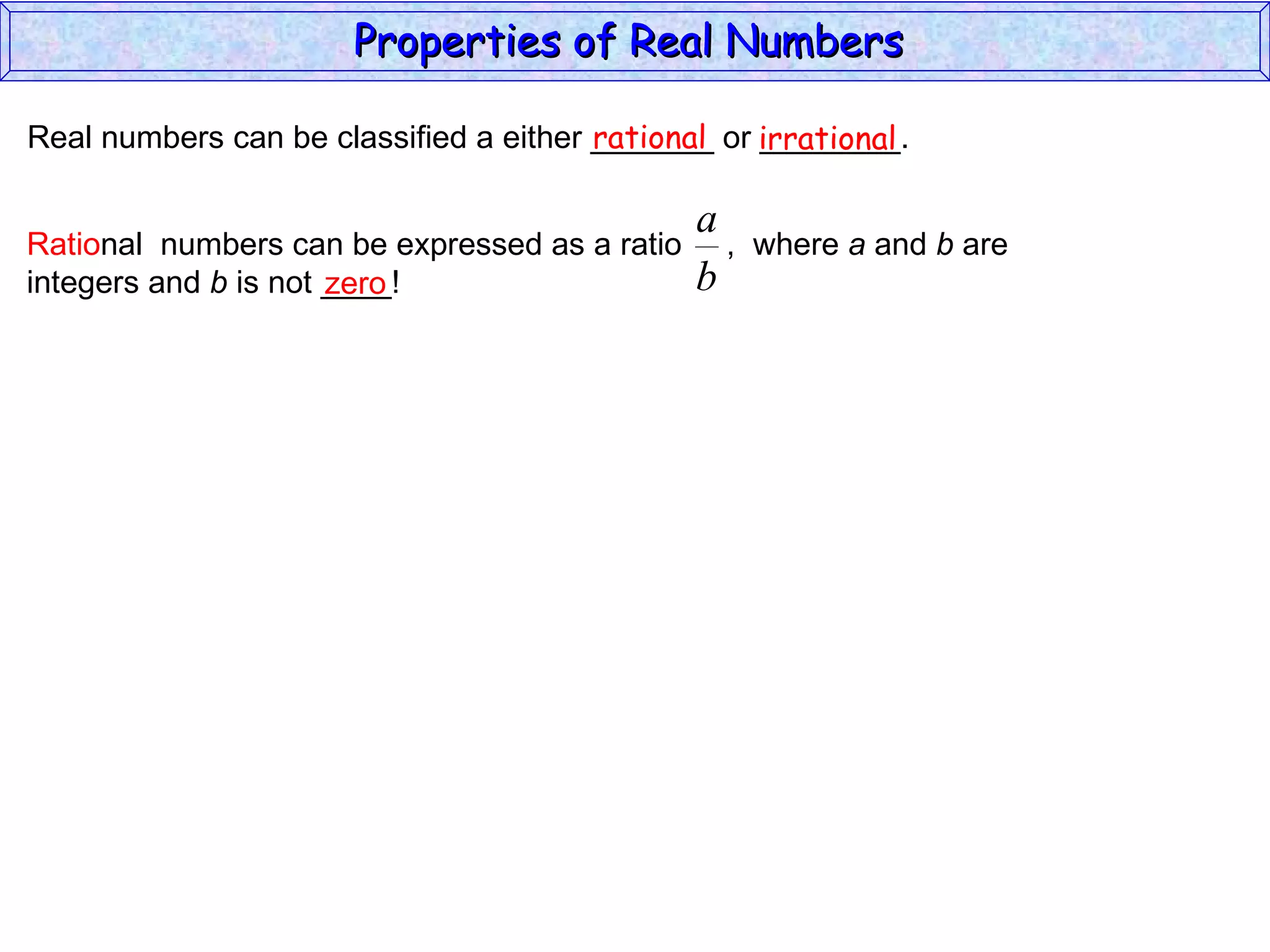
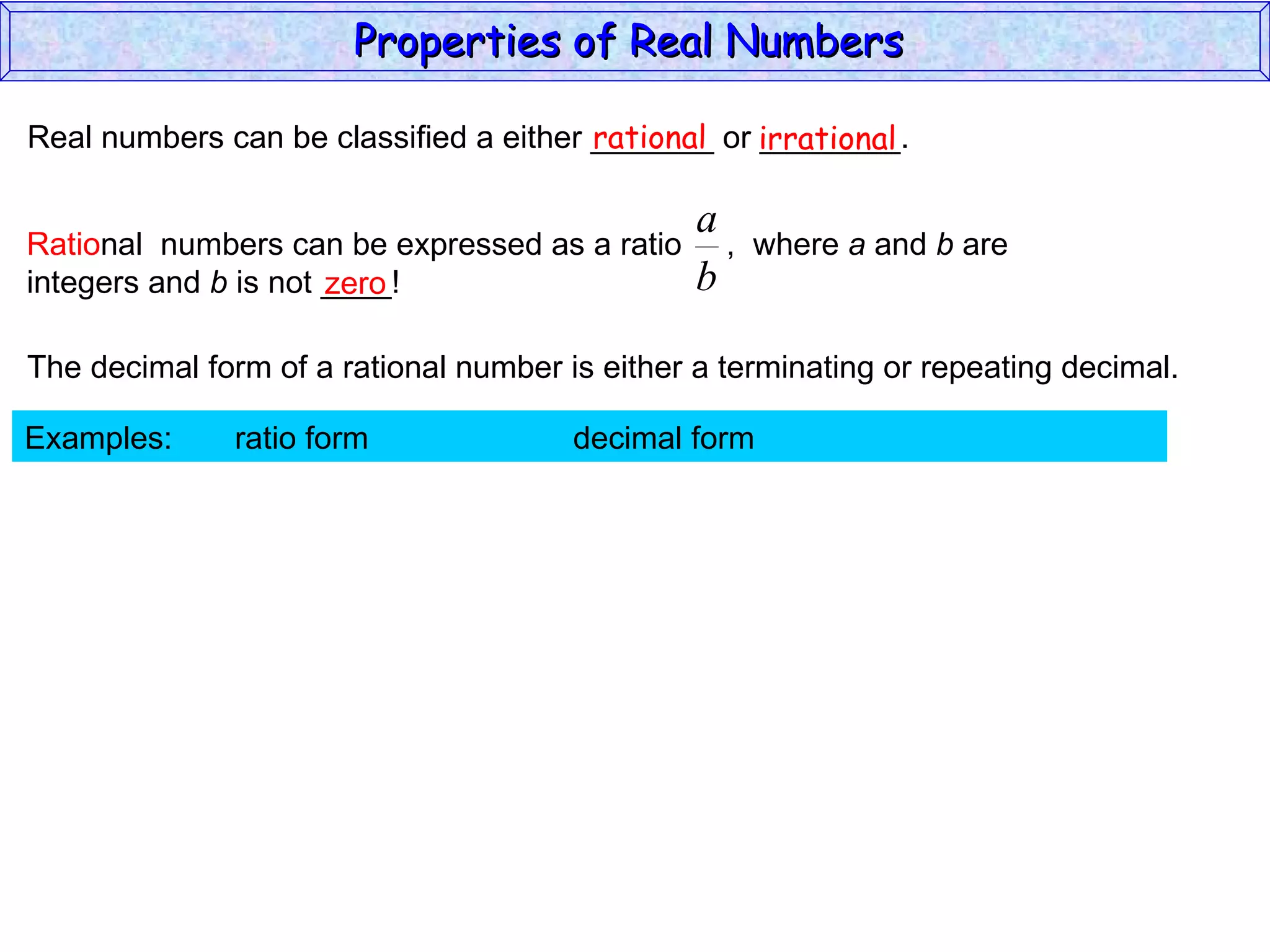
