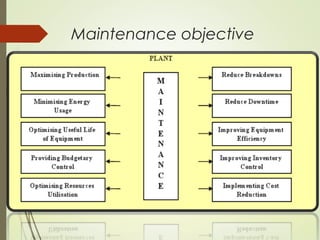
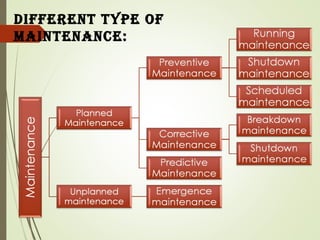
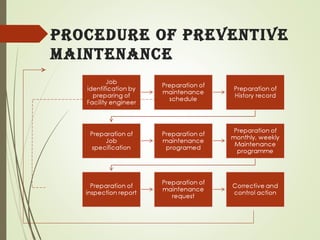
Maintenance is important to keep equipment operational and minimize costs. There are different types of maintenance including preventive, which is planned to reduce failures, and corrective, which repairs equipment after failure. Preventive maintenance has various benefits like extending equipment life and reducing downtime. It involves inspection, servicing, calibration and other activities. Maintenance objectives aim to increase reliability and minimize production costs. Proper maintenance management includes planning activities and tracking them in schedules.