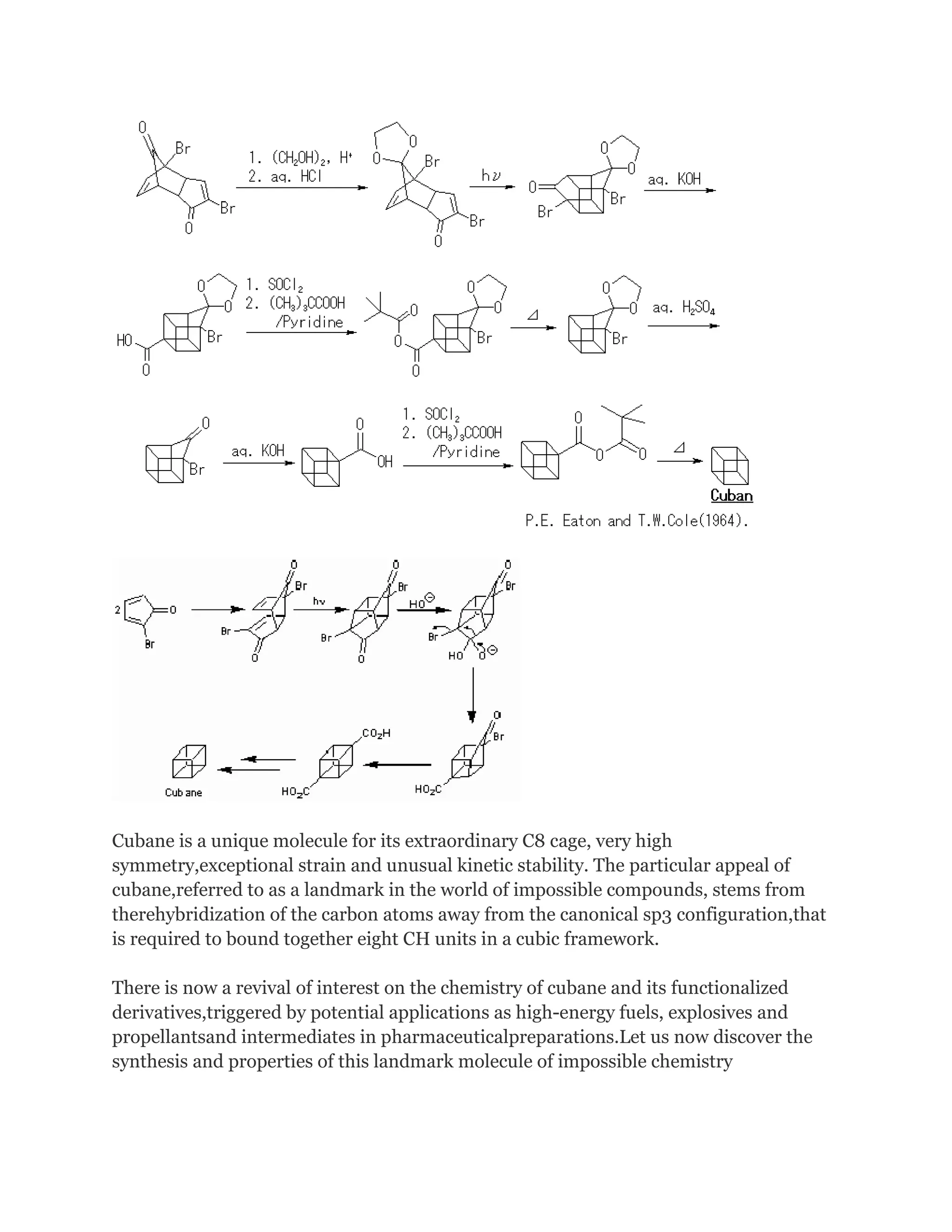
Cubane is a synthetic hydrocarbon molecule consisting of eight carbon atoms arranged at the corners of a cube, with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon. It was first synthesized in 1964 and is one of the Platonic hydrocarbons. Cubane has highly strained bonds due to the 90-degree bonding angles of the carbon atoms. Researchers are studying cubane and its derivatives for applications as high-energy fuels, explosives, and in medicine and nanotechnology due to its high density and ability to store large amounts of energy. The original synthesis of cubane involved multiple steps starting from a cyclopentenone.
![The Magic of Cubane!
By
DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO
Cubane[1]
Pentacyclo[4.2.0.02,5.03,8.04,7]octane
CAS 277-10-1
Cubane (C8H8) is a synthetic hydrocarbon molecule that consists of
eight carbon atoms arranged at the corners of a cube, with one hydrogen atom attached
to each carbon atom. A solid crystalline substance, cubane is one of the Platonic
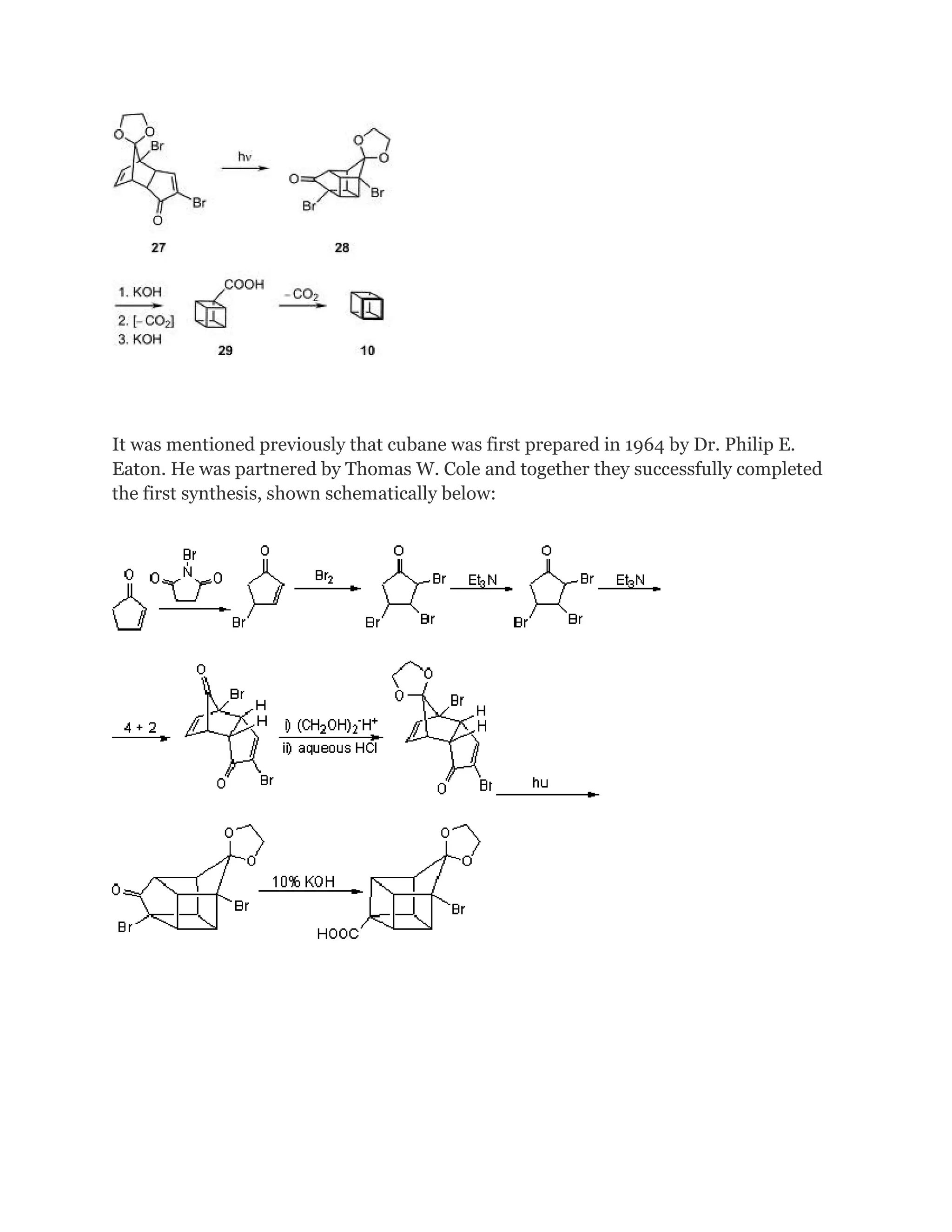
hydrocarbons. It was first synthesized in 1964 by Philip Eaton, a professor of chemistry
at the University of Chicago.[2]
Before Eaton and Cole's work, researchers believed that cubic carbon-based molecules
could not exist, because the unusually sharp 90-degree bonding angle of the carbon
atoms was expected to be too highly strained, and hence unstable. Once formed, cubane
is quite kinetically stable, due to a lack of readily available decomposition paths.
