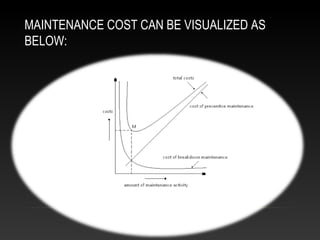
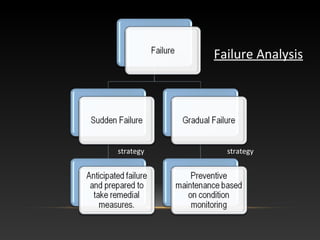
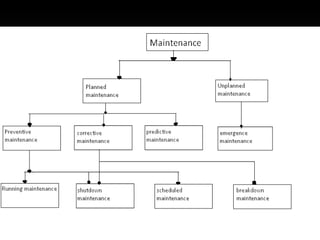
This presentation discusses maintenance management. It introduces the objectives of maintenance, which include increasing reliability, enabling quality, maximizing equipment life, and minimizing costs and interruptions. It describes the different types of maintenance, including preventive, corrective, predictive, running, scheduled, shutdown, and breakdown maintenance. It also outlines some of the benefits of failure statistics as well as limitations. Additionally, it examines maintenance costs, which can be visualized as costs associated with downtime, spare parts, labor, inefficient operations, and replacements.