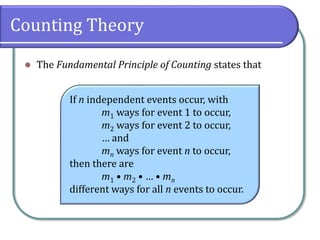
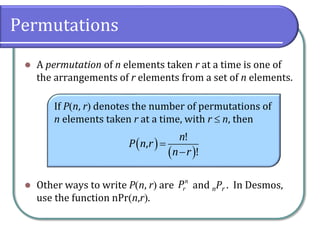
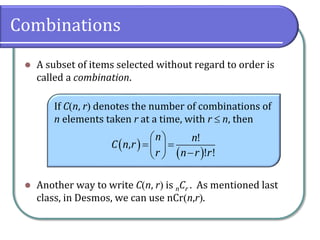
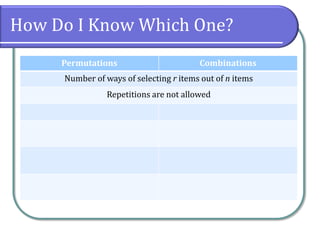
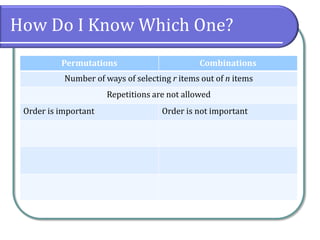
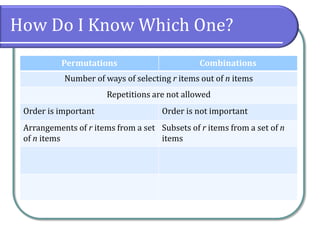
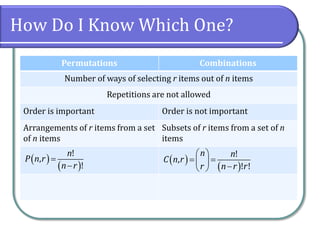
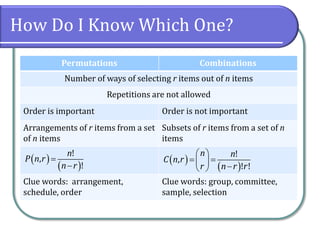
This document discusses counting theory and introduces permutations and combinations. It defines the fundamental principle of counting as the number of ways independent events can occur by multiplying the number of possibilities for each event. Permutations are arrangements of items where order matters, while combinations are subsets of items where order does not matter. Formulas and examples are provided to calculate permutations and combinations. Guidance is given on determining whether a problem requires permutations or combinations based on whether order is important.