The other Platonic hydrocarbons are dodecahedrane and tetrahedrane.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/themagicofcubane-140210033357-phpapp02/75/The-magic-of-cubane-1-2048.jpg)
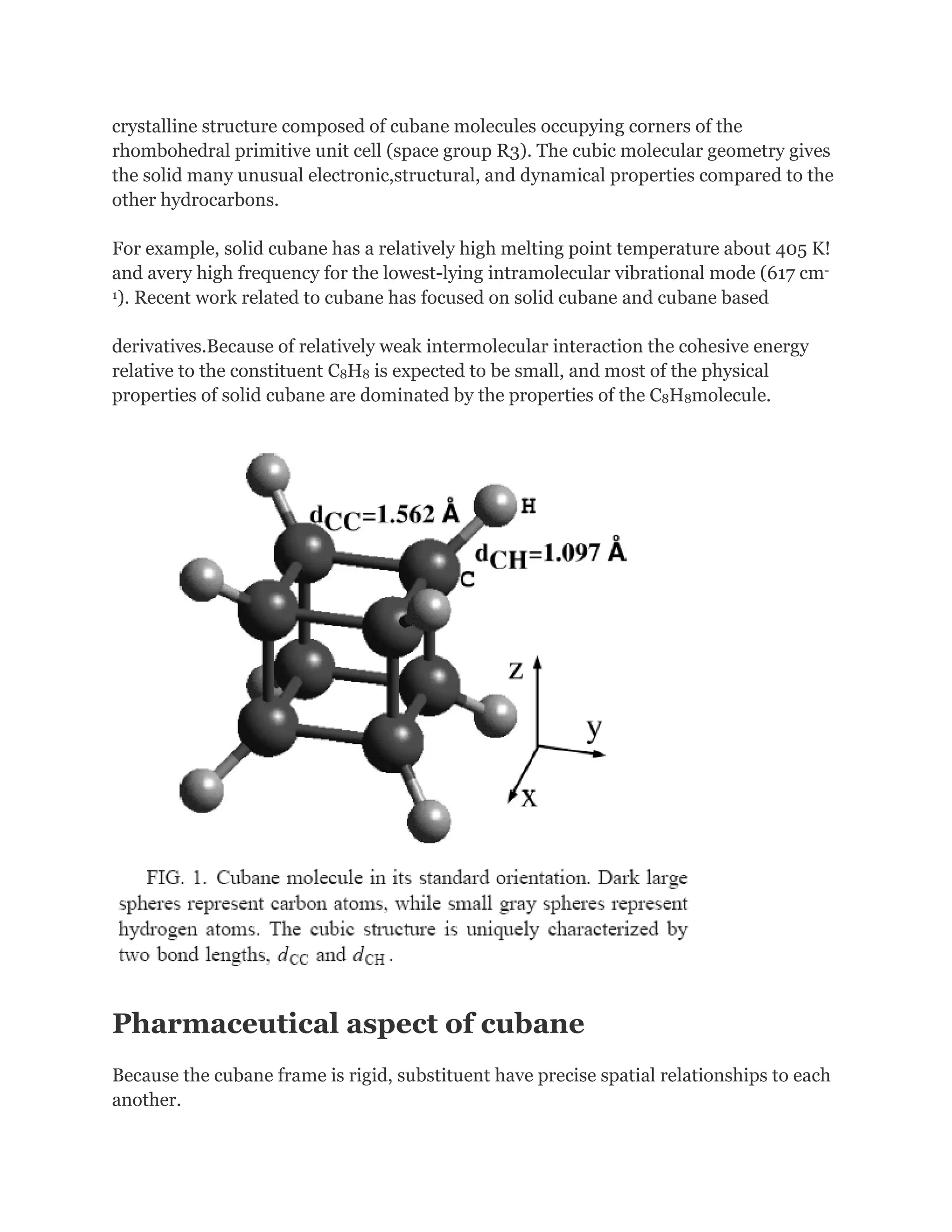
![Cubane and its derivative compounds have many important properties. The 90-degree
bonding angle of the carbon atoms in cubane means that the bonds are highly strained.
Therefore, cubane compounds are highly reactive, which in principle may make them
useful as high-density, high-energyfuels and explosives (for
example, octanitrocubane and heptanitrocubane).
Cubane also has the highest density of any hydrocarbon, further contributing to its
ability to store large amounts of energy, which would reduce the size and weight of fuel
tanks in aircraft and especially rocket boosters.
Researchers are looking into using cubane and similar cubic molecules
inmedicine and nanotechnology.
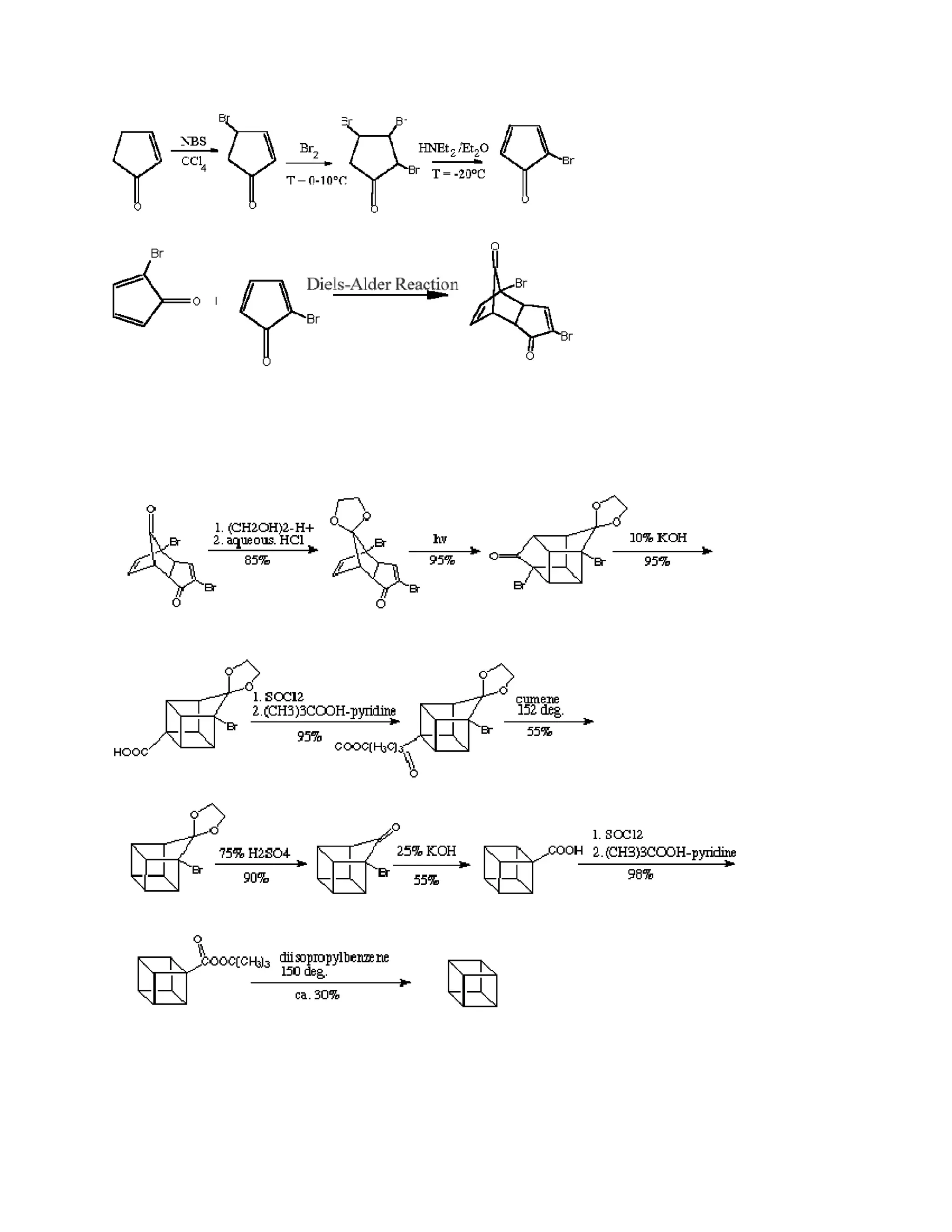
Synthesis
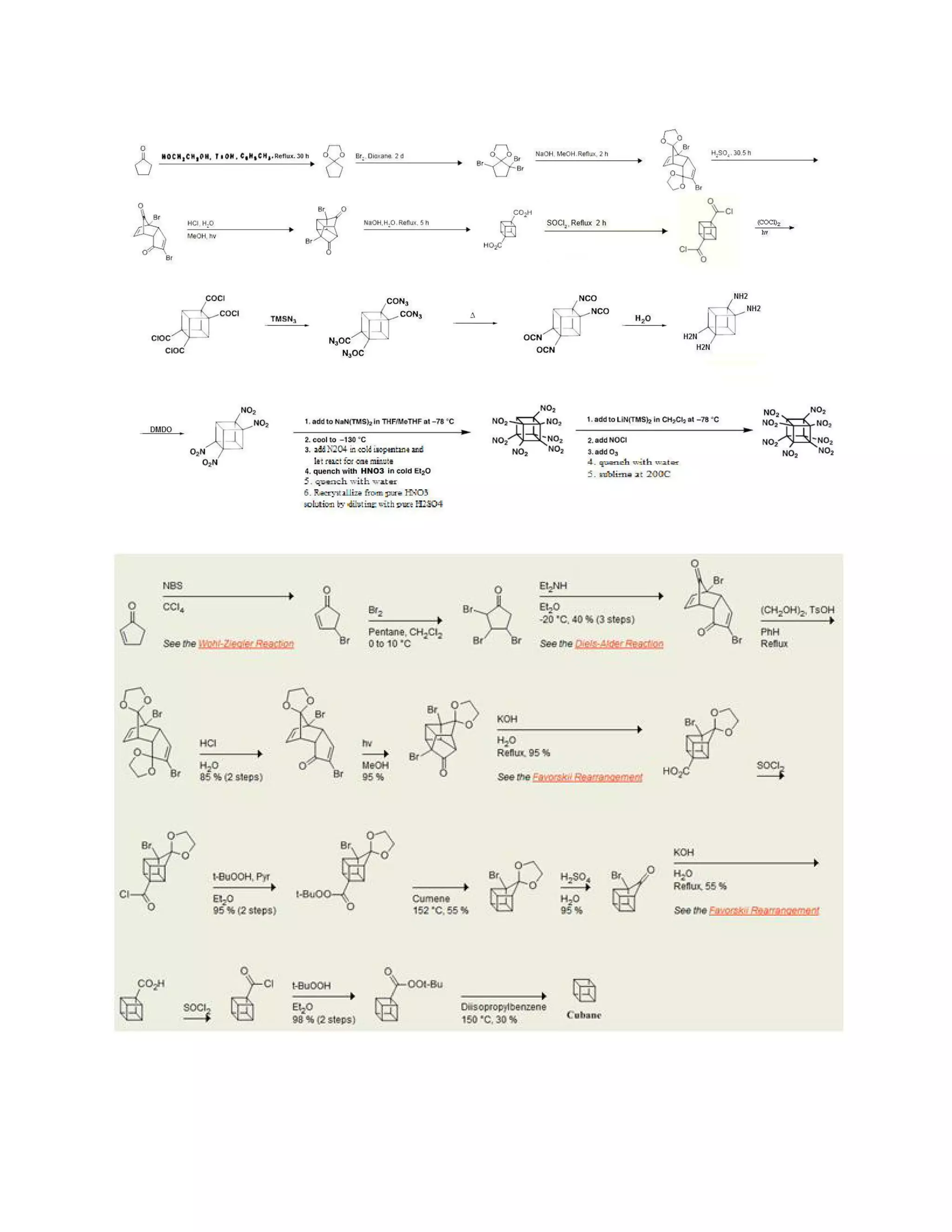
The original 1964 cubane organic synthesis is a classic and starts from 2cyclopentenone (compound 1.1 in scheme 1):[2][3]
Reaction with N-bromosuccinimide in carbon tetrachloride places an allylic bromine
atom in 1.2 and further bromination with bromine in pentane -methylene chloride gives
the tribromide 1.3. Two equivalents of hydrogen bromide are eliminated from this
compound with diethylamine in diethyl ether to bromocyclopentadienone 1.4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/themagicofcubane-140210033357-phpapp02/75/The-magic-of-cubane-2-2048.jpg)
![In the second part (scheme 2), the spontaneous Diels-Alder dimerization of 2.1 to 2.2 is
analogous to the dimerization of cyclopentadiene to dicyclopentadiene. For the next
steps to succeed, only the endo isomer should form; this happens because the bromine
atoms, on their approach, take up positions as far away from each other, and from the
carbonyl group, as possible.
