site selection and environmental aspects of hazardous w 2
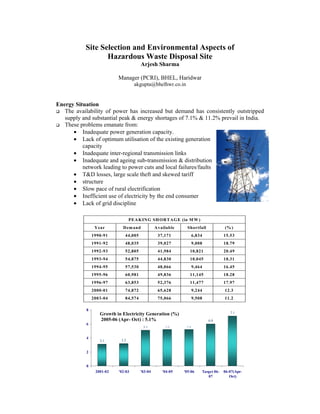
- 1. Site Selection and Environmental Aspects of Hazardous Waste Disposal Site Arjesh Sharma Manager (PCRI), BHEL, Haridwar akgupta@bhelhwr.co.in Energy Situation The availability of power has increased but demand has consistently outstripped supply and substantial peak energy shortages of 7.1% 11.2% prevail in India. These problems emanate from: · Inadequate power generation capacity. · Lack of optimum utilisation of the existing generation capacity · Inadequate inter-regional transmission links · Inadequate and ageing sub-transmission distribution network leading to power cuts and local failures/faults · TD losses, large scale theft and skewed tariff · structure · Slow pace of rural electrification · Inefficient use of electricity by the end consumer · Lack of grid discipline PEAKING SHORTAGE (in MW) Year Demand Available Shortfall (%) 1990-91 44,005 37,171 6,834 15.53 1991-92 48,035 39,027 9,008 18.79 1992-93 52,805 41,984 10,821 20.49 1993-94 54,875 44,830 10,045 18.31 1994-95 57,530 48,066 9,464 16.45 1995-96 60,981 49,836 11,145 18.28 1996-97 63,853 52,376 11,477 17.97 2000-01 74,872 65,628 9,244 12.3 2003-04 84,574 75,066 9,508 11.2 3.1 5.1 5.2 5.2 6.0 7.1 3.2 8 6 4 2 0 2001-02 '02-03 '03-04 '04-05 '05-06 Target 06- 07 06-07(Apr- Oct) Growth in Electricity Generation (%) 2005-06 (Apr- Oct) : 5.1%
- 2. Likely Capacity Addition During X Plan (MW) Total Capacity Anticipated Units Expected During Nov’06- Mar’07 Units Commissioned Mid Term Appraisal Target Sector Central 19,817 10,865 5,314 16,179 State 12,240 4,948 6,060 11,008 Private 4,899 1,931 1,524 3,455 Total 36,956 17,744 12,898* 30,642 * Based on latest reviews by CEA/ BHEL Year-wise Capacity Addition Programme in XI Plan (MW) 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 Thermal 3430 6350 9580 11700 16950 Gas 977 387 750 0 0 Nuclear 1440 1220 0 500 0 Hydro 2450 2328 2055 4330 4422 TOTAL 8297 10285 12385 16530 21372 Capacity Addition Programme in First Three Years Of XII Plan (MW) 2012-13 2013-14 2014-15 Thermal 17725 15070 10800 Gas 0 0 0 Nuclear 700 3400 2700 Hydro 8024 5067 5097 TOTAL 26449 23537 18597 2012-15 (1st three years of 12th Plan) 43595 0 6800 18188 68583
- 3. Capacity Addition Programme in First Three Years of XII Plan (MW) C O M M IS S IO N IN G Y E A R 2 0 1 2 - 1 3 2 0 1 3 - 1 4 2 0 1 4 - 1 5 T H E R M A L 1 7 7 2 5 1 5 0 7 0 1 0 8 0 0 G A S 0 0 0 N U C L E A R 7 0 0 3 4 0 0 2 7 0 0 H Y D R O 8 0 2 4 5 0 6 7 5 0 9 7 T O T A L 2 6 4 4 9 2 3 5 3 7 1 8 5 9 7 T H E R M A L 0 0 0 G A S 0 0 0 N U C L E A R 0 0 0 H Y D R O 0 0 0 T O T A L 0 0 0 T H E R M A L 5 8 5 5 2 2 6 0 8 0 0 G A S 0 0 0 N U C L E A R 0 0 0 H Y D R O 0 0 0 T O T A L 5 8 5 5 2 2 6 0 8 0 0 T H E R M A L 5 8 5 5 2 2 6 0 8 0 0 G A S 0 0 0 N U C L E A R 0 0 0 H Y D R O 0 0 0 T O T A L 5 8 5 5 2 2 6 0 8 0 0 T H E R M A L 1 1 8 7 0 1 2 8 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 G A S 0 0 0 N U C L E A R 7 0 0 3 4 0 0 2 7 0 0 H Y D R O 8 0 2 4 5 0 6 7 5 0 9 7 T O T A L 2 0 5 9 4 2 1 2 7 7 1 7 7 9 7 T O T A L P L A N O R D E R E D O N B H E L O R D E R E D / B E IN G O R D E R E D O N O T H E R S T O T A L O R D E R E D Y E T T O B E O R D E R E D Capacity Addition Programme During XI Plan (2007-2012) Fuel- Mix Central Sector State Sector Private Sector Total Thermal 25,860 16,152 4,102 46,114 Hydro 11,289 2,637 3,263 17,189 Nuclear 3,160 0 0 3,160 Total 40,309 18,789 7,365 66,463 In addition, 14,000 MW through Non- Conventional Energy Sources. Captive capacity not included. Capacity Addition - Perspective Programme Present installed capacity - 1,28,000 MW. Installed capacity by March,2007 ~ 1,41,000 MW. Targeting economic growth rate of 8-10% pa Projected installed capacity by 2012 - 2,07,000 MW Thereafter, doubling of capacity every 10 years. Projected installed capacity by 2030 - 8,00,000 MW.
