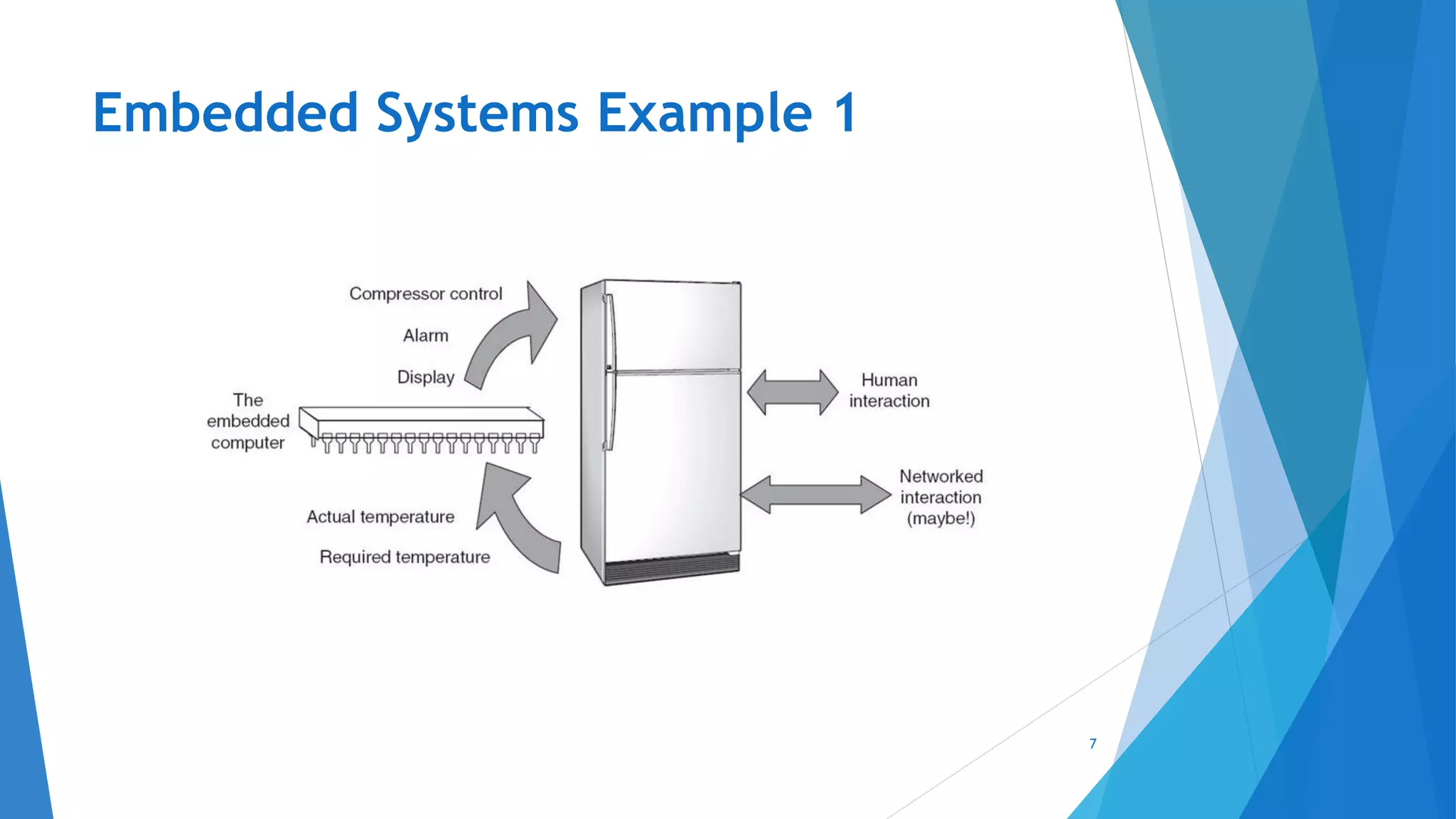
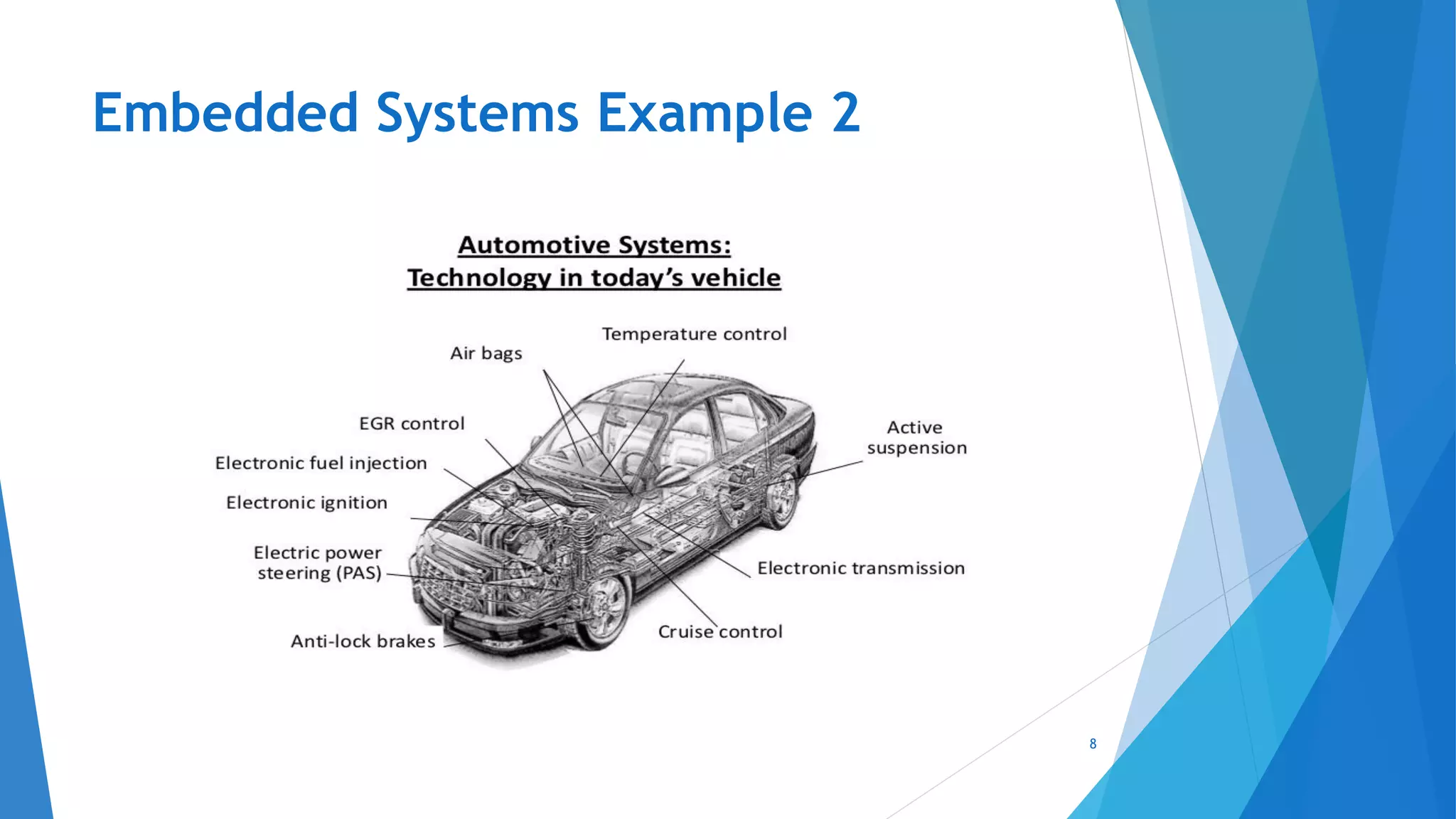
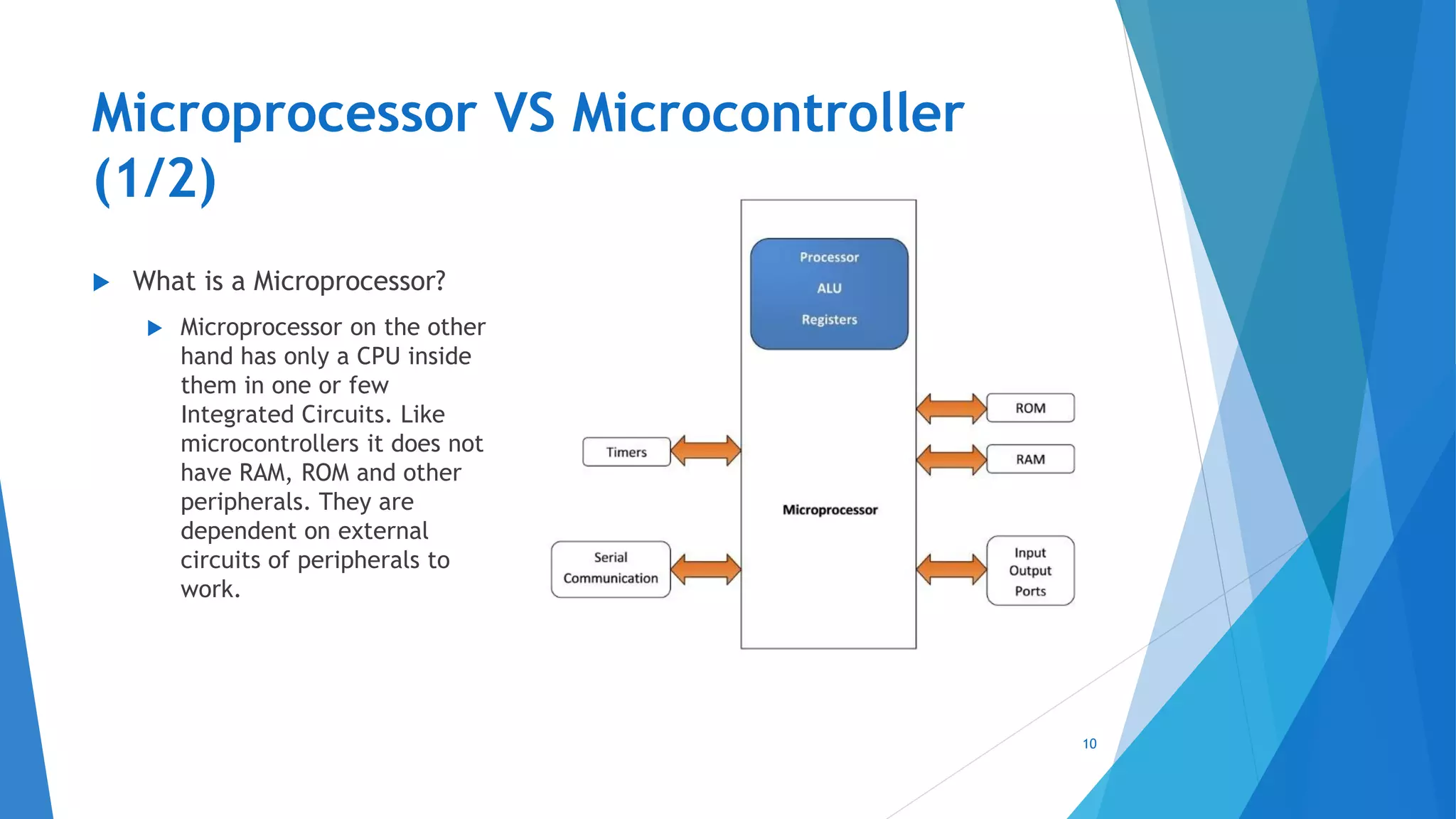
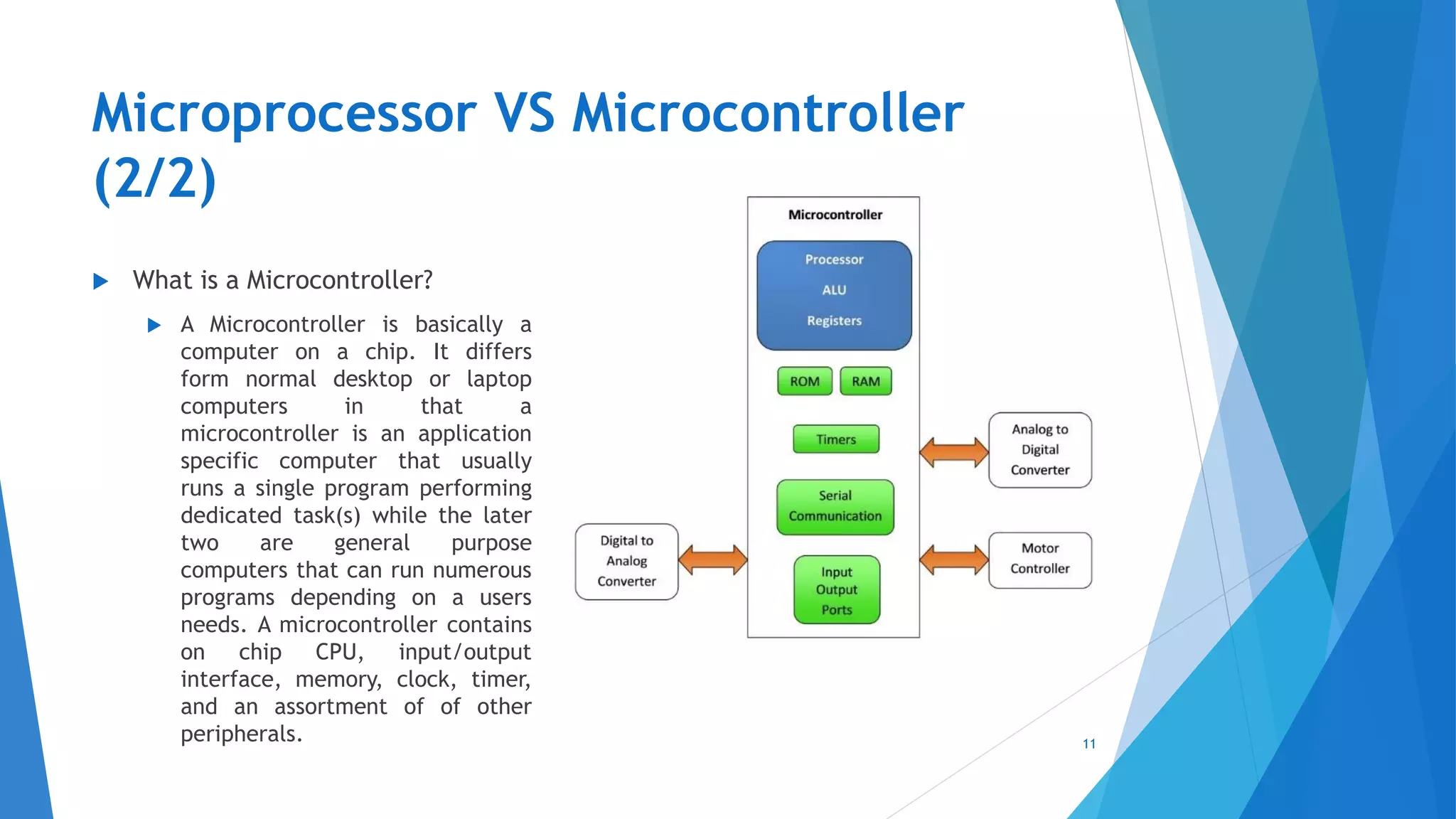
