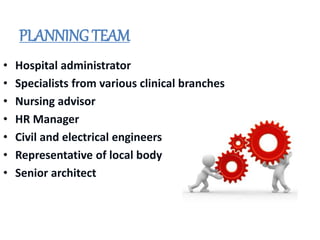
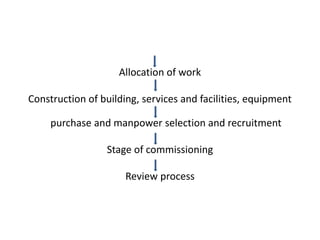
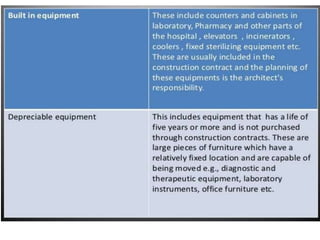
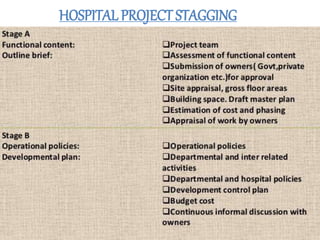
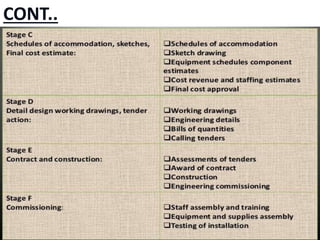
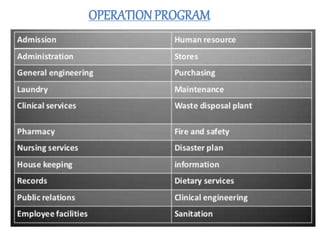
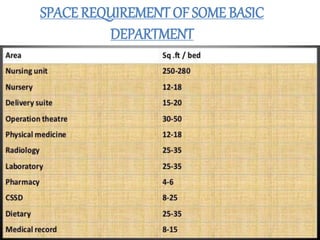
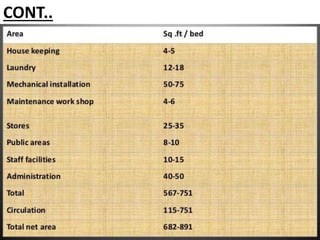
This document discusses the planning process for building a new hospital. It emphasizes that planning is key, involving assessing needs, financial planning, designing appropriate facilities, and anticipating future changes. The planning team should include medical experts and administrators who will determine bed count, equipment needs, and space requirements for departments. Proper site selection, building design, and staff training are also important to ensure the new hospital can function effectively once opened.