- 4. Ordering Status of Capacity Addition Programme in XI Plan and in First Three Years of XII Plan (Thermal Sets) (MW) A TOTAL PLANNED CAPACITY I) XI PLAN 48010 ii) XII PLAN (1st 3 YEARS) 43595 TOTAL 91605 B ORDERED I) ON BHEL 12970 ii) ON OTHERS ALREADY ORDERED 7775 BEING ORDERED 9560 30305 C YET TO BE ORDERED (A) - (B) 61300 D 74270 TOTAL LOAD FOR BHEL FOR COMMG IN 2007-2015 (8 YRS) CONSIDERING 100% BALANCE ORDERS ON BHEL (C ) + (B-i) E AVERAGE ANNUAL LOAD ON BHEL 9284 Environmental Implications Projected installed capacity by 2012 - 2,07,000 MW Projected Raw Material Consumption Coal consumption - 1.2 lacs MT/hr Water Consumption - 152 lacs m3/day (6210 cusec) Projected waste generation Ash Generation (34%) ESP Eff 99.93% - 40000 MT/hr SPM released into atmosphere - 357 MT/hr SOX released into atmosphere(0.4% S) - 1200 MT/hr Hazardous Waste Any waste which by reason of any of its Physical, Chemical, Reactive, Toxic, Flammable, Explosive or Corrosive characteristics causes danger or is likely to cause danger to health or environment, whether alone or when in contact with other waste or substances. Basel Convention/ Declaration The Basel Convention (Article 4) requires each party to minimise waste generation and to ensure, to the extent possible, the availability of disposal facilities within its own territory.
- 5. With the objective of environmentally sound management (ESM) of hazardous wastes, the Convention aimed at protecting human health and the environment by minimizing hazardous waste production to the extent possible. 1989 Adoption - After a public outcry against the indiscriminate dumping of hazardous wastes in developing countries by developed-world industries, a diplomatic conference held in Basel, Switzerland, adopted the Convention. 1992 Basel Convention enters into force. 1995 Ban Amendment - The Amendment calls for prohibiting exports of hazardous wastes (for any purpose) 1999 Ministerial Declaration - The Basel Declaration -special emphasis on minimizing hazardous waste. 1998 Classification and Characterizations of Wastes Status of Hazardous Waste Generation S.N. State Recyclable Incinerable Disposal Total 1. Andhra Pradesh 61820 5425 43853 111098 2. Assam - - 166008 166008 3. Bihar 2151 75 24351 26577 4. Chandigarh - - 305 305 5. Delhi - - - 1000 6. Goa 873 2000 3725 6598 7. Gujarat 235840 34790 159400 430030 8. Haryana - - 31046 31046 9. Him. Pradesh - 63 2096 2159 10. Karnataka 47330 3328 52585 103243 11. Kerala 93912 272 60538 154722 12. Maharastra 847436 5012 1155398 2007846 13. Madhya Pradesh 89593 1309 107767 198669 14. Orissa 2841 - 338303 341144 15. J Kashmir - - - 1221 16. Pondicherry 8730 120 43 8893 17. Punjab 9348 1128 12233 22709 18. Rajasthan 9697 17587 95023 122307 19. Tamilnadu 193507 4699 196002 394208 20. Uttar Pradesh 36819 61395 47572 145786 21. West Bengal 45233 50894 33699 129826 Total 1685130 188097 2529947 4405395
- 6. Hazardous Waste Sites Identified Remarks Sites Waste Generating Units S.N. State 1. Andhra Pradesh 478 2 Vishakhapattanam, Medak 2. Assam 18 - 3. Bihar 31 2 Muzaffarpur 4. Chandigarh 37 - 5. Gujarat 2948 22 11 Nos. operational 6. Haryana 42 2 Faridabad, Sonepat 7. Himachal Pra. 71 1 Baddi 8. Karnataka 413 5 Kolar Distt. 9. M.P. + Chattis. 183 16 Bhopal, Raipur 10. Maharastra 3953 8 At six places 11. Orissa 78 7 12. Punjab 619 7 Ropar, Ludhiana 13. Rajasthan 36 1 Pali (Likely) 14. Tamilnadu 1088 8 Serserri, Mannalur 15. U.P. 768 8 Sonebhadra, Moradabad 16. W. Bengal 234 1 Haldia 17. Delhi - - 18. Goa 25 - 19. Kerala 65 - 20. Pondicherry 15 - Gaps Recommendations Survey and Inventorisation of hazardous wastes Setting up of Hazardous wastes and treatment facility Identification of sites for disposal Insufficient information on the quantity and risks associated Inadequate monitoring and enforcement of regulations; Lack of awareness of the risk to health, safety and environment Lack of proper infrastructure for safe containment/disposal.
