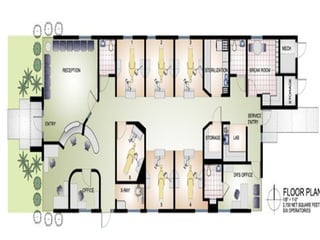
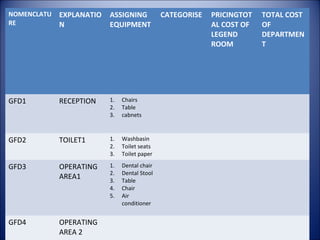
The document discusses guidelines for medical equipment planning in hospitals. It outlines the roles and responsibilities of the hospital administrator, architect, and medical equipment planner in determining equipment needs based on the scale and specialties of the hospital. Equipment is categorized as built-in, depreciable, and non-depreciable, with examples provided. Key drivers for equipment planning include need, technology, service, price, and training. Guidelines are prescribed by organizations like USFDA and certifications like ISO are important to ensure equipment quality.