In this way the like-dipole interactions are minimized in the transition state for this
reaction step. Both carbonyl groups are protected as acetals with ethylene glycol and ptoluenesulfonic acid inbenzene; one acetal is then selectively deprotected with
aqueous hydrochloric acid to 2.3
In the next step, the endo isomer 2.3 (with both alkene groups in close proximity) forms
the cage-like isomer 2.4 in a photochemical [2+2] cycloaddition.
The bromoketone group is converted to ring-contracted carboxylic acid 2.5 in
a Favorskii rearrangement with potassium hydroxide. Next, the
thermal decarboxylation takes place through the acid chloride (with thionyl chloride)
and thetert-butyl perester 2.6 (with t-butyl hydroperoxide and pyridine) to 2.7;
afterward, the acetal is once more removed in 2.8. A second Favorskii rearrangement
gives 2.9, and finally another decarboxylation gives 2.10 and 2.11.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/themagicofcubane-140210033357-phpapp02/75/The-magic-of-cubane-3-2048.jpg)
![The cube motif occurs outside of the area of organic chemistry. Prevalent non-organic
cubes are the [Fe4-S4] clusters found pervasively iron-sulfur proteins. Such species
contain sulfur and Fe at alternating corners. Alternatively such inorganic cube clusters
can often be viewed as interpenetrated S4 and Fe4 tetrahedra. Many organometallic
compounds adopt cube structures, examples being (CpFe)4(CO)4, (Cp*Ru)4Cl4,
(Ph3PAg)4I4, and (CH3Li)4.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/themagicofcubane-140210033357-phpapp02/75/The-magic-of-cubane-4-2048.jpg)
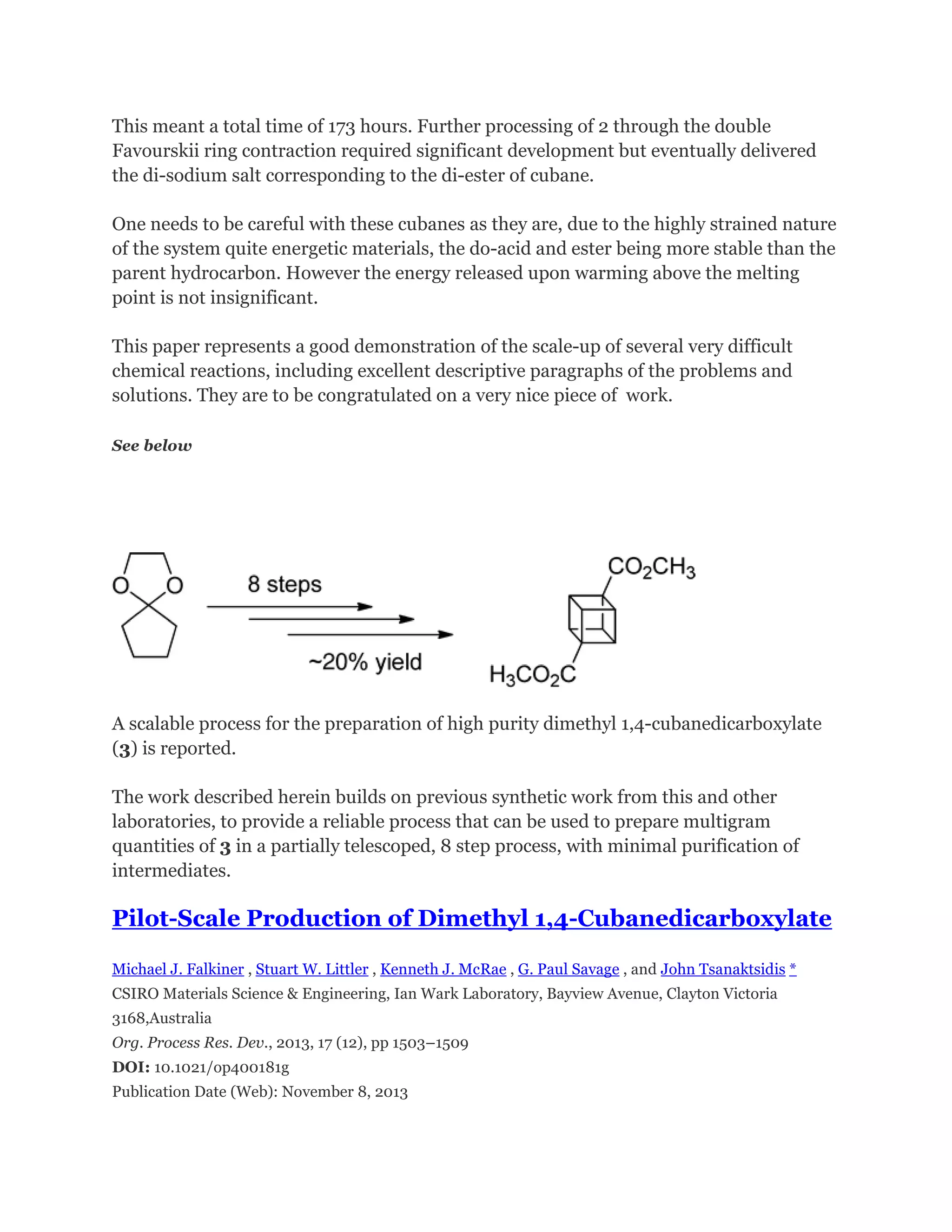
![Since the synthesis of the cubane-1,4-dicarboxylic acid has become shorter and easier,
a new decarboxylation method has also devised to give increased yields of the final
cubane product.
This has allowed the scale of production reach multikilogram batches in places
(Fluorochem in California and EniChem Synthesis in Milan) eventhough cubane and its
derivatives remain expensive to purchase.
