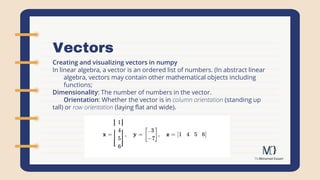
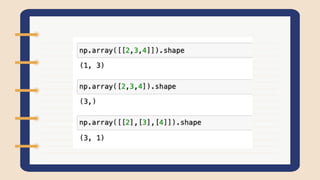
Linear algebra has a history dating back to the 17th century, with matrices originally used to store sets of numbers like geometric coordinates and systems of equations. In the 20th century, matrices and vectors were applied to multivariate mathematics, physics, economics and more. Modern linear algebra is computational and taught through coding applications in graphics, statistics, data science and AI, as computers efficiently work with matrices. Vectors are ordered lists of numbers that can be added by summing corresponding elements, and the dot product of vectors can be calculated using NumPy's np.dot() function.