- 7. Pathways of Exposure to Health Hazards Plants Waste Management Human Animals Food chain Gaseous emissions Leachate Ground water Infection Food chain drinking water Surface water Runoff Organics, Heavy metal, Toxicity Contaminati on of Soil Water Open dump Air pollution Bacteria, Pests Method Advantages Disadvantages Can cause air pollution Proper operation/management /maintenance Can’t destroy non organic and metallic toxicity Volume reduction Minimum land requirement Safer than land fill Detoxification of waste Converts waste to solid Heat can be recovered Incineration Settlement require maintenance. Requires proper planning, design operation Large volume can be disposed Cost effective Filled land can be reused Secure Land fill - Health Hazard, Insects, Rodents - Air Pollution - Water Pollution - Aesthetics Problem Open - Inexpensive Dumping Time taking May need investment Unavailability of appropriate tech. May be costlier than products made by using virgin raw material Waste reduction Resource conservation Saving Lesser cost of treatment disposal Reuse May polluted ground water May cause underground explosions etc . Unpredictable No land required No treatment required Deep well injection - Needs segregation - Can be done only non hazardous organic wastes - Hazardous waste may creep in not properly segregated, Water pollution, Hazards - Easy - Get manure Composting ( Vermi composting)/ Land application
- 8. Impacts Associated with Disposal Sites Environmental Impacts Health Impacts Aesthetic Basic Approach in Hazardous Waste Management Identification of Hazardous waste generation. Inventorization of hazardous waste Waste characteristics Qunatification of hazardous waste Identification of sites for disposal- Their ranking Conducting EIA Implementing/ Operation of disposal sites Site Selection Collection of preliminary data · Topographic maps · Soil maps · Land use plans · Transportation maps · Water use plans · Flood plain maps · Geologic maps · Aerial photographs / Satellite imagery · Ground water maps · Rainfall data · Wind map Impacts Chemical Entities Biological Entities Social Impacts Air Environment Water Environment Land Environment • Gaseous emissions • SPM • Fire • Intermediate decomposition products • Toxic constituents • Animals • Birds • Pathogens • Activities of adjoining population • Odour • Litter • Vision • Changes in Soil Properties • Land Contamination • Surface Ground Water Pollution
- 9. · Seismic data · Site visit · Preliminary Boreholes Geophysical investigation Selection of two best ranked sites Environmental Impact Assessment for the two sites for the following parameters. · Ground water quality · Surface water quality · Air quality – gases, dust , litter, odour · Land use alteration · Drainage alteration · Soil erosion · Ecological impacts · Noise · Aesthetics – visual, vermin, flies · Traffic alteration Preliminary Assessment for Selection of Candidate site Preliminary Assessment · Candidate sites to be identified based on the satellite imageries and topographical sheets of the area. · Preliminary studies with respect to their prominent features, surrounding establishments and their proximity to drinking water sources, habitation and present usage etc. has to be done. Rejection or knockout criteria · Characteristics of land · Geology, Hydro-geology · Ground Water Conditions · Ecological considerations Preliminary Assessment for Rejection Criteria Unstable geological features like – Unstable or weak soils: organic soil, soft clay or clay-sand mixtures, soils that lose strength with compaction or with wetting, clays with a shrink-swell character, sands subject to subsidence and hydraulic influence. Subsidence owing to subsurface mines, oil or gas withdrawal; or solution-prone subsurface Flood prone areas Areas within 500 meter from water supply zone and within 200 meter from property line Natural depression and valleys where water contamination is likely Areas of ground water recharge and extremely high water table zone Unique habitation areas, close to national parks with scenic beauty Areas with high population, unique archaeological, historical and religious interests Agricultural and forest lands and existing dump sites The identified site are excluded if the following conditions are existing : · An unfavourable local hydro-geological situation, e.g. springs or drinking water wells within very close proximity to the chosen area