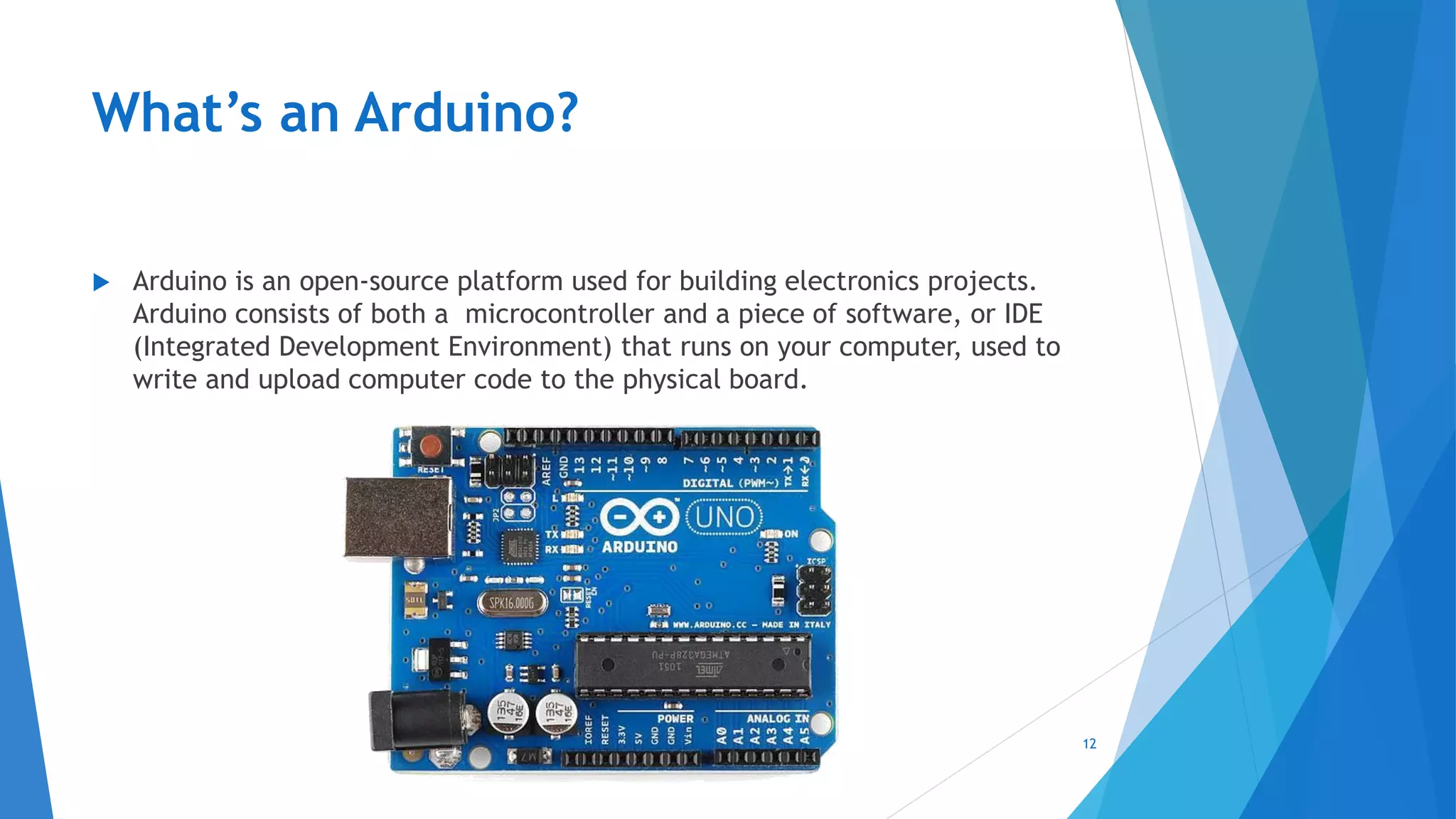
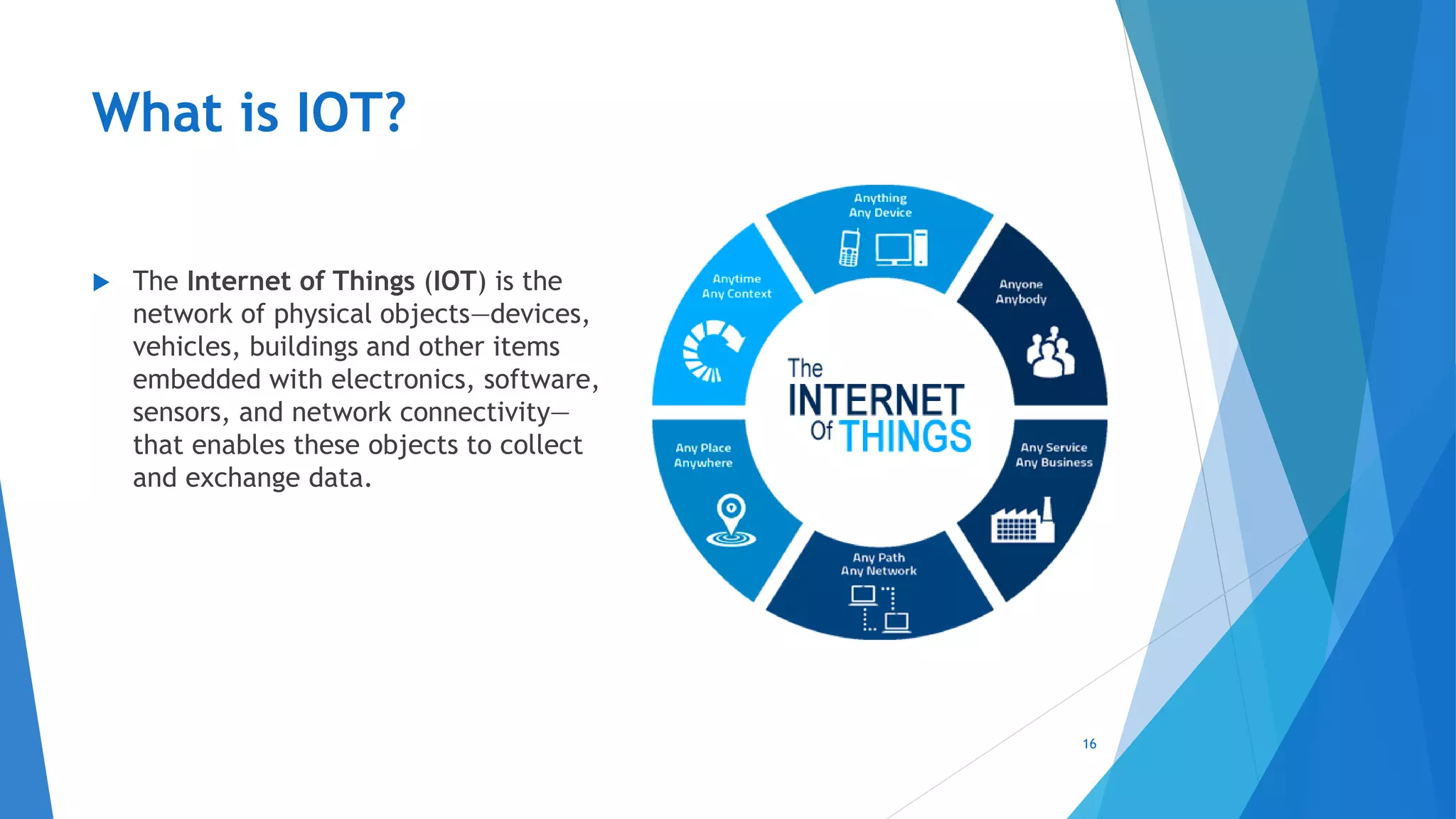
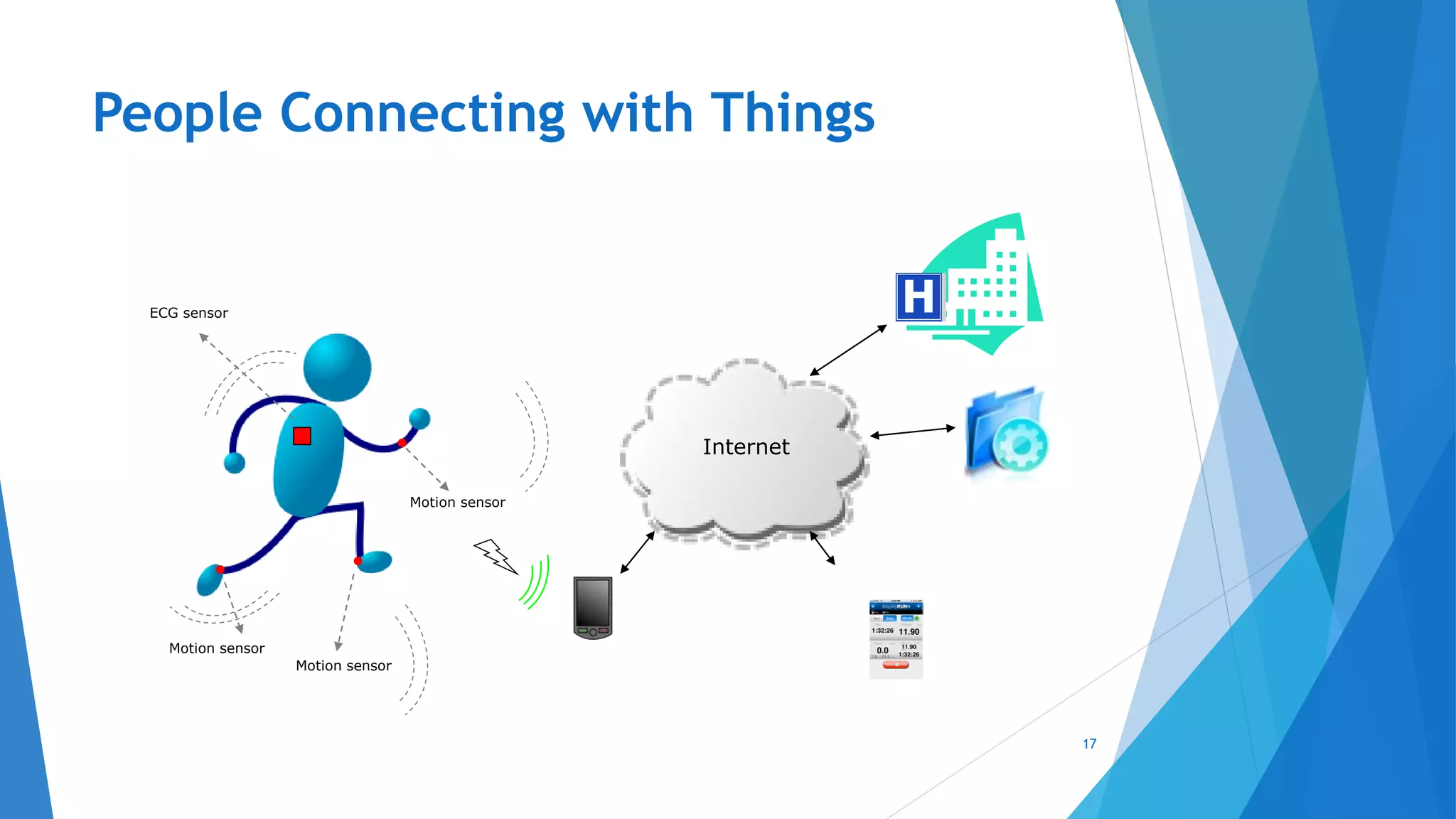