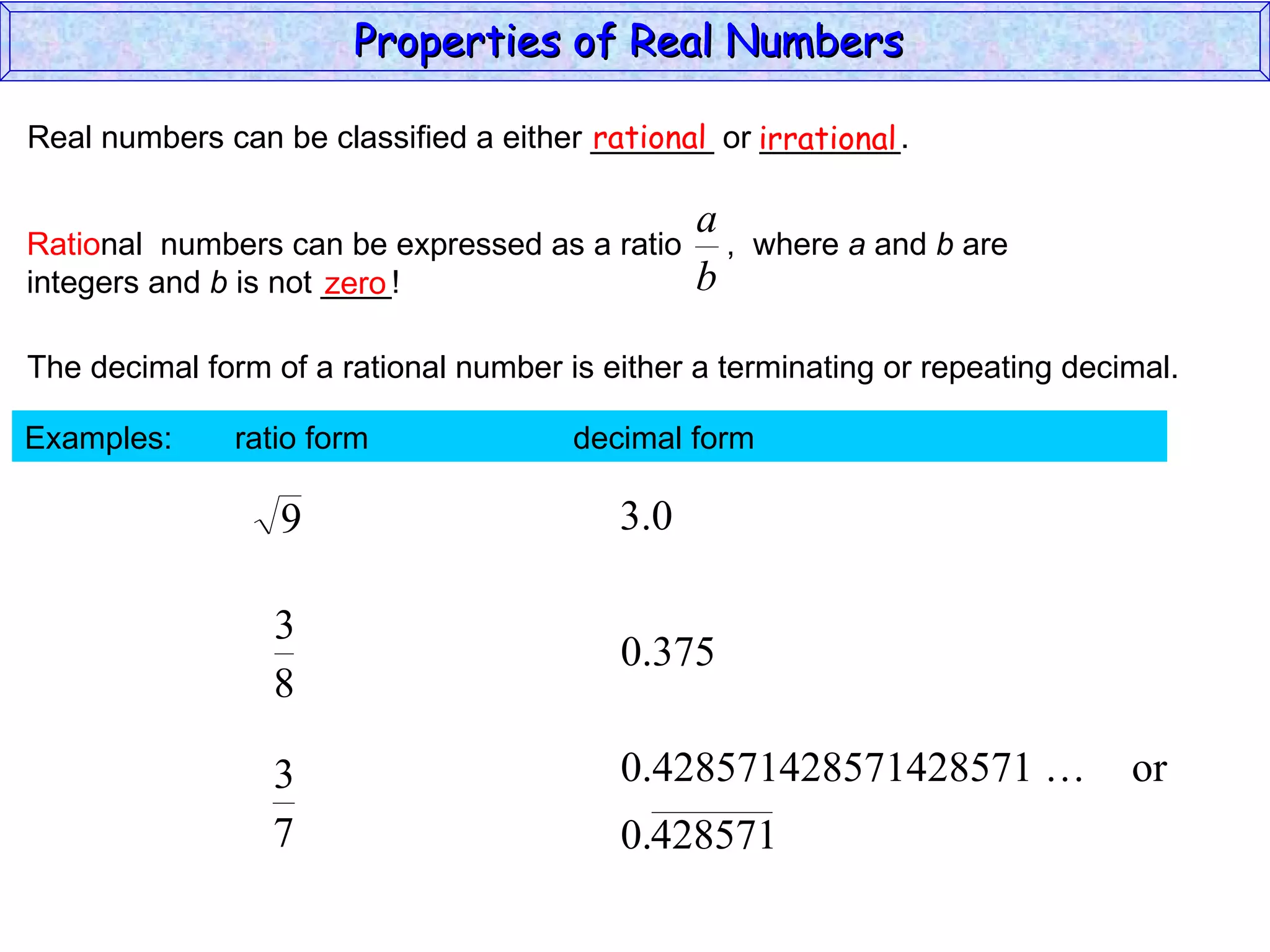
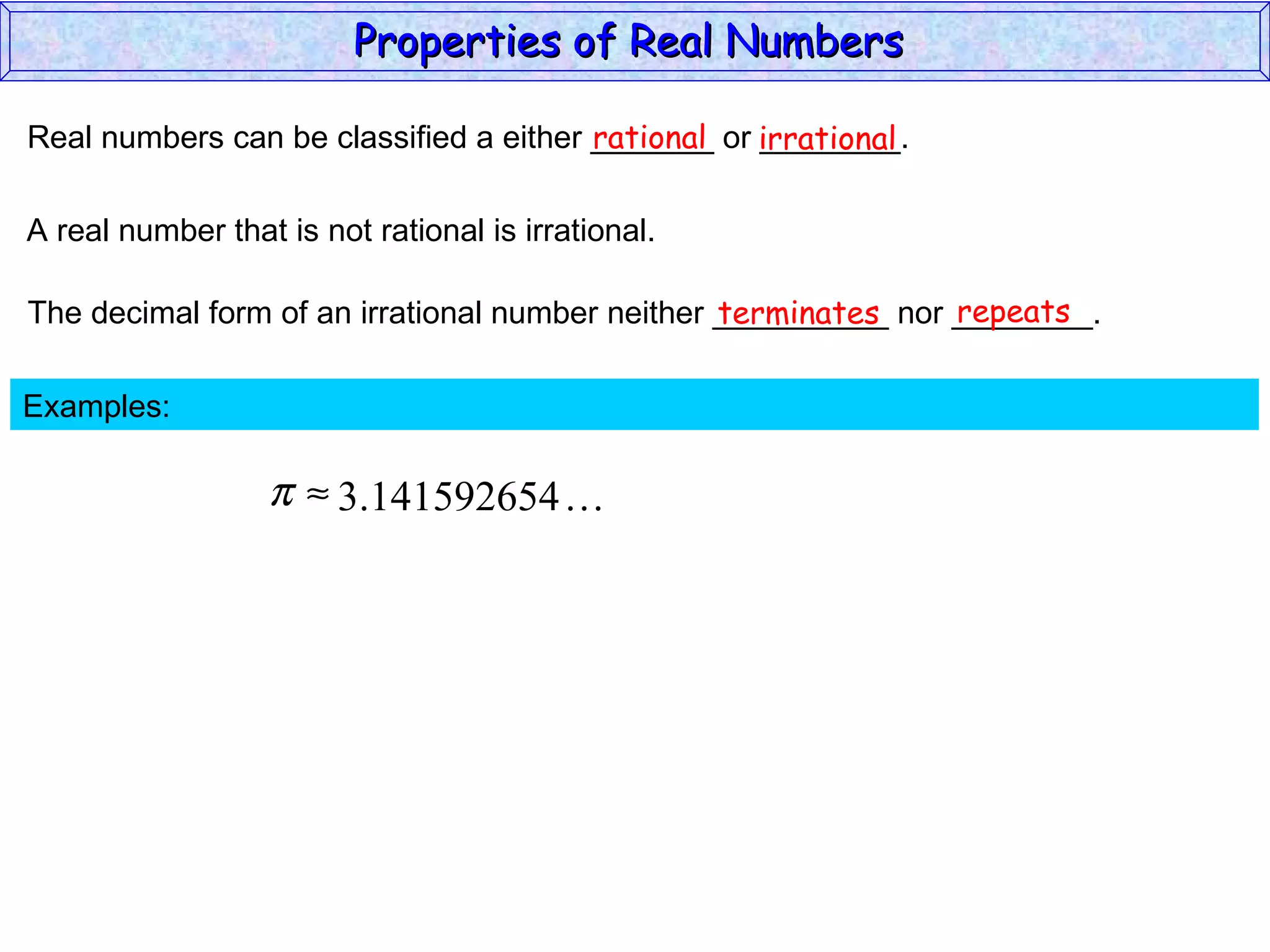