Cuneane may be produced from cubane by a metal-ion-catalyzed σ-bond
rearrangement.[4][5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/themagicofcubane-140210033357-phpapp02/75/The-magic-of-cubane-9-2048.jpg)
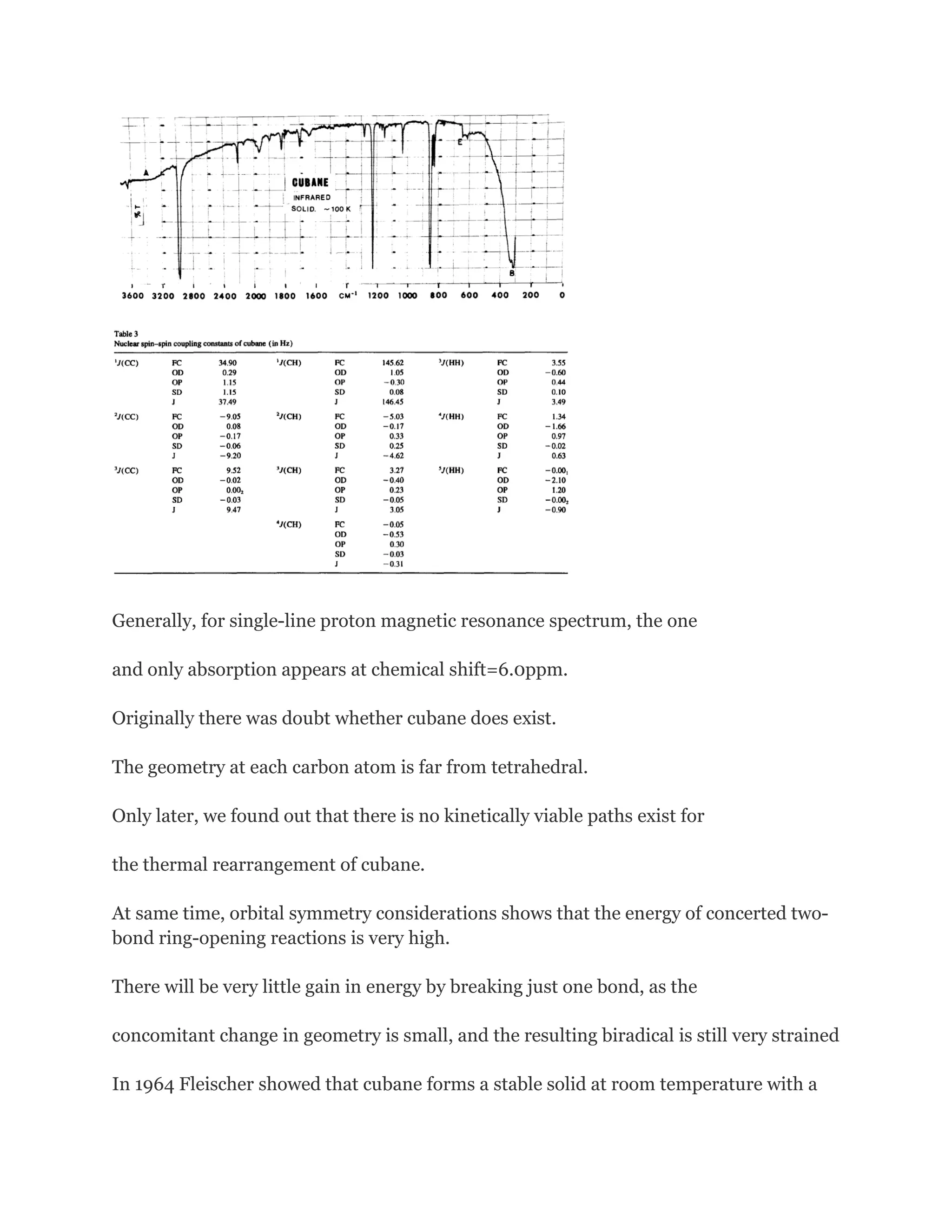
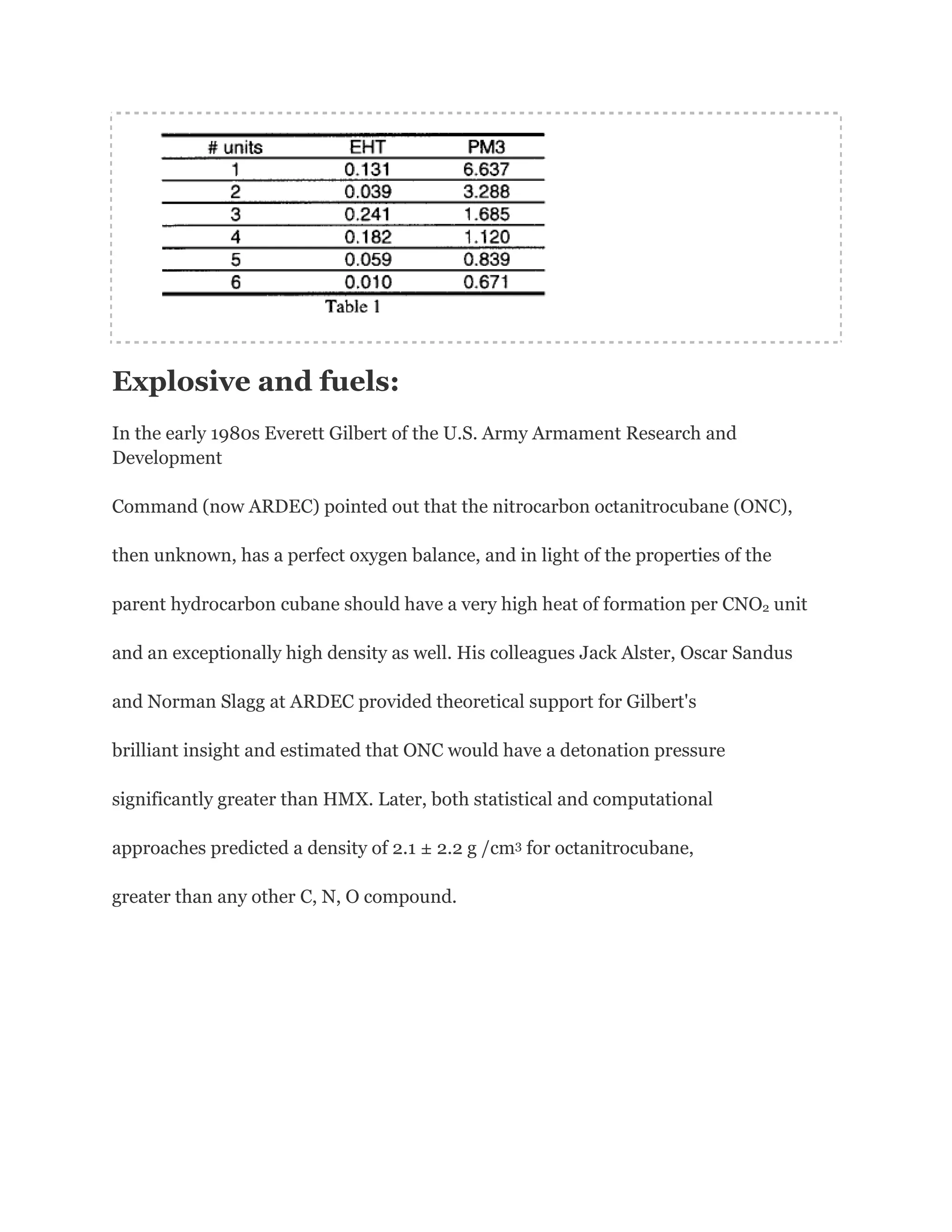
![Cubanehas the highest strain energy (166kcal/mol) of any
organiccompounds available in multi gram amount. It is a
kineticallystable compound and only decomposite above
220 Celsius Degree.It is also one of the most dense
hydrocarbons ever know.However, although many physical
properties of cubane have been measured, in1980 and
before, cubane was considered just a laboratory curiosity
of interest only to academics.It changed, in early 1980s
when Gilbert of U.S ArmyArmament and Development
Command (now ARDEC) pointed out that cubane'svery
high heat of formation and its exceptionally high density
could make certain cubanederivatives important
explosives.
The
effectiveness of an explosive is dependent on the
energentics of the decomposition reaction,
the number of moles and molecular weight of the gaseous
products and also the density.
The more mols of of an explosive that can be packed into
the limited volume the better. .
Highly nitrated cubanes can be predicted to be very dense
and very powerful explosives.
Octanitrocubane is calculated to be 15~30%more powerful
than HMX.
