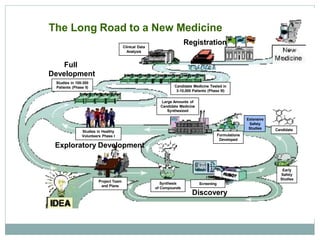
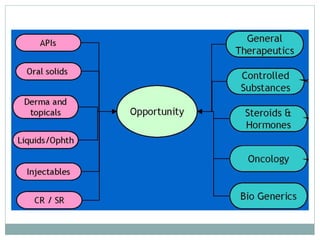
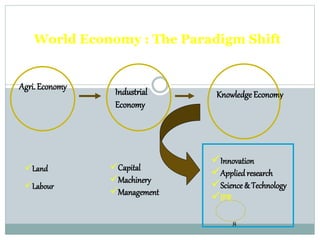
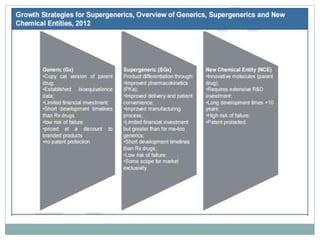
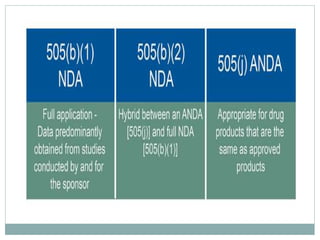
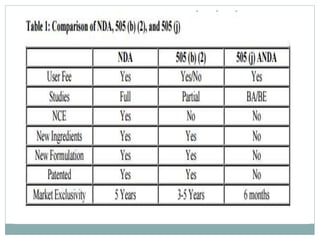
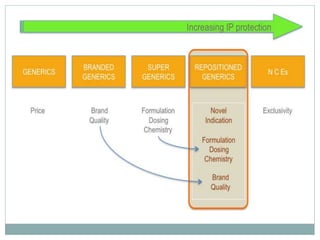
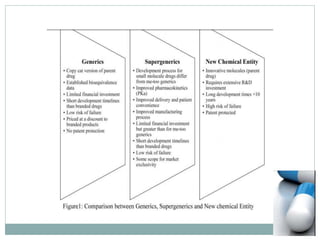
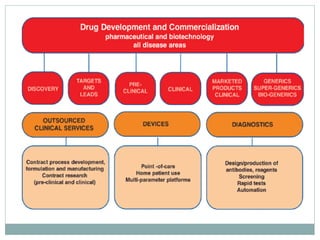
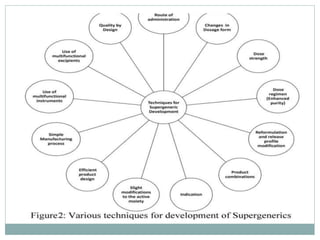
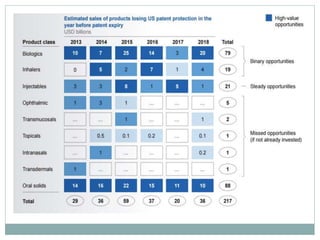
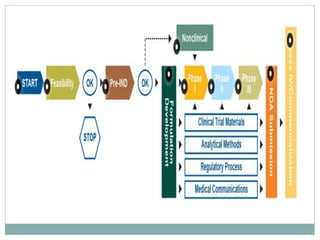
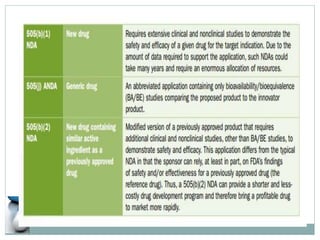
The document discusses supergenerics, which are generic drugs that offer improved features over existing generics. Supergenerics can provide a lower-risk alternative to developing new drugs and offer shorter development timelines compared to new chemical entities. The 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway allows supergenerics to incorporate existing clinical data, reducing development costs versus the traditional 505(b)(1) new drug application process. Supergenerics aim to create value through improved formulations, delivery methods, or other enhancements compared to existing generics while maintaining a known safety profile. This offers the potential for temporary market exclusivity and competitive advantages for generic drug companies.