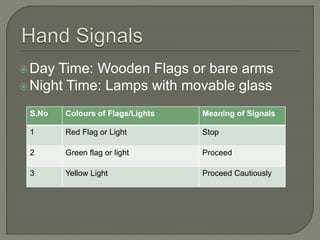
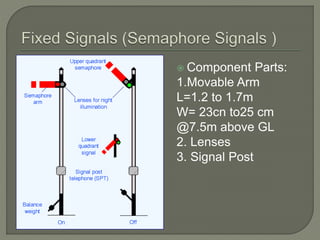
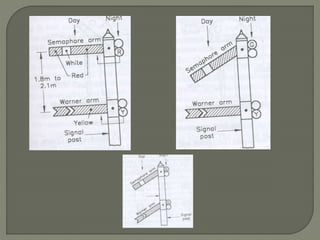
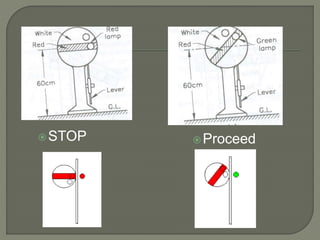
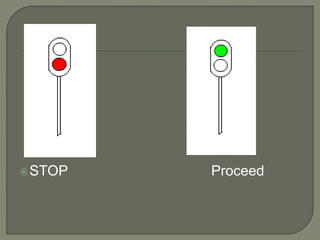
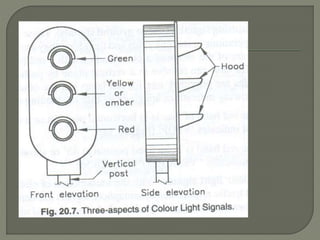
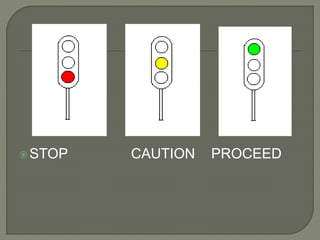
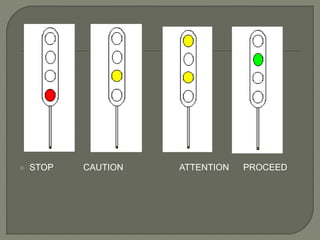
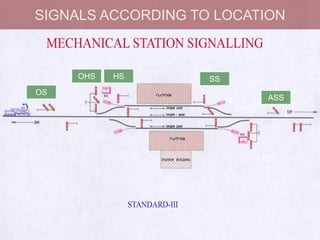
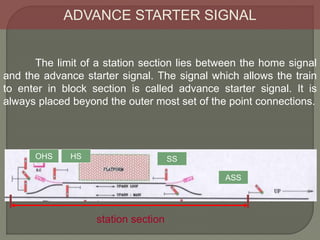
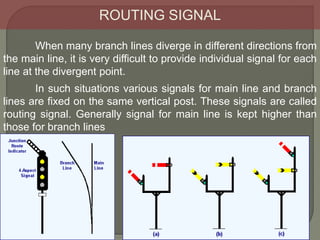
The document discusses different types of railway signaling systems. It describes signals that provide facilities for efficient train movement, ensure safety between trains, and maximize track utility. The key types discussed include detonating signals for fog conditions, fixed visual signals, semaphore signals, warner signals, shunting signals, colored light signals, and reception/departure signals like home and starter signals that control train entry and exit at stations.