Cubane, which CA index name is
Pentacyclo[4.2.0.02,5.03,8.04,7]octane
(7CI,8CI,9CI),has exceptional structure, strain and](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/themagicofcubane-140210033357-phpapp02/75/The-magic-of-cubane-11-2048.jpg)

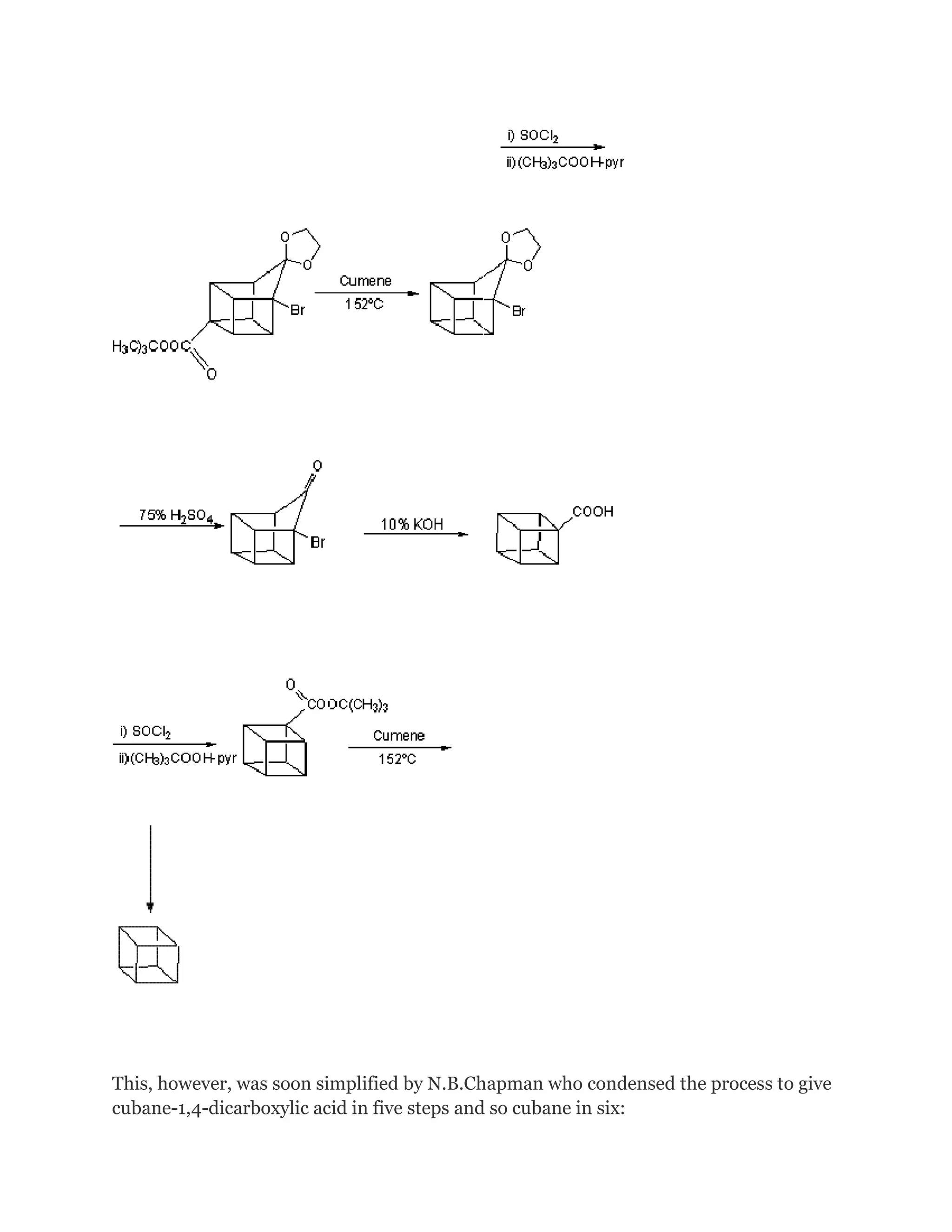
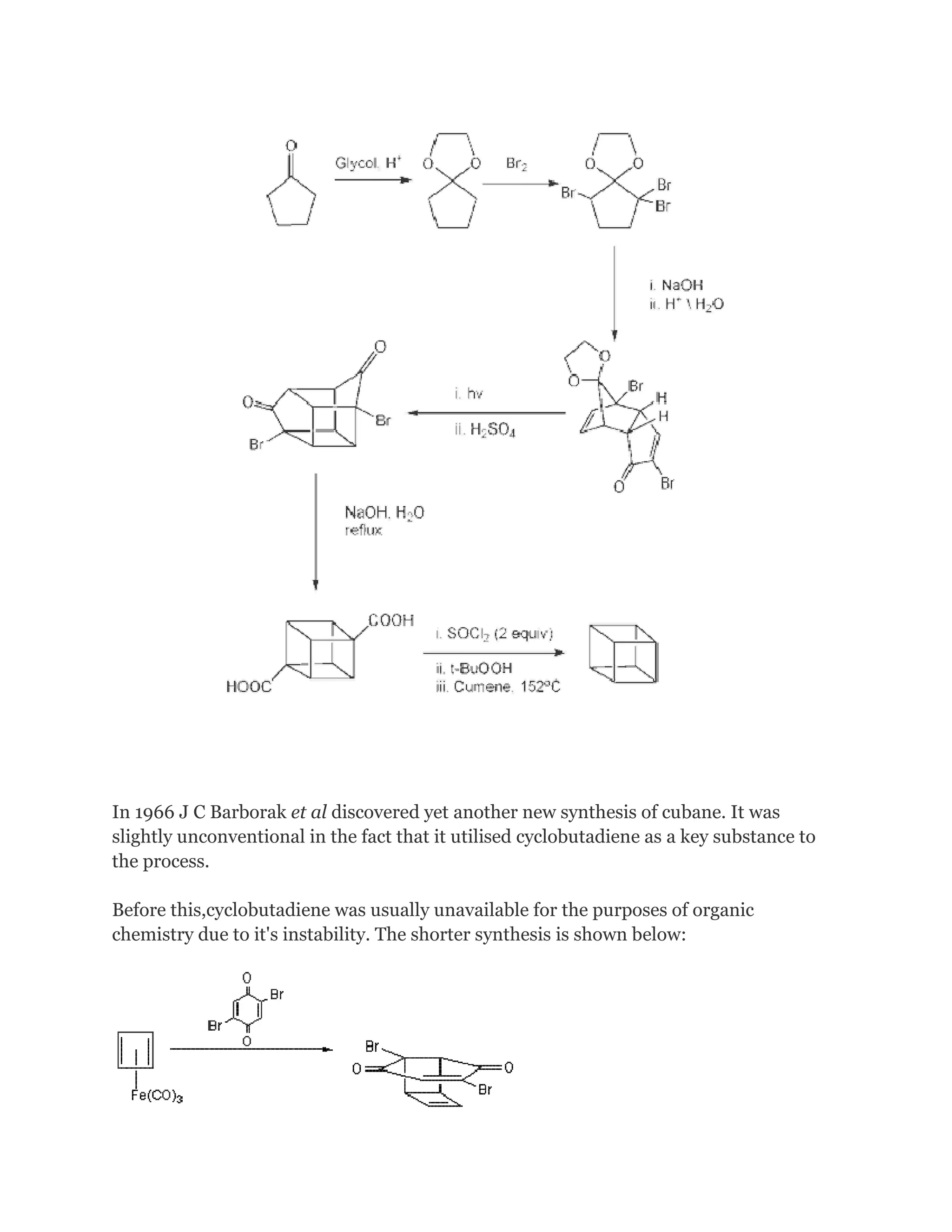
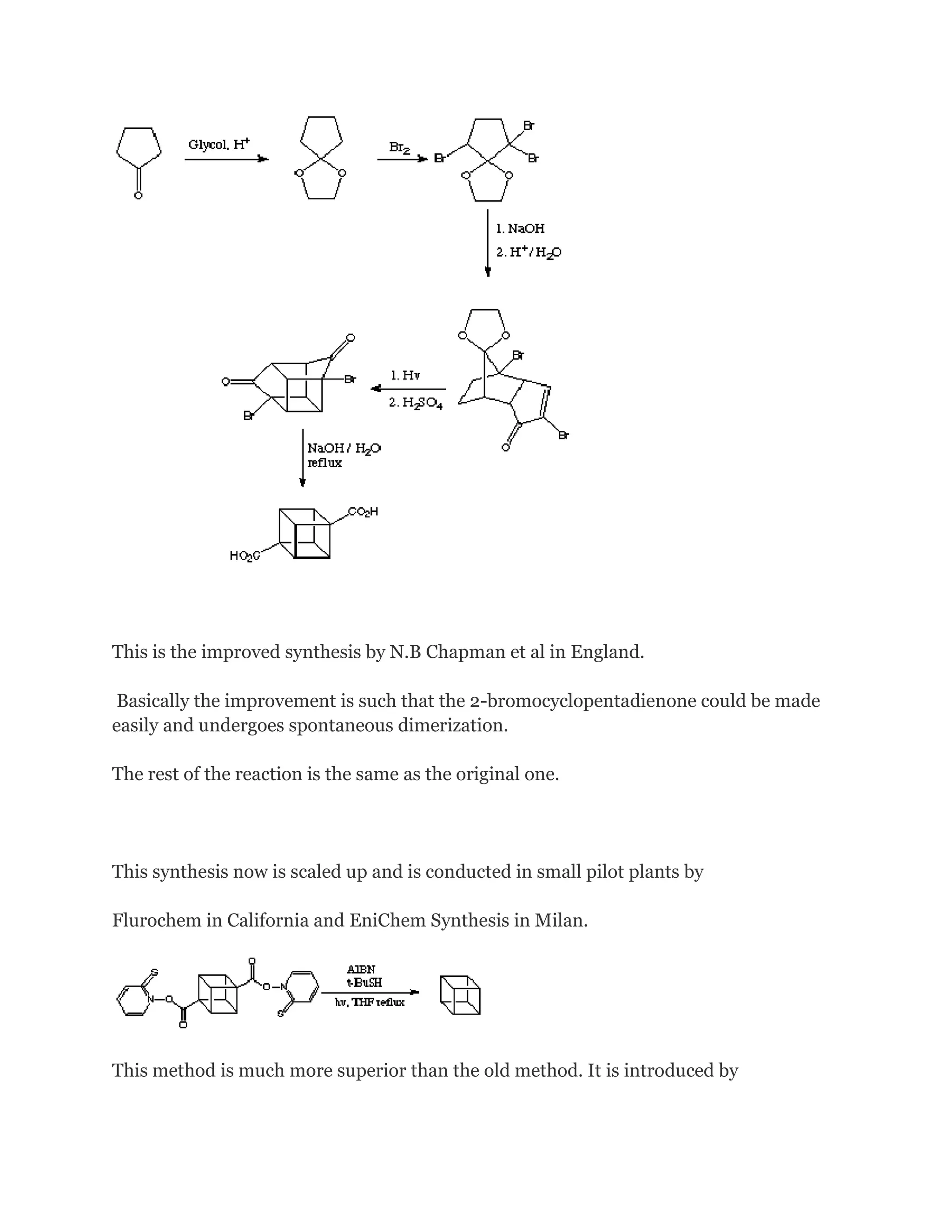
![The stereospecific in situ [4 + 2] (Diels-Alder) cyclodimerization of 4-bromocyclopentadienone
is the key in this kinetically controlled synthesis. However, it is still a tricky matter
and a few years later after this synthesis is published, N.B.Chapman et al in England
following up
this work and improved this synthesis.