- 10. · Extremely bad access, i.e. no existing access roads to the selected area which may involve · Long distance more than 5 km from main roads · Access roads passing densely populated areas · Great differences in altitude between the area of waste collection and the selected site · Very intense agricultural use · Inadequate available area · Difficult geological situation, danger of mass movements, too steep slopes, strata-bound groundwater etc. Secure Landfill Detailed Site Investigation The main objective of the detailed evaluation is to assign the relative rank to the potential sites among themselves. Before taking up detail evaluation, base line data regarding the site and it's surroundings have to be collected on · Ambient air quality · Water quality · Ambient Noise quality · Soil quality Compacted soil of low permeability Monitoring WGealls s Wat er To Leachate Treatment Plant To Gas recovery SystemProtective Clay layer Solid Waste Leachate collection sump Leachate collection removal syLsteeamchate detection , collection removal system Protecti ve liners Drain pipes Surface Runoff diversion
- 11. The sites have to be investigated for · Site Specific Information; proximity to the waste source, slope at site, topography, accessibility, meteorology etc. · Hydro-geology/Geology; Ground water table fluctuation, ground water direction, ground water quality, depth to bed rock, soil type, geo-technical features etc · Socio-economic Features; land use, demography, transportation impact etc. Site Selection Through Ranking Attribute and Site Sensitive Index Site sensitive index graded in 4 categories Receptor related attributes influencing human habitation in the vicinity Environment related attributes covering pollution pathways Accessibility related attributes covering house distance Socio-economic related attributes influencing social environment Waste management related attributes covering composition and quality of the waste Geological related attributes covering hydro geological aspects Development of Site Sensitivity Index Sr. No. Attribute 0.0-0.25 0.25-0.5 0.5-0.75 0.75-1.0 Accessibility Related 1. Type of road National highway State highway Local road No road 2. Distance from collection area 10 km 10-20 km 20-25 km 25 km Receptor Related 3. Population within 500 meters 0 to 100 100 to 250 250 to 1000 1000 4. Distance to nearest drinking water source 5000 m 2500 to 5000 m 1000 to 2500 m 1000 m 5. Use of site by nearby residents Not used Occasional Moderate Regular 6. Distance to nearest building 3000 m 1500 to 3000 m 500 to 1500 m 500 m 7. Land use/Zoning Completel y remote (zoning not applicable) Agricultural Commercial or industrial Residential 8. Decrease in property value with respect to distance 5000 m 2500 to 5000 m 1000 to 2500 m 1000 m 9. Public utility facility within 2 kms Commerci al and industrial area National heritage Hospital Air port
- 12. Sr. No. Attribute 0.0-0.25 0.25-0.5 0.5-0.75 0.75-1.0 10. Public acceptability Fully accepted Acceptance with suggestions Acceptance with major changes Non acceptance Environmental Related 11. Critical environment Not a critical environment Pristine natural areas Wetlands, flood plains, and preserved areas Major habitat of endangered or threatened species 12. Distance to nearest surface water 8000 m 1500 to 8000 m 500 to 1500 m 500 m 13. Depth to ground water 30 m 15 to 30 m 5 to 15 m 5 m 14. Contamina-tion No contamina-tion Soil contamina-tion only Biota-contamina-tion Air, water or food contamina-tion 15. Water quality Confirming to standard Potable Polluted Highly polluted 16. Air quality Confirming to residential standards Confirming to industrial standards Polluted Highly polluted 17. Soil quality No contamina-tion Average Contami-nated Highly contami-nated Socio-economic Related 18. Health No problem Moderate High Severe 19. Job opportunities High Moderate Low Very low 20. Odour No odour Moderate odour High odour Intensive foul odour Sr. No. Attribute 0.0-0.25 0.25-0.5 0.5-0.75 0.75-1.0 21. Vision Site not seen Site partly seen (25%) Site partly seen (75%) Site fully seen Waste Management Practice Related 22. Waste quantity/day 250 tonnes 250 to 1000 tonnes 1000 to 2000 tonnes 2000 tonnes 23. Life of site 20 years 10-20 years 2-10 years 2 years Climatological Related 24. Precipitation effectiveness index* 31 31 to 63 63 to 127 127 25. Climatic features contributing to Air pollution No problem Moderate High Severe Geological Related 26. Soil permeability 1 X 10-7 cm/sec. 1 X 10-5 to 1 x 10-7 cm/sec. 1 X 10-3 to 1 x 10-5 cm/sec. 1 X 10-3 cm/sec. 27. Depth to bedrock 20 m 10 to 20 m 3 to 10 m 3 m 28. Susceptibility to erosion and run-off Not susceptible Potential Moderate Severe 29. Thickness of bedrock 20 m 20-10 m 10-2 m 2 m 30. Physical characteris-tics of rock Massive Weathered Highly weathered 31. Depth of soil layer 5 m 2-5 m 1-2 m 1 m 32. Slope pattern 1% 1-2% 2-5% 10% 33. Seismicity Zone I Zone II Zone III Zone IV V * Precipitation effectiveness index is the ratio of annual precipitation of annual evaporation
- 13. Ranking Methodology Using Delphi Technique Weightage allocation based on importance and pairwise comparison Site score calculation based on site sensitive index and individual attribute weightage Facilitates in the selection of the best available site Site with least score will be less sensitive to impact hence most acceptable Worksheet for Ranking of Sites Name of site : Location : Attribute Attribute measurement Sensitivity index Weightage Attribute score Accessibility Related Type of road 25 Distance from collection point 35 Total 60 Receptor related Population within 500 meters 50 Distance to nearest drinking 55 water source Use of site by nearby residents 25 Distance to nearest building 15 Land use/Zoning 35 Decrease in property value with 15 respect to distance Public utility facility within 2 kms 25 Public acceptability 30 Total 250 Attribute Attribute measurement Sensitivity index Weightage Attribute score Environmental Related Critical environments 45 Distance to nearest surface 55 water Depth to ground water 65 Contamination 35 Water quality 40 Air quality 35 Soil quality 30 Total 305 Socio-economic Related Health 40 Job opportunities 20 Odour 30 Vision 20 Total 110 Waste Management Practice Related Waste quantity/day 45 Life of site 40 Total 85
- 14. Aggregating Score for Site Selection The site suitability decreases with increase in the total score Total Score Site Description 300 Less sensitive to the impacts (preferable) 300 to 750 Moderate 750 Highly sensitive to the impacts (undesirable) A Safe and Sound Handling Attribute Attribute measurement Sensitivity index Weightage Attribute score Climatological Related Precipitation effectiveness index 25 Climatic features contributing to Air pollution 15 Total 40 Geological Related Soil permeability 35 Depth to bedrock 20 Susceptibility to 15 erosion run-off Physical characteristics of rock 15 Depth of soil layer 30 Slope pattern 10 Seismicity 20 Total 150 Grand Total 1000
- 15. Environment Management Plan Air Quality Monitoring and Management · Periodic Monitoring of air quality · Maintenance of grass cover · Black top roads · Odor control by rapid stabilization · Minimizing working distances internally · Green belt development to attenuate noise · Silencers to generators and vehicles Water Quality – Surface and Ground · Clean water diversion · Proper leachate management · Periodic Monitoring · Double composite liner system · Effective drainage system · Appropriate capping · Spill control procedures Activity wise Mitigation Measures During · Site Clearance · Construction · Operation · Closure · Post-closure Phase EMP should also delineate the environmental monitoring plan for compliance of various environmental regulations