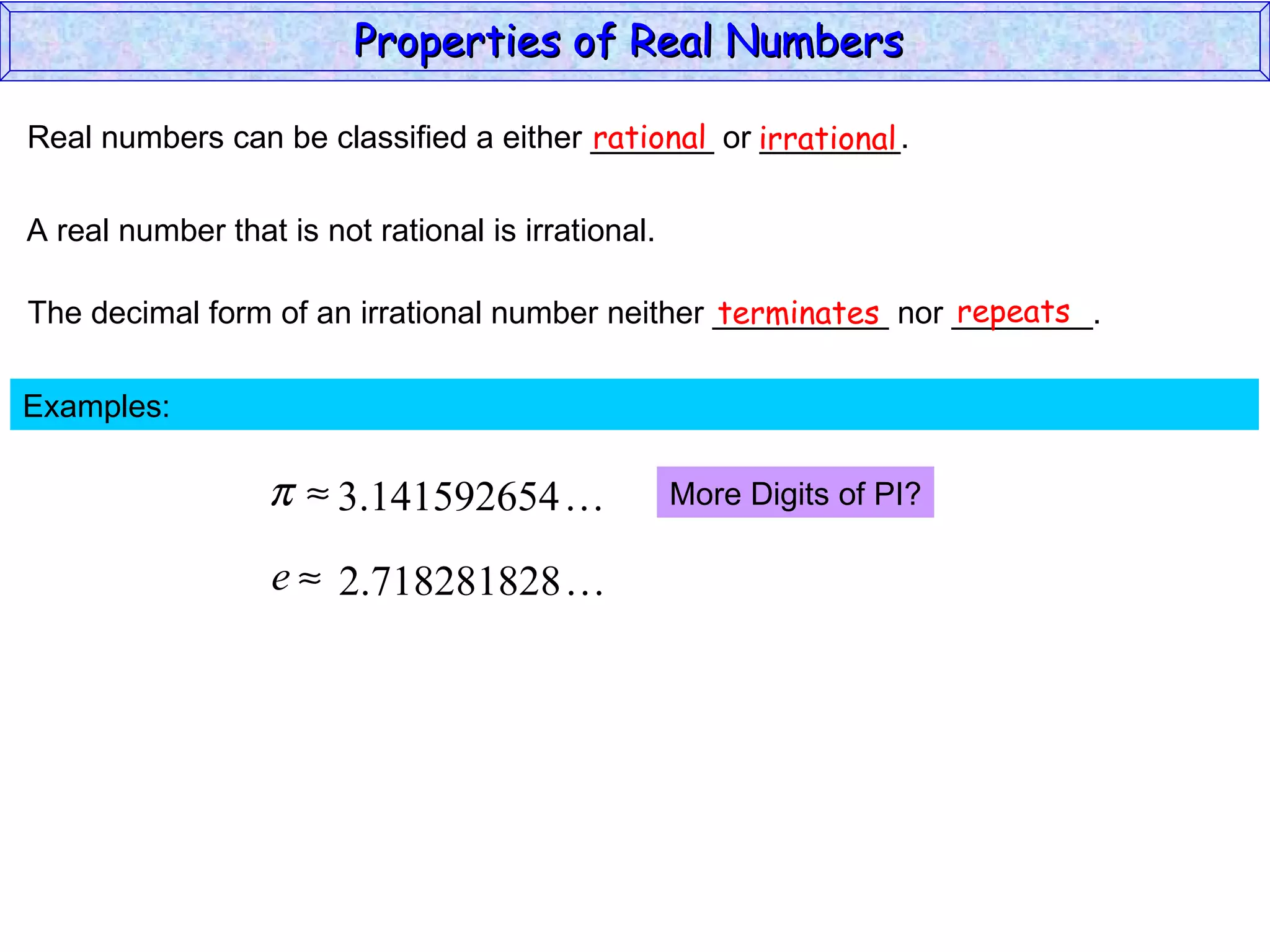
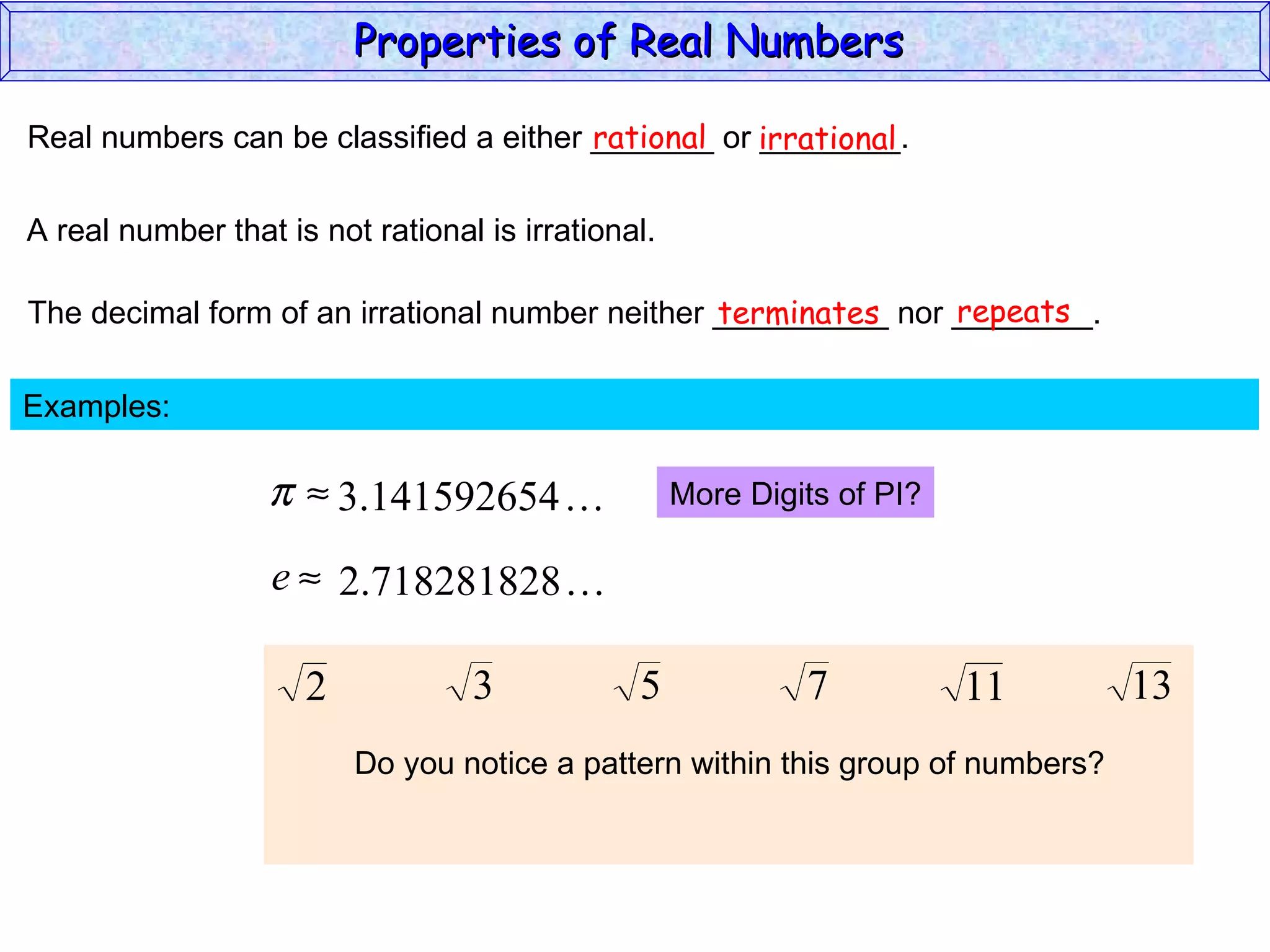