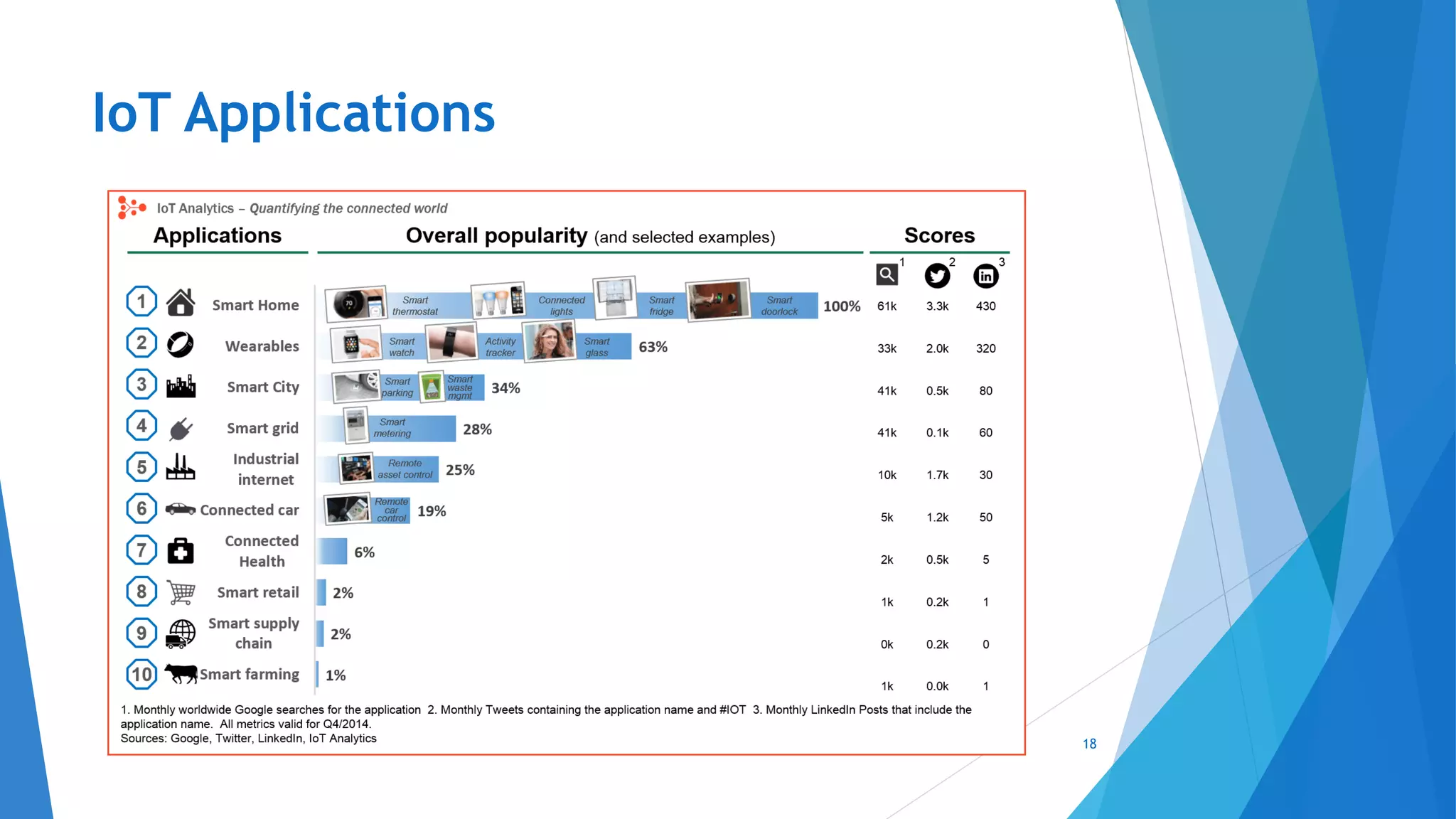
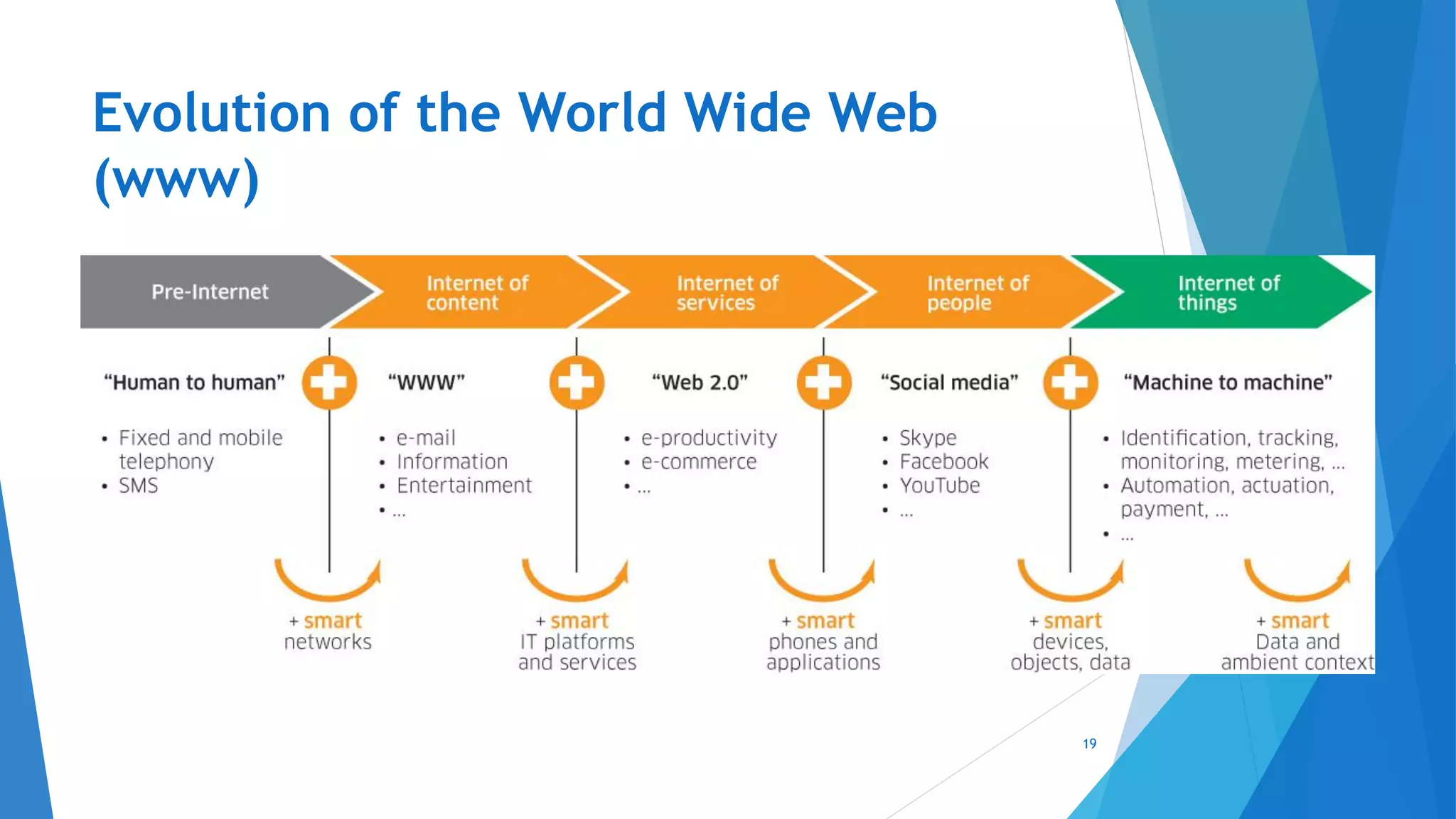
This document provides an introduction to embedded systems and the Internet of Things (IoT). It defines embedded systems as hardware and software components that perform dedicated tasks as part of larger machines. Embedded systems are designed for specific tasks without human intervention and must meet real-time performance constraints. Examples are given of embedded systems applications. It then discusses microprocessors versus microcontrollers. The document introduces Arduino, an open-source hardware and software platform used to build electronics projects, and describes its various components. It defines IoT as the network of physical objects embedded with electronics that collect and share data over the internet. Applications and evolution of IoT are briefly outlined.