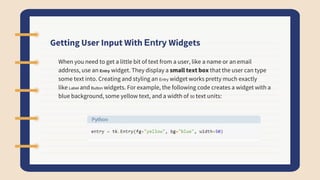
The document discusses Tkinter, a Python GUI package. It describes how to create basic GUI elements like labels, buttons, and entry widgets to get user input. It also covers geometry managers for laying out widgets and getting/setting widget properties.