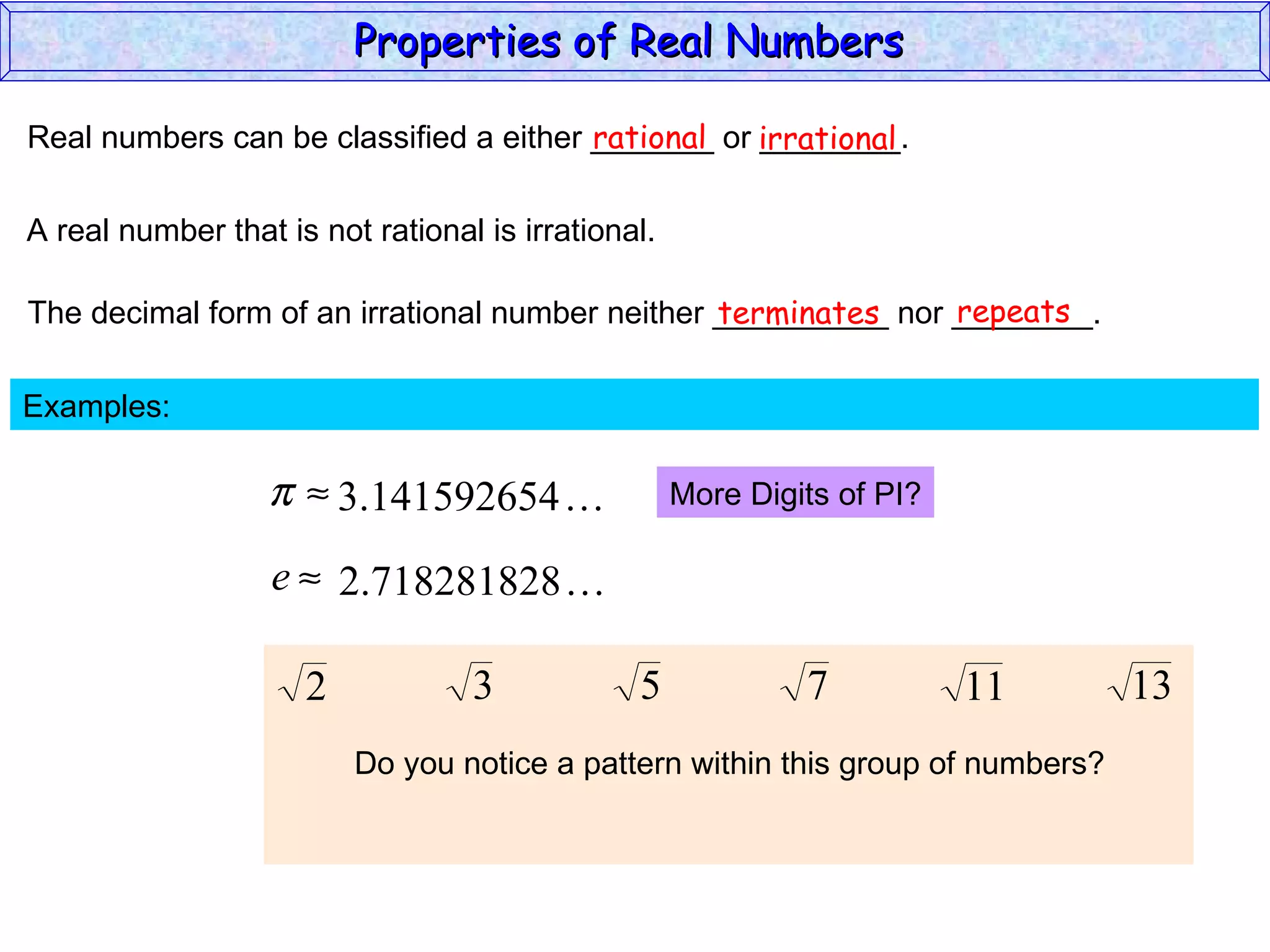
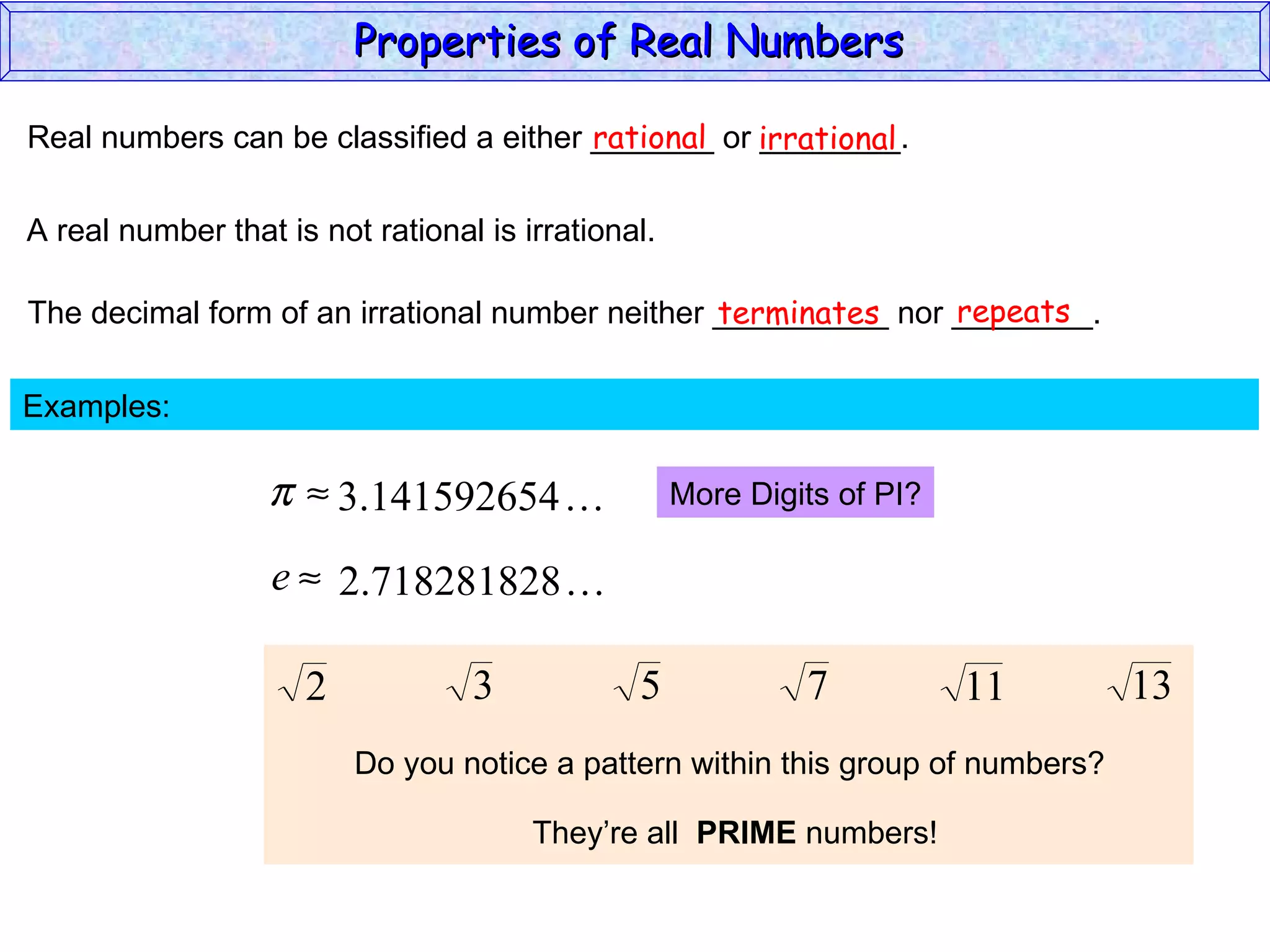
