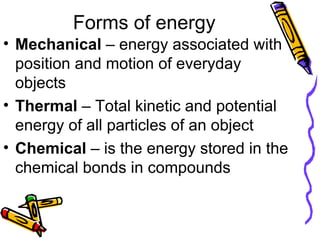
The document discusses different forms of energy including kinetic energy, which depends on an object's mass and speed, and potential energy, which can be gravitational or elastic. It provides examples of calculating kinetic energy for a flying bird and gravitational potential energy for a diver. The document also categorizes the main forms of energy as mechanical, thermal, chemical, electrical, electromagnetic, and nuclear, and notes that nuclear power plants use nuclear energy to generate electricity by splitting atoms to heat water and spin turbines.