Why cubane is stable?
The reason for this, unappreciated at the time of the early predictions of
instability, is that there are no kinetically viable paths along which cubane
can rearrange thermally.
On one hand, orbital symmetry considerations raise the energy of
concerted two-bond ring opening reactions. On theother, there is little to be
gained by breaking just one bond as there is concomitantly only a small
change in geometry, and the resulting biradical is still very strained.
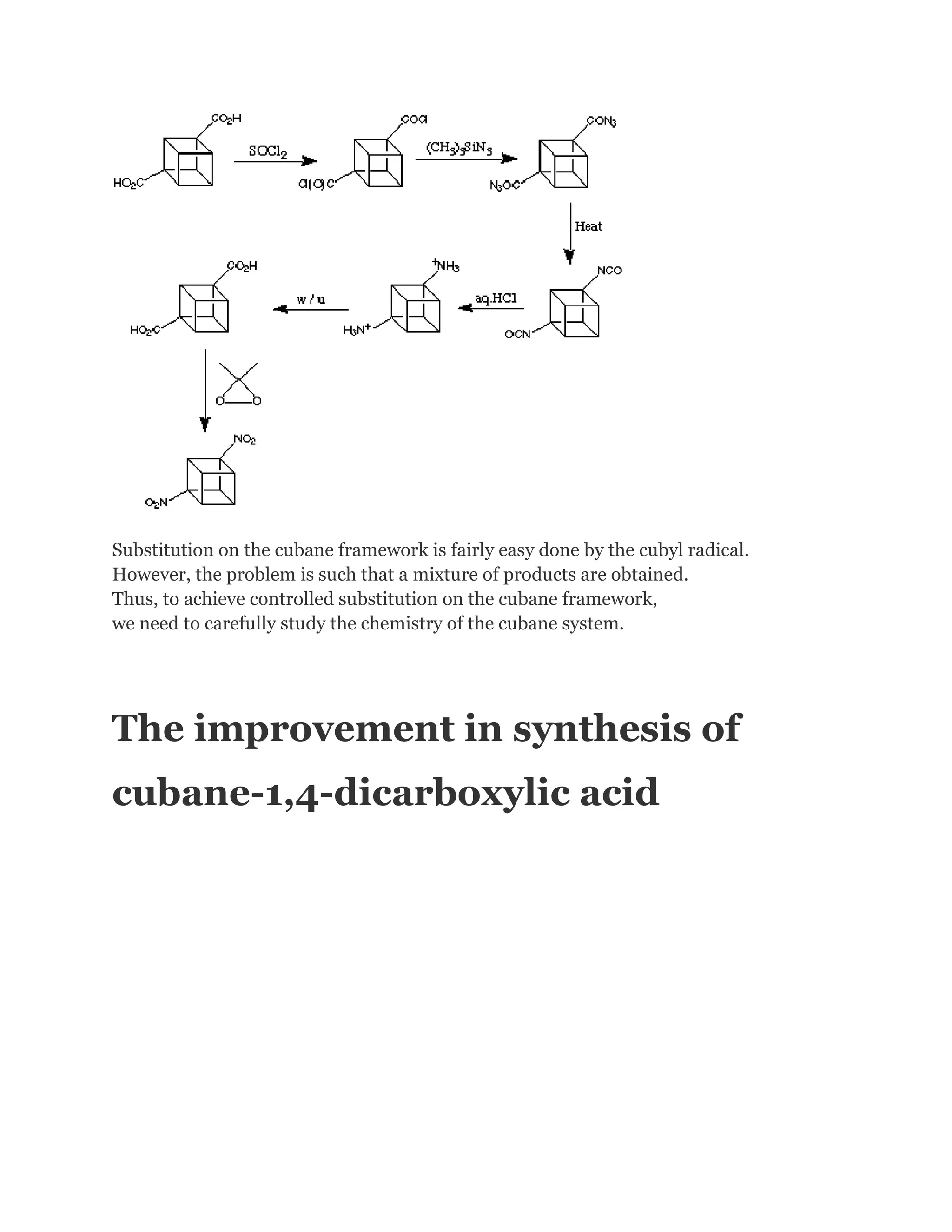
Functional group transformation
Functional groups on the cubane system generally behaves very well.Functional group transformation can
be applied successfully.For example, the preparation of 1,4-dinitrocubane from cubane-1,4-dicarboxylic
acid.(The mechanism is provided on the right hand side.) Classical methodology is used here.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/themagicofcubane-140210033357-phpapp02/75/The-magic-of-cubane-15-2048.jpg)









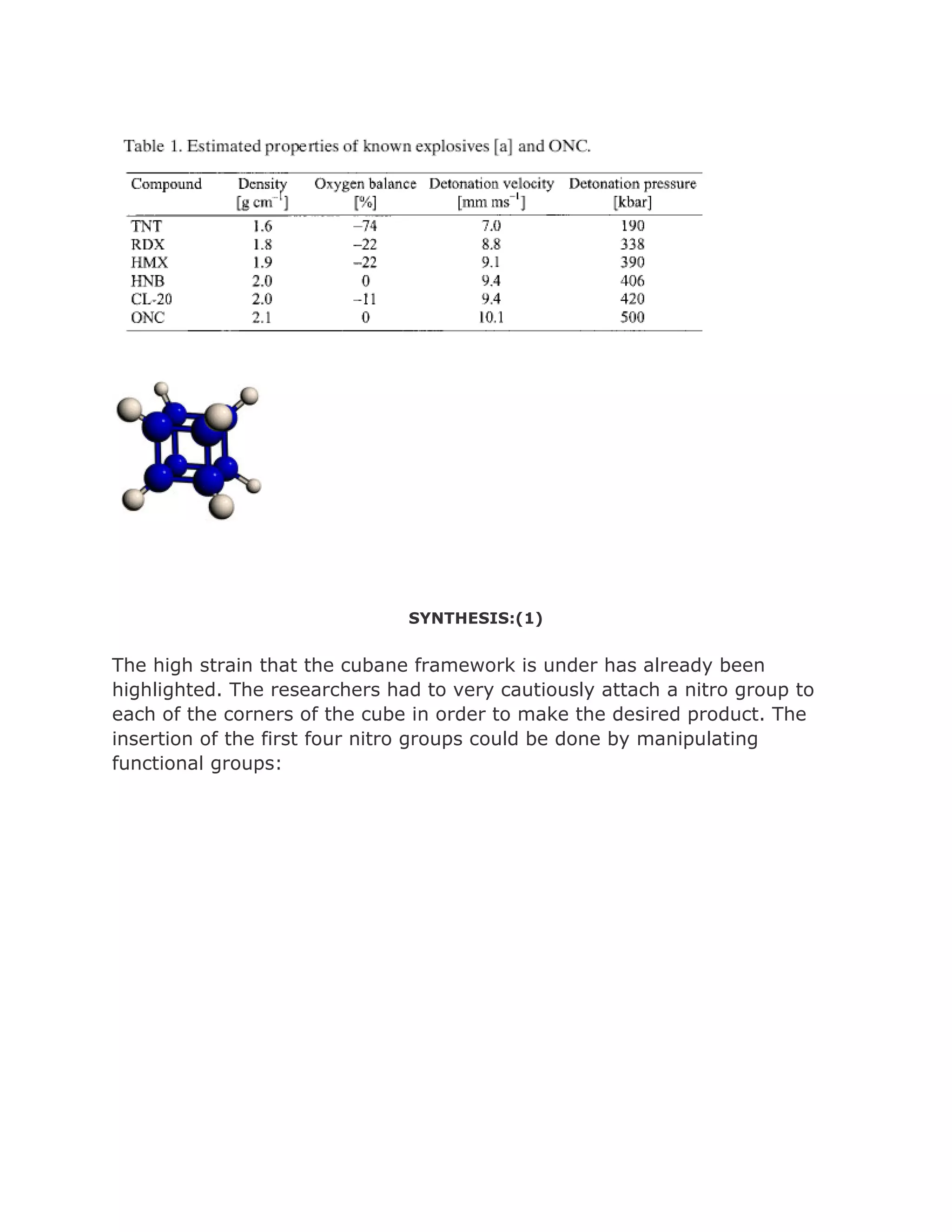
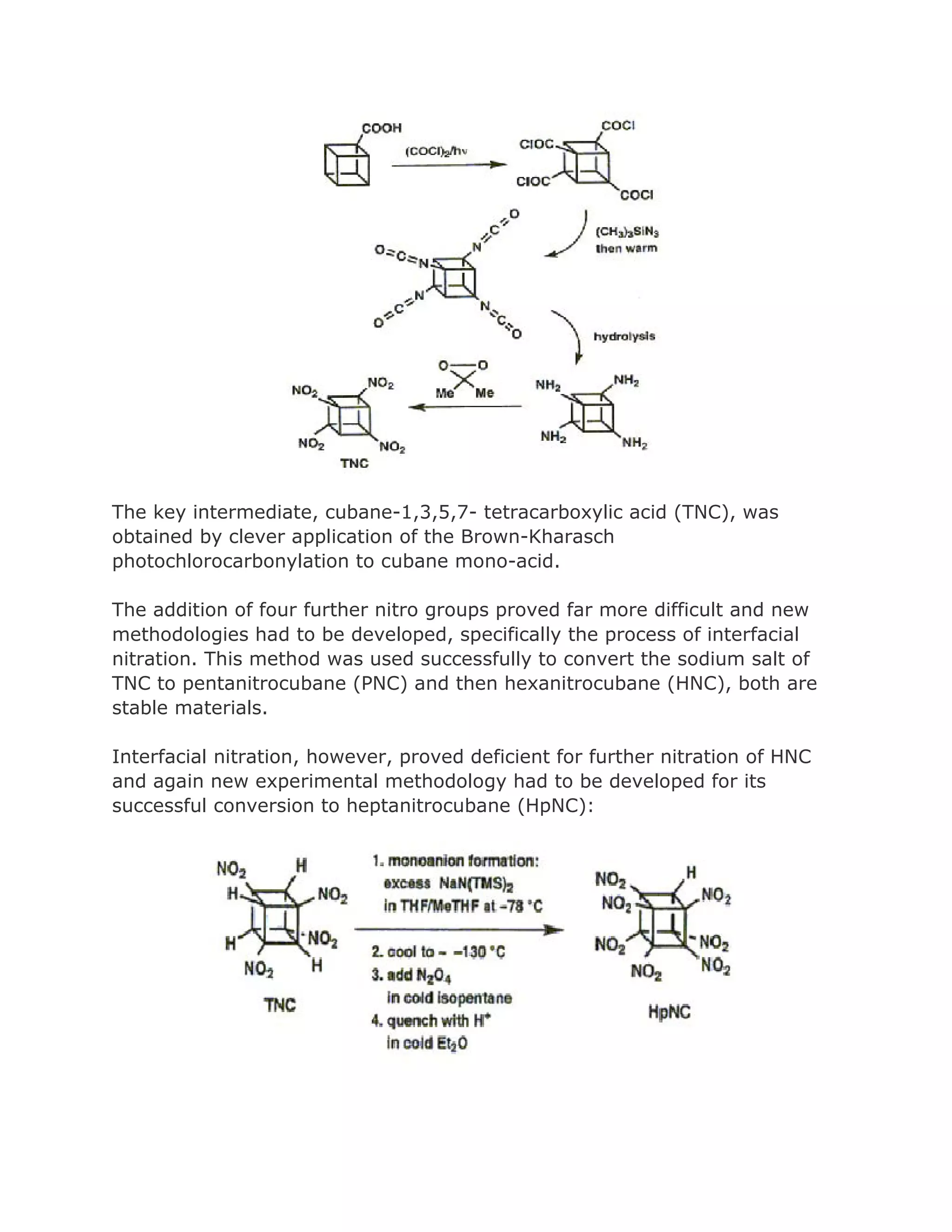
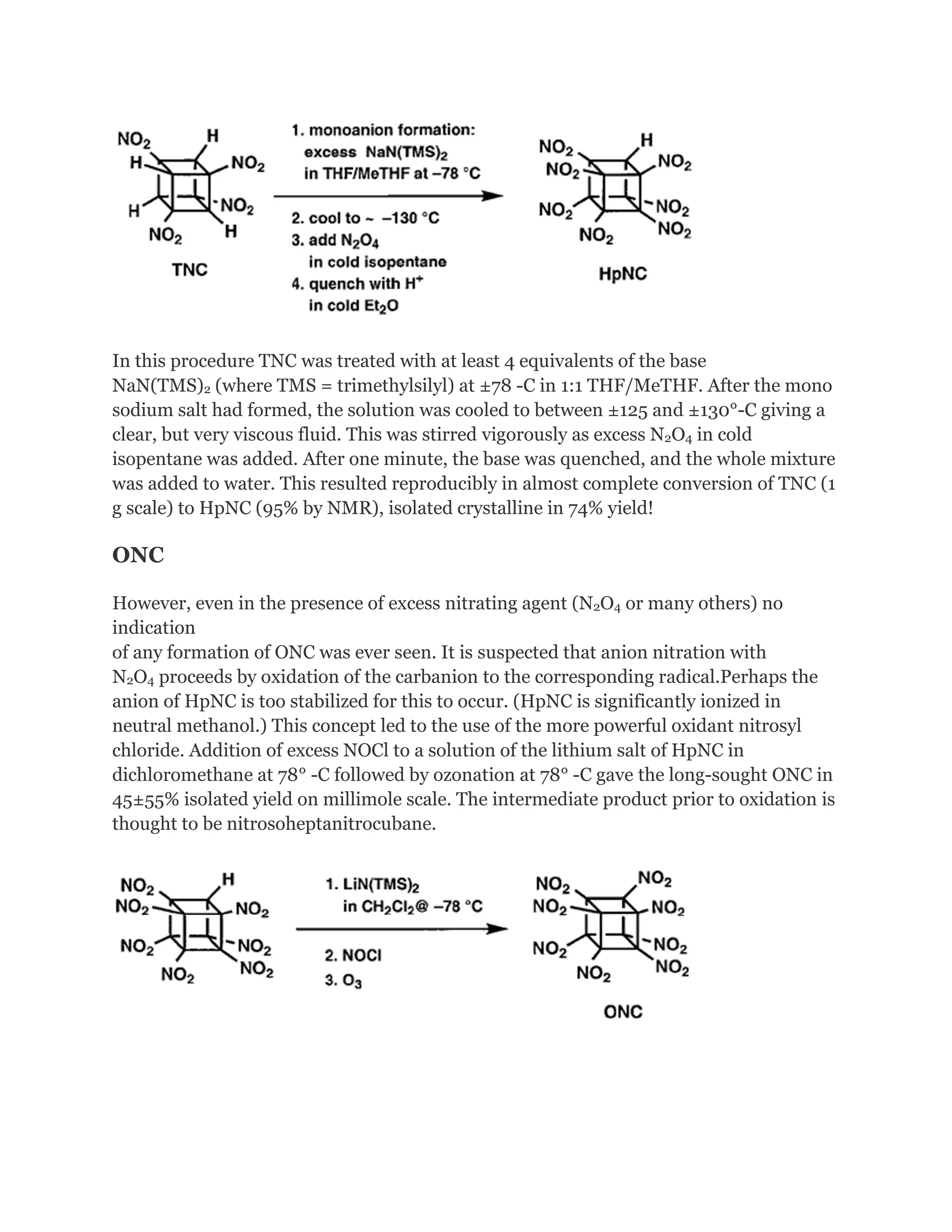
![Addition of excess NOCl to a solution of the lithium salt of HpNC in dichloromethane at 78°C gave the long-sought ONC:
DIFF TYPES
For the last planned post in my Unnatural Products series, I’m going to write about
Eaton’s 1981 synthesis of pentaprismane.[A] At the time, unnatural hydrocarbons were
hot targets, and as the next largest prismane on the list this target was the subject of
much research by groups around the world. Perhaps Eaton's biggest rivals were the
groups of Paquette and Petit, and in fact all three had, at various times, synthesised
hypostrophene as an intended precursor to the target.
Unfortunately, the ‘obvious’ [2 + 2] disconnection from pentaprismane turned out to be
a dead end and the photochemical ring closure was unsuccessful. The 1970s and early](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/themagicofcubane-140210033357-phpapp02/75/The-magic-of-cubane-32-2048.jpg)
![1980s saw the publication of a number of other similarly creative, but sadly ill-fated,
approaches based on various ring contractions, and the compound gained a well-earned
reputation for extraordinary synthetic inaccessibility.
Eaton’s route began, as with the cubane and dodecahedrane syntheses previously