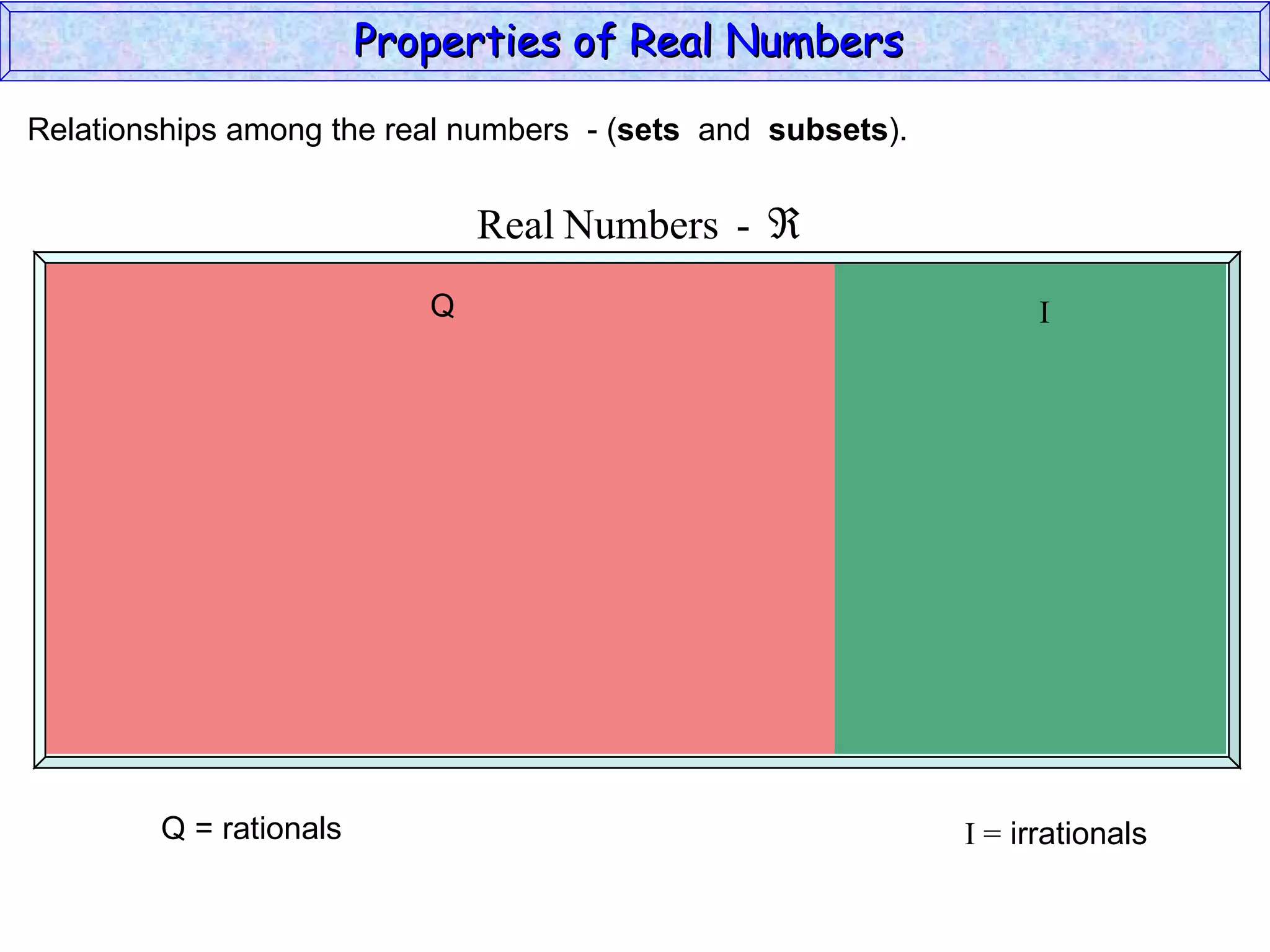
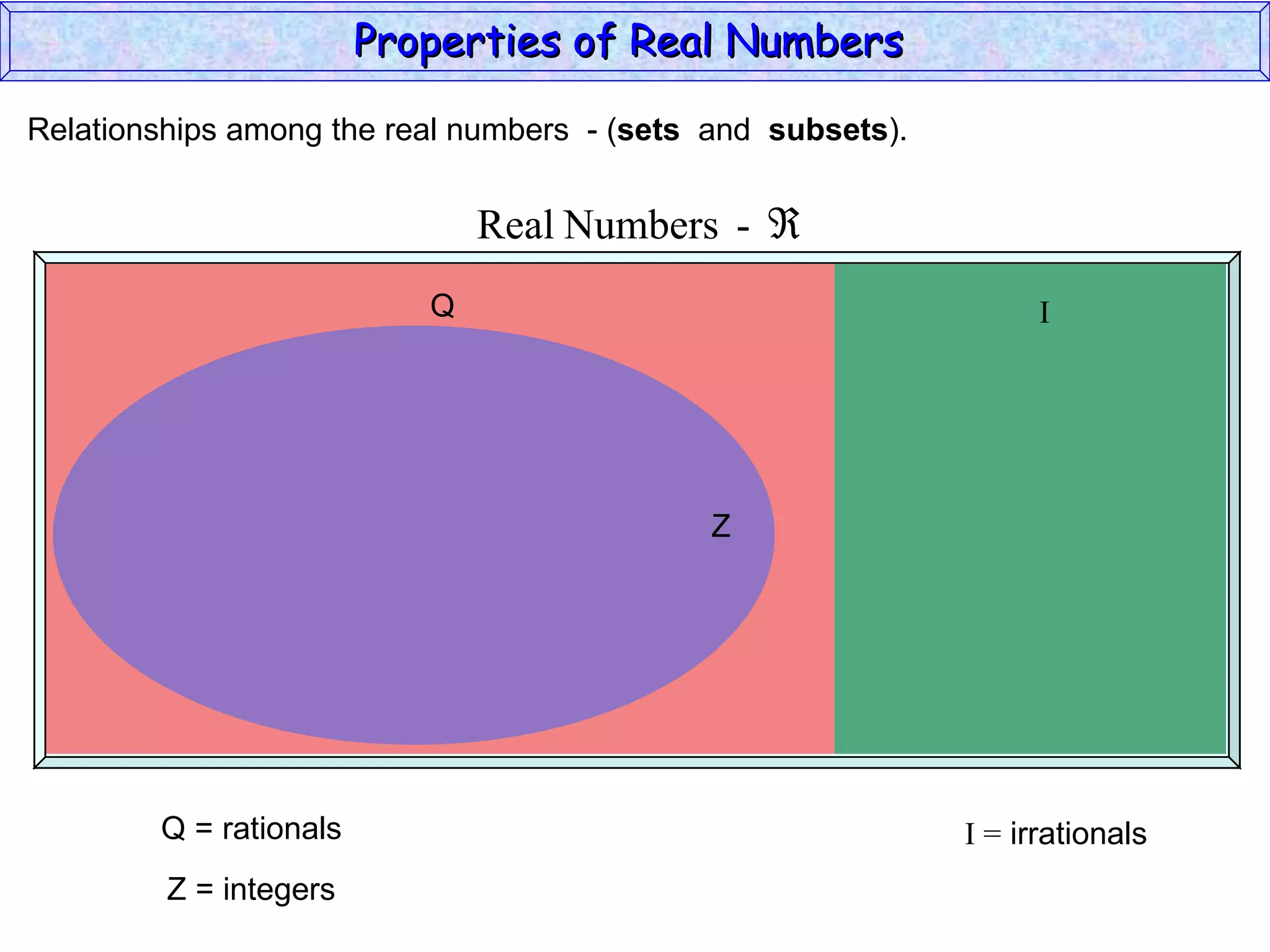
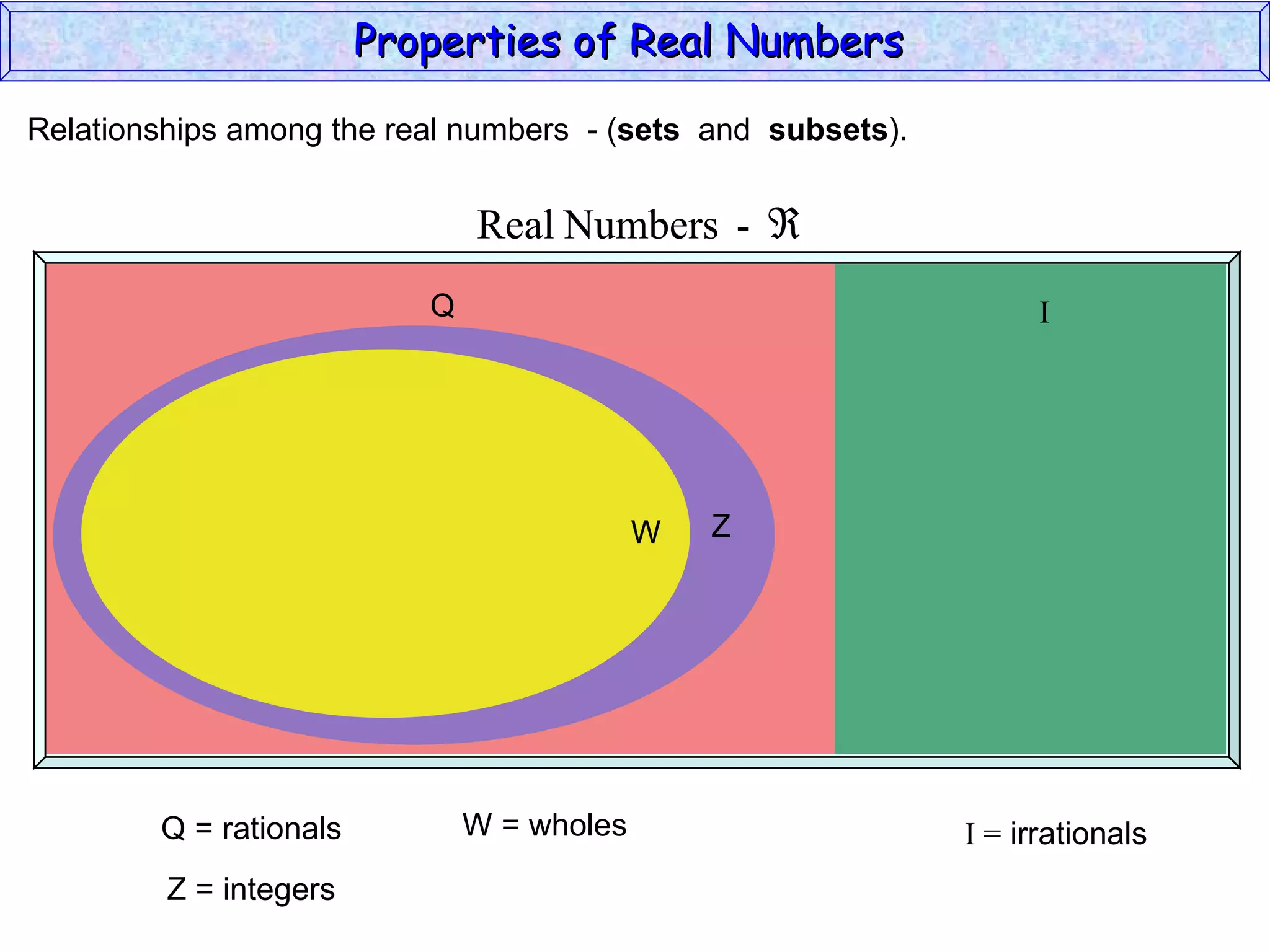