covered in this series, with a Diels-Alder reaction. The diene used was the known
tetrachlorocyclopentadienone acetal shown that upon heating neat with benzoquinone
produced the endo adduct shown in excellent yield. Next, an even higher yielding
photochemical [2 + 2] reaction was used to close the cage-like structure by cyclobutane
formation. Treatment with lithium in liquid ammonia simultaneously reduced both
ketones and removed all four chlorine atoms. The resulting diol was converted to the
ditosylate, which, under carefully controlled conditions with sodium iodide in HMPA,
underwent a mono-Finkelstein reaction to give the iodotosylate shown. When this was
treated with t-BuLi halogen-lithium exchange, followed by an extraordinary
fragmentation, gave a diene reminiscent of hypostrophene shown above. However, the
extra carbon atom in the skeleton made all the difference, and unlike the parent
compound, this did undergo a [2 + 2] cycloaddition when exposed to UV light. Finally,
acetal hydrolysis gave homopentaprismane in 34% yield from benzoquinone, putting the
group a single ring contraction from victory.[B]
With significant amounts of homopentaprismanone in hand, the group now intended to
employ the transformation that had been the cornerstone of their cubane synthesis –
the Favorskii rearrangement. Unfortunately, this required the introduction of a leaving
group in the ketone α-position, a transformation made incredibly difficult due to the
strained system and Bredt’s rule, which prevented enolisation.[C] Eventually a six-step
sequence (!) to introduce a tosyloxy group was devised, beginning with a Baeyer-Villiger
reaction using m-CPBA. A remarkable CH oxidation with RuO4, generated in situ, then
gave the hydroxylactone. Treatment of this with diazomethane gave the corresponding](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/themagicofcubane-140210033357-phpapp02/75/The-magic-of-cubane-33-2048.jpg)
![δ-ketoester in almost quantitative yield. The group then reformed the starting
norbornane-like bridge through use of an unusual acyloin type reaction effected by
treatment with sodium in liquid ammonia. Finally, oxidation of the secondary alcohol
and tosylation gave the Favorskii precursor, apparently preparable in muti-gram
quantities.