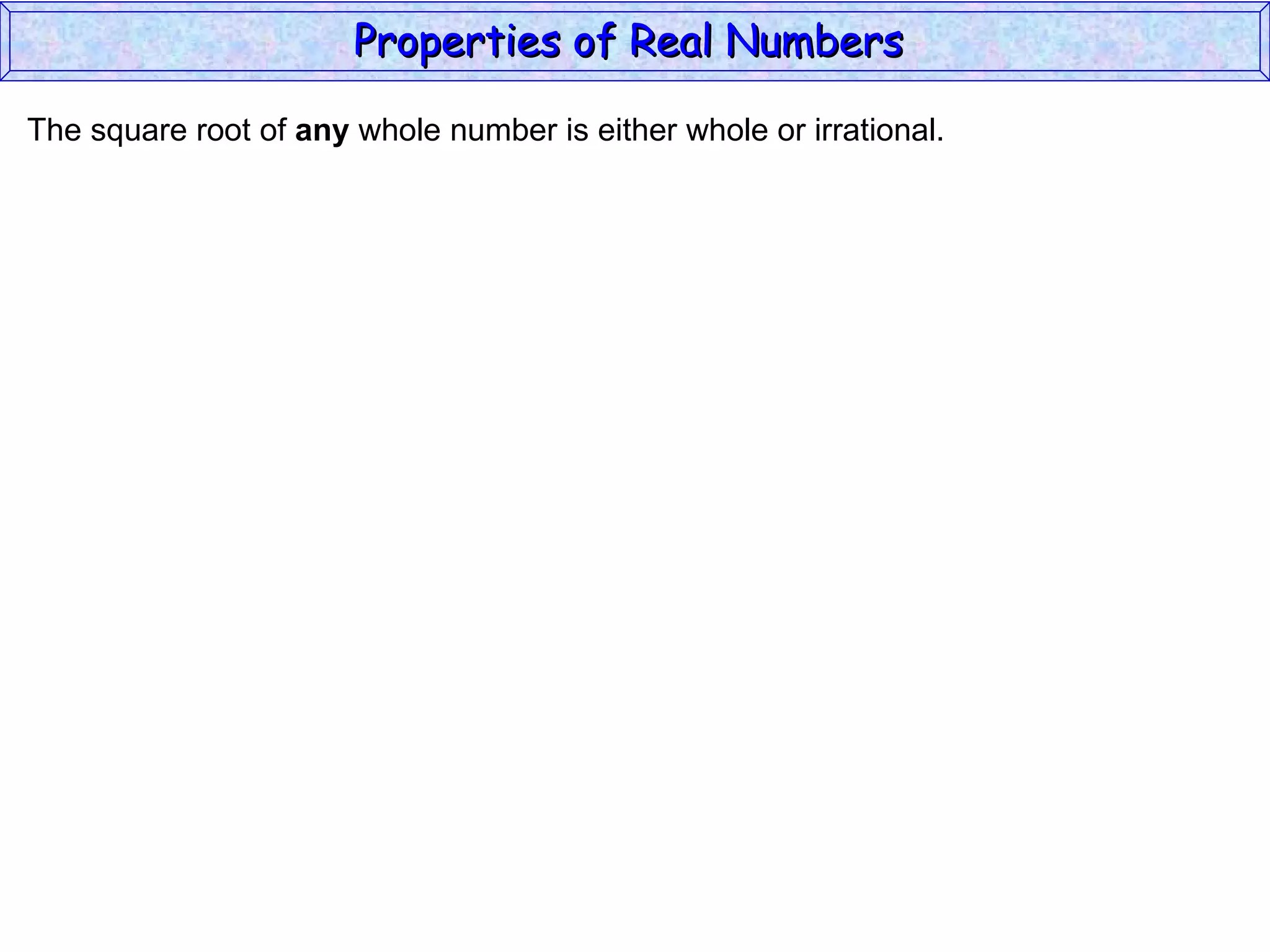
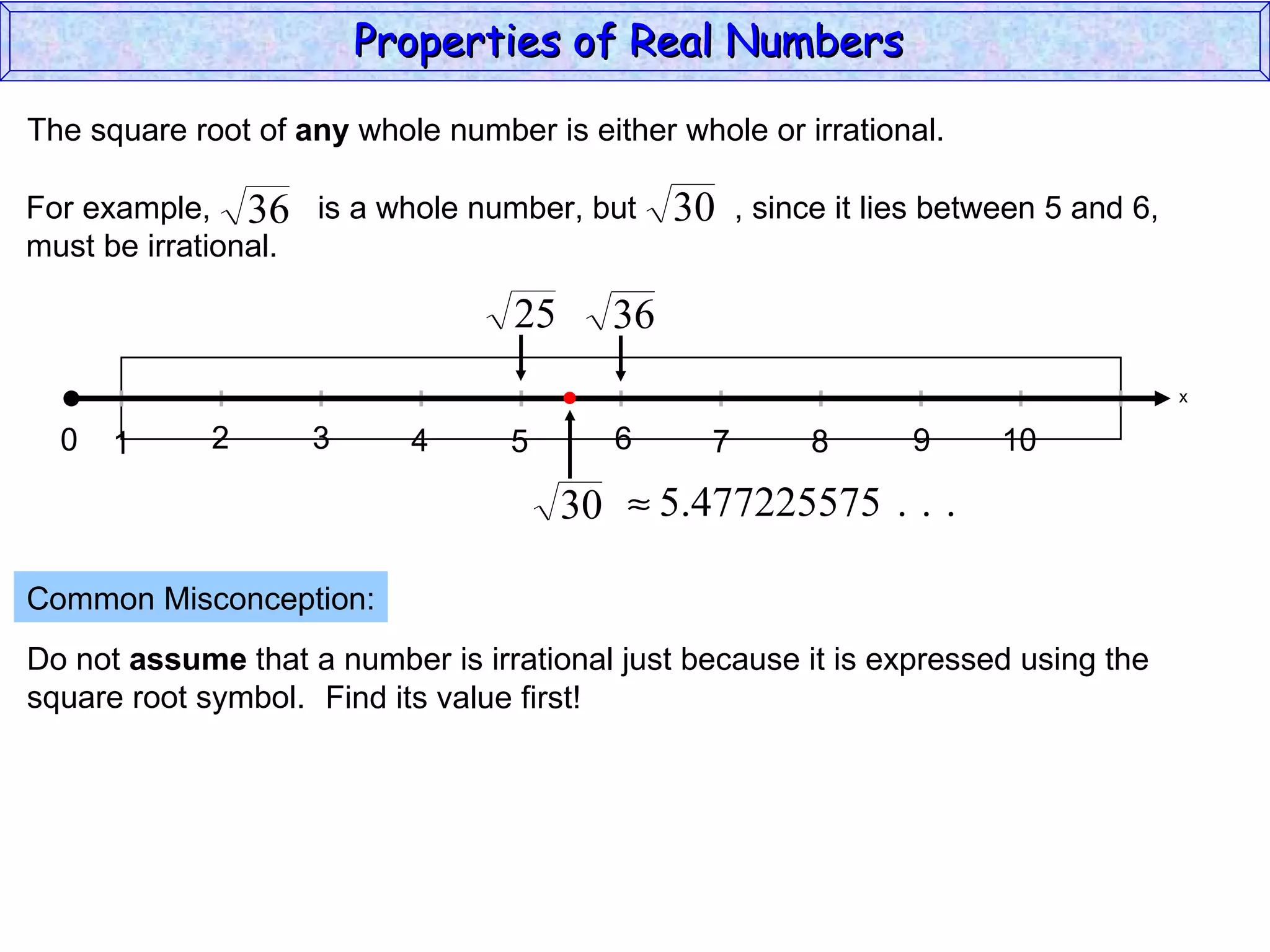
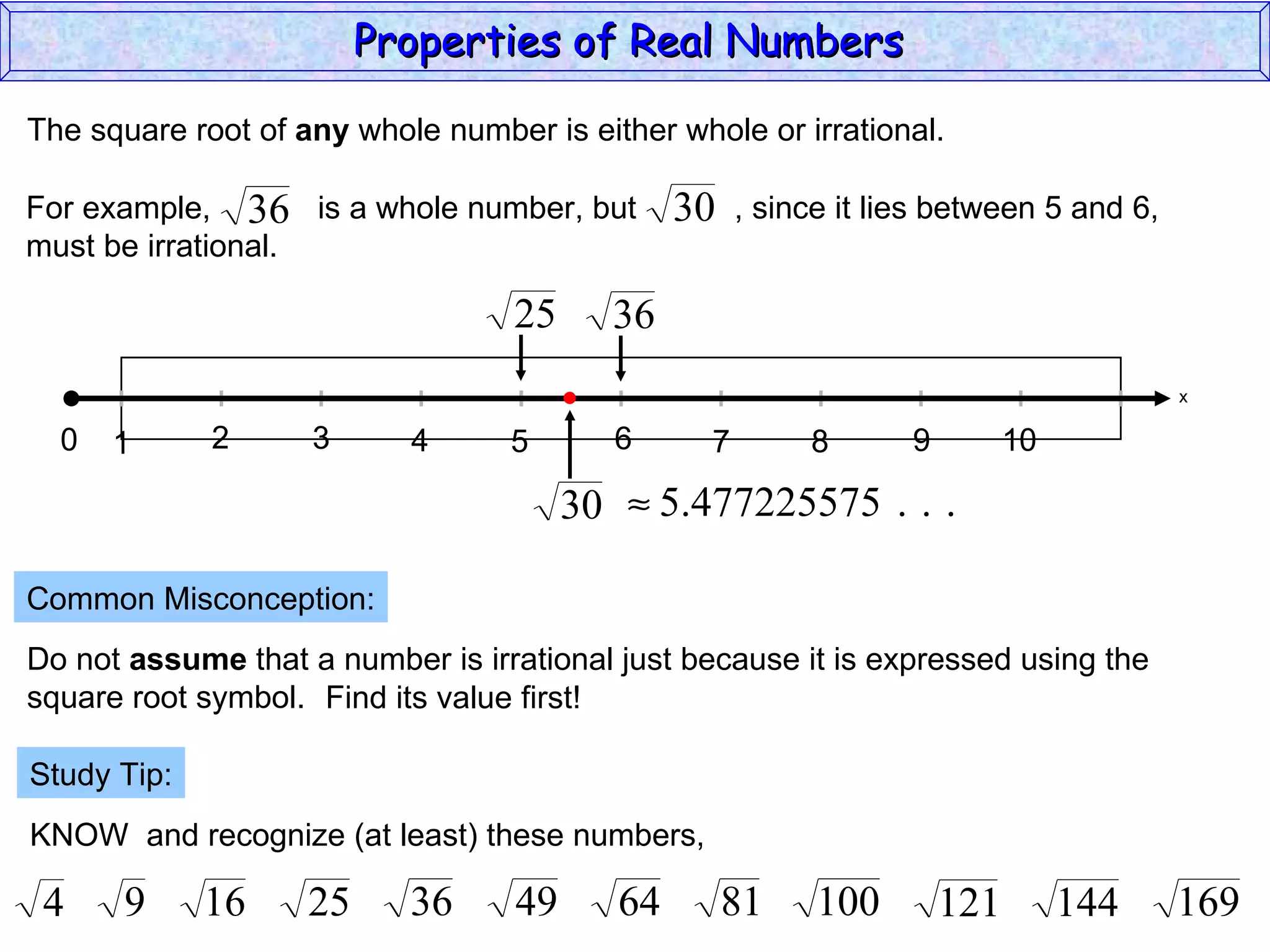
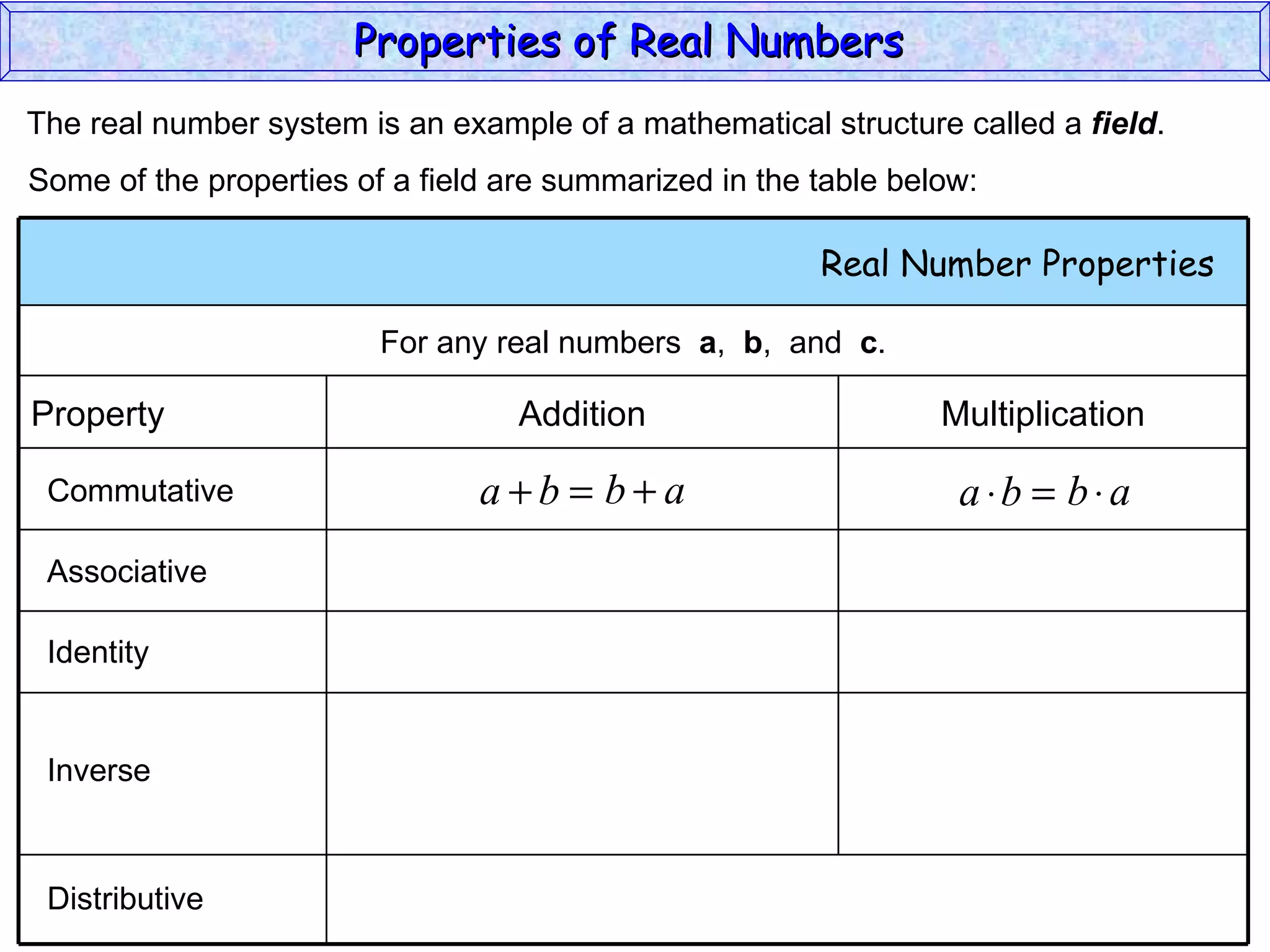
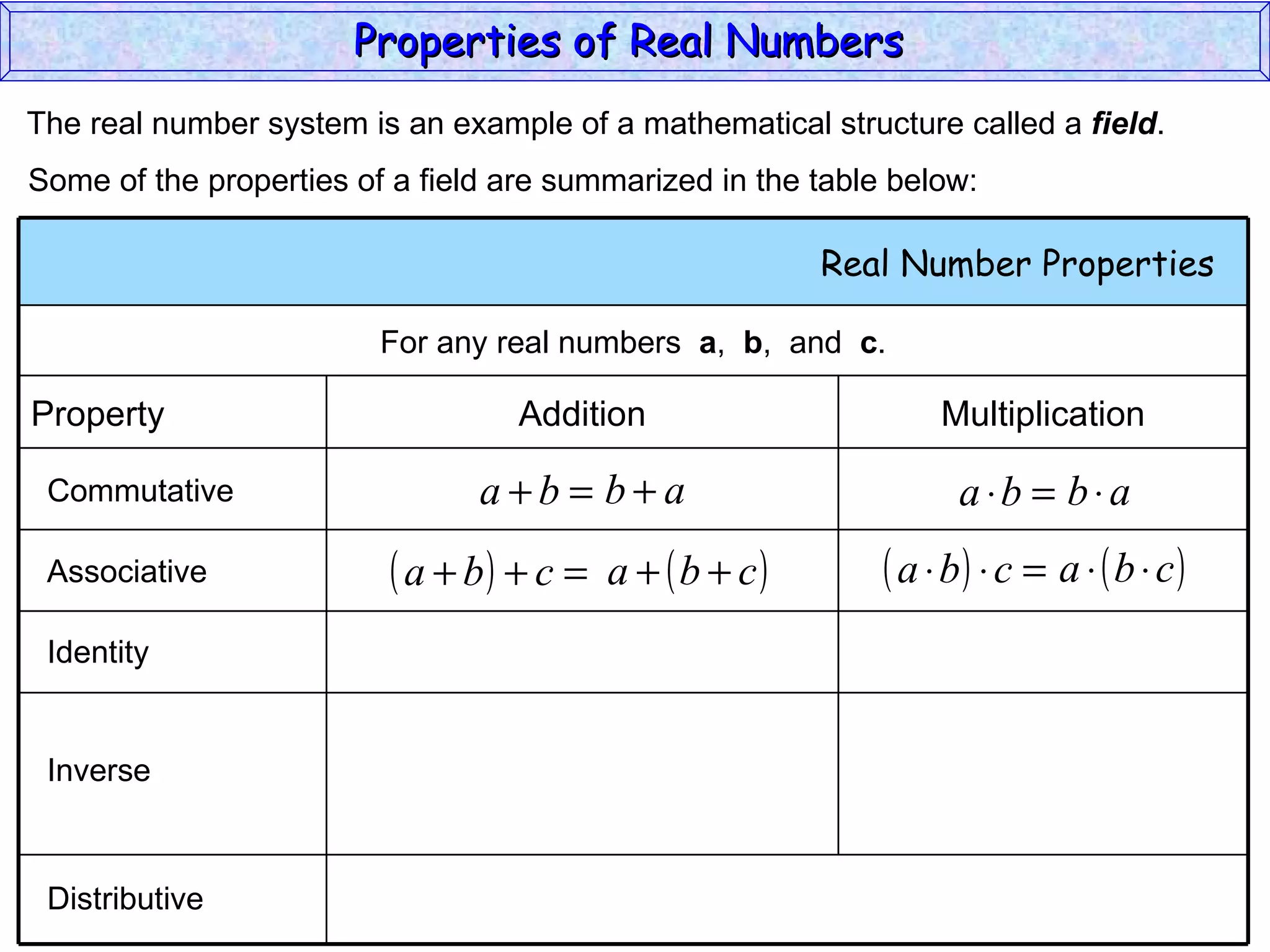
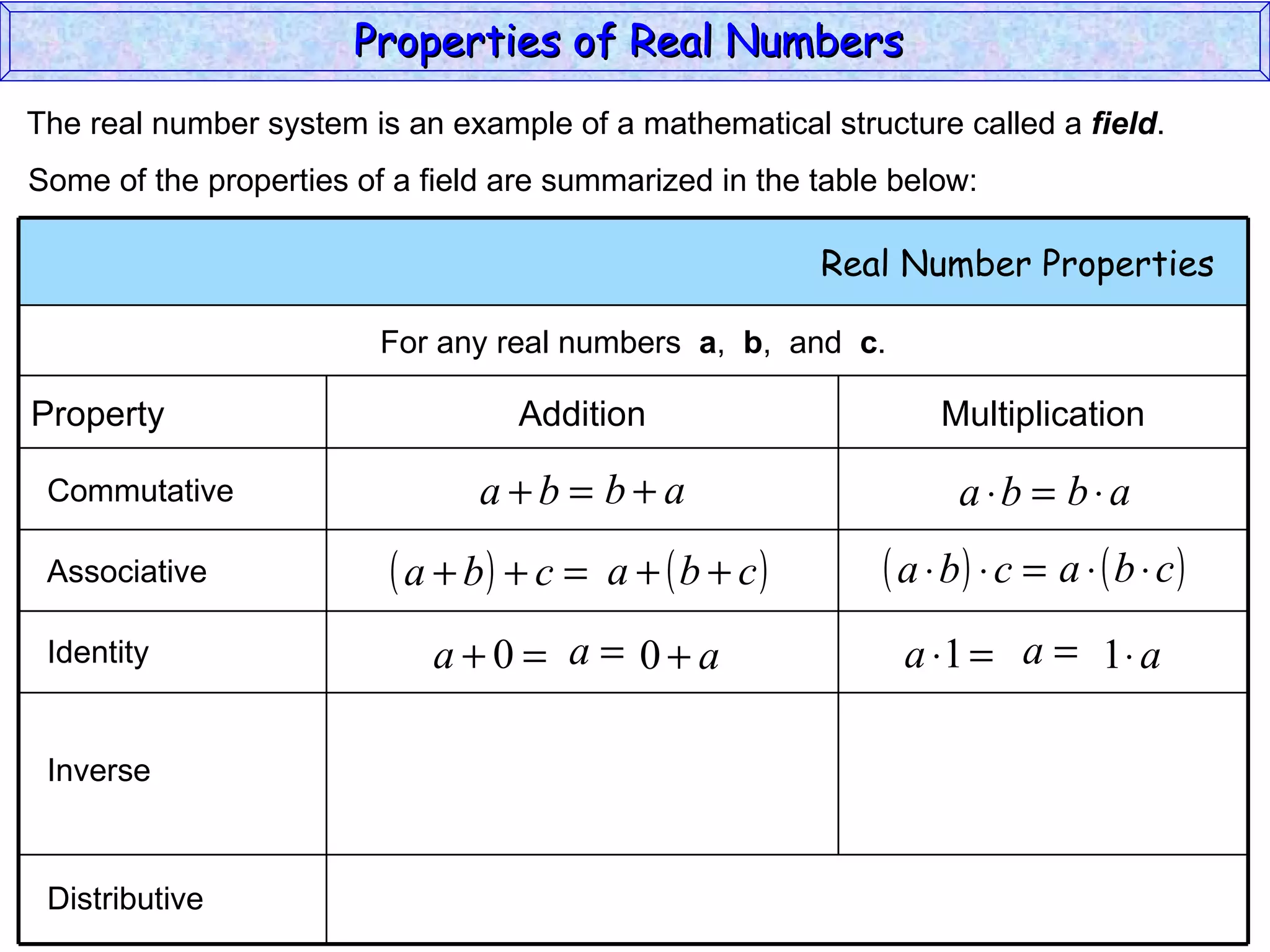