Treatment with aqueous potassium hydroxide solution effected Favorskii
rearrangement in excellent yield, especially considering that this was the first time the
elusive pentaprimane ring system had been prepared. Finally, Eaton used the three-step
decarboxylation he had developed for cubane to remove the extraneous acid and give
pentaprismane in 18 steps. Awesome.[D]
References and suchlike
1. A J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1981, 103, 2134. Much like Eaton’s seminal cubane paper,
the title is a single word, ‘Pentaprismane’. I love the lack of hype.
2. B Although Petit had prepared this compound a full decade earlier, his
approach relied on a cycloaddition of the difficult to prepare cyclobutadieneiron
tricarbonyl with the acetal of tropone, and proved difficult to scale up. In fact, in
his own paper Eaton rather directly described it as ‘conceptually fascinating [but]
useless synthetically’.
3. C Eaton uses the phrase ‘invasion at the bridgehead’, which I find delightfully
evocative. Makes it sound like a second world war campaign. Apparently the](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/themagicofcubane-140210033357-phpapp02/75/The-magic-of-cubane-34-2048.jpg)
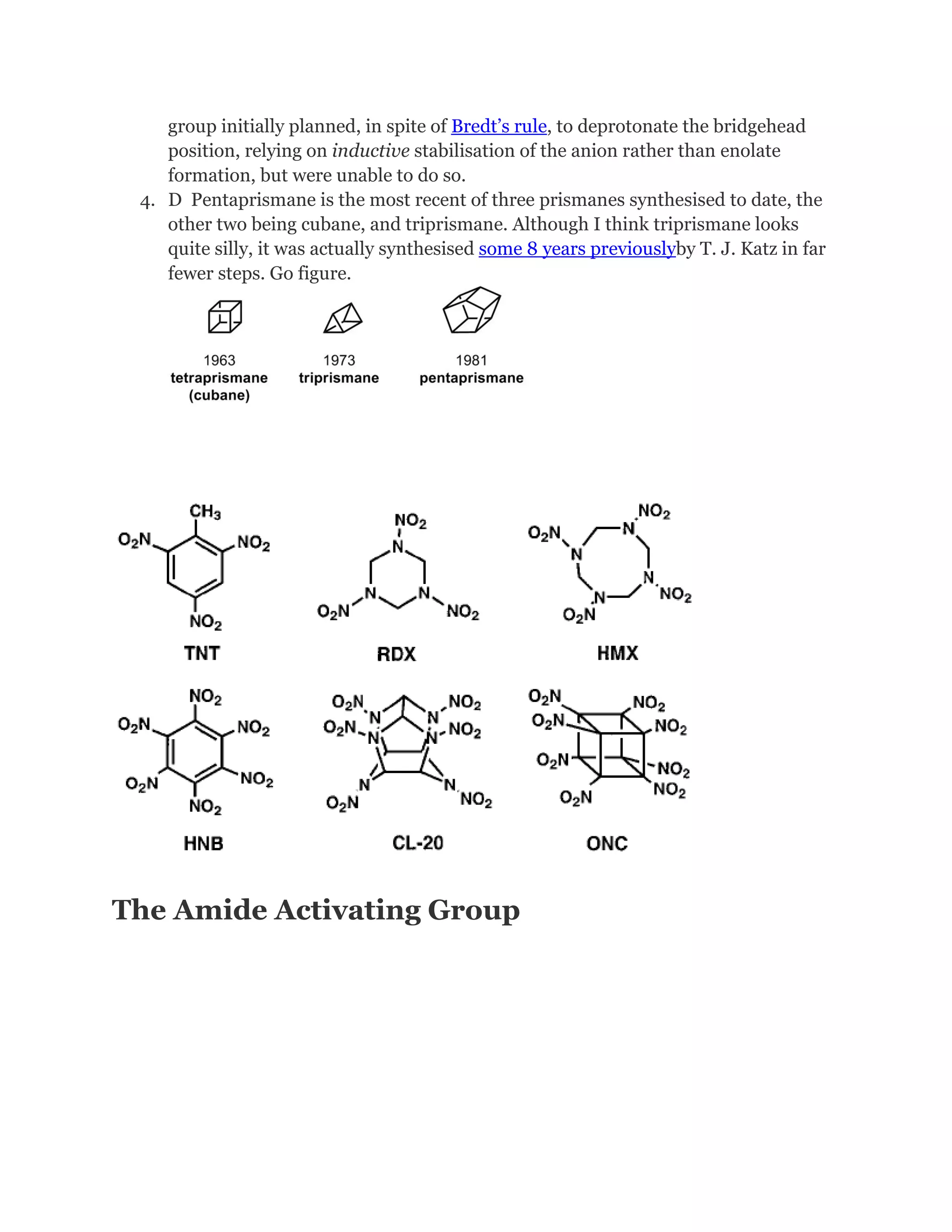

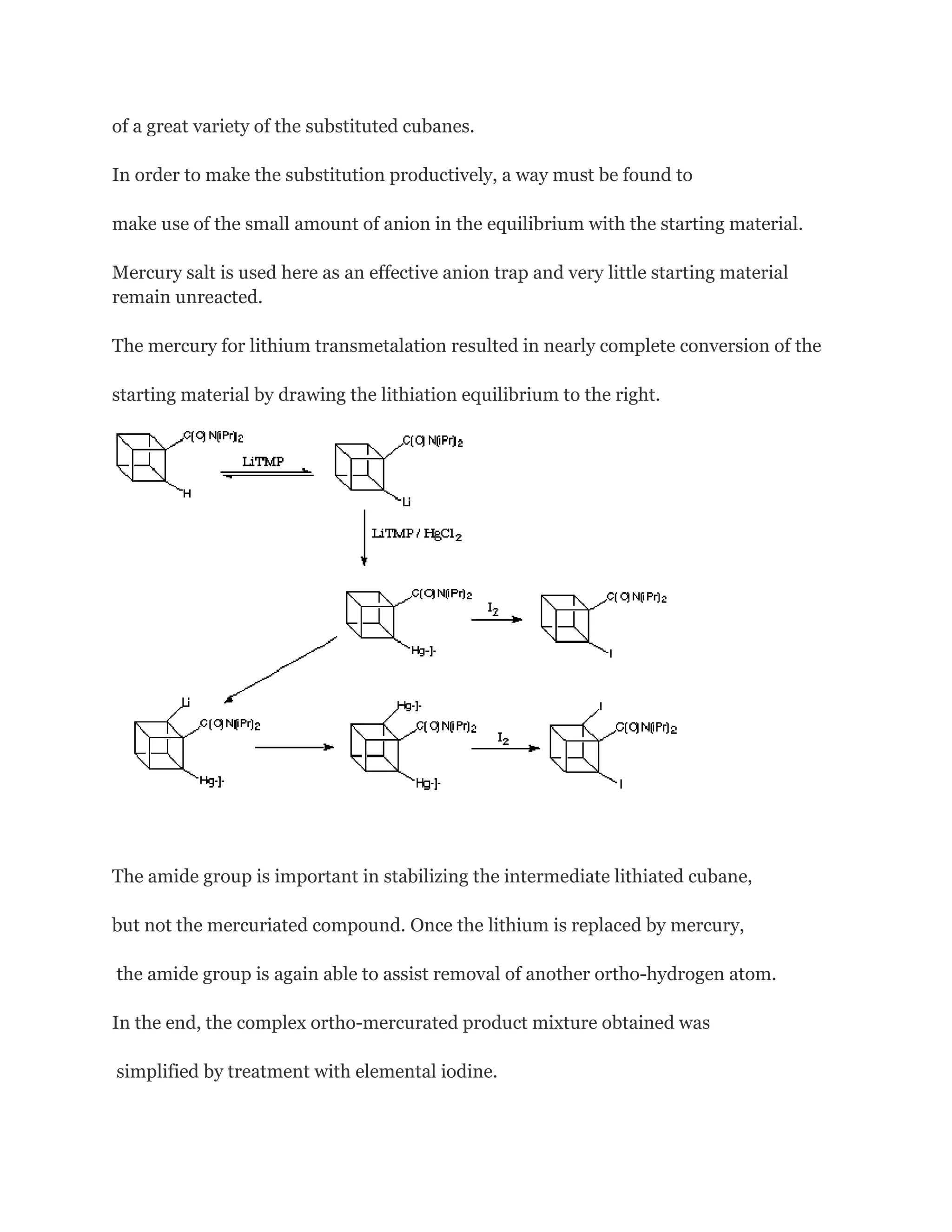


![Dimethyl cubane-1,4-dicarboxylate
dimethyl 1,4-cubanedicarboxylate;
1,4-cubanedicarboxylic acid dimethyl*ester;
methyl 4-(methoxycarbonyl)pentacyclo[4.2.0.0<2,5>.0<3,8>.0<4,7>]octanecarboxylate
Pentacyclo(4.2.0.0(2,5).0(3,8).0(4,7))octane-1,4-dicarboxylic acid dimethyl ester
CAS 29412-62-2
Molecular Weight:
220.2213
Molecular Formula:
C12H12O4
Density:
1.684g/cm3
Boiling Point(℃):
270°C at 760 mmHg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/themagicofcubane-140210033357-phpapp02/75/The-magic-of-cubane-53-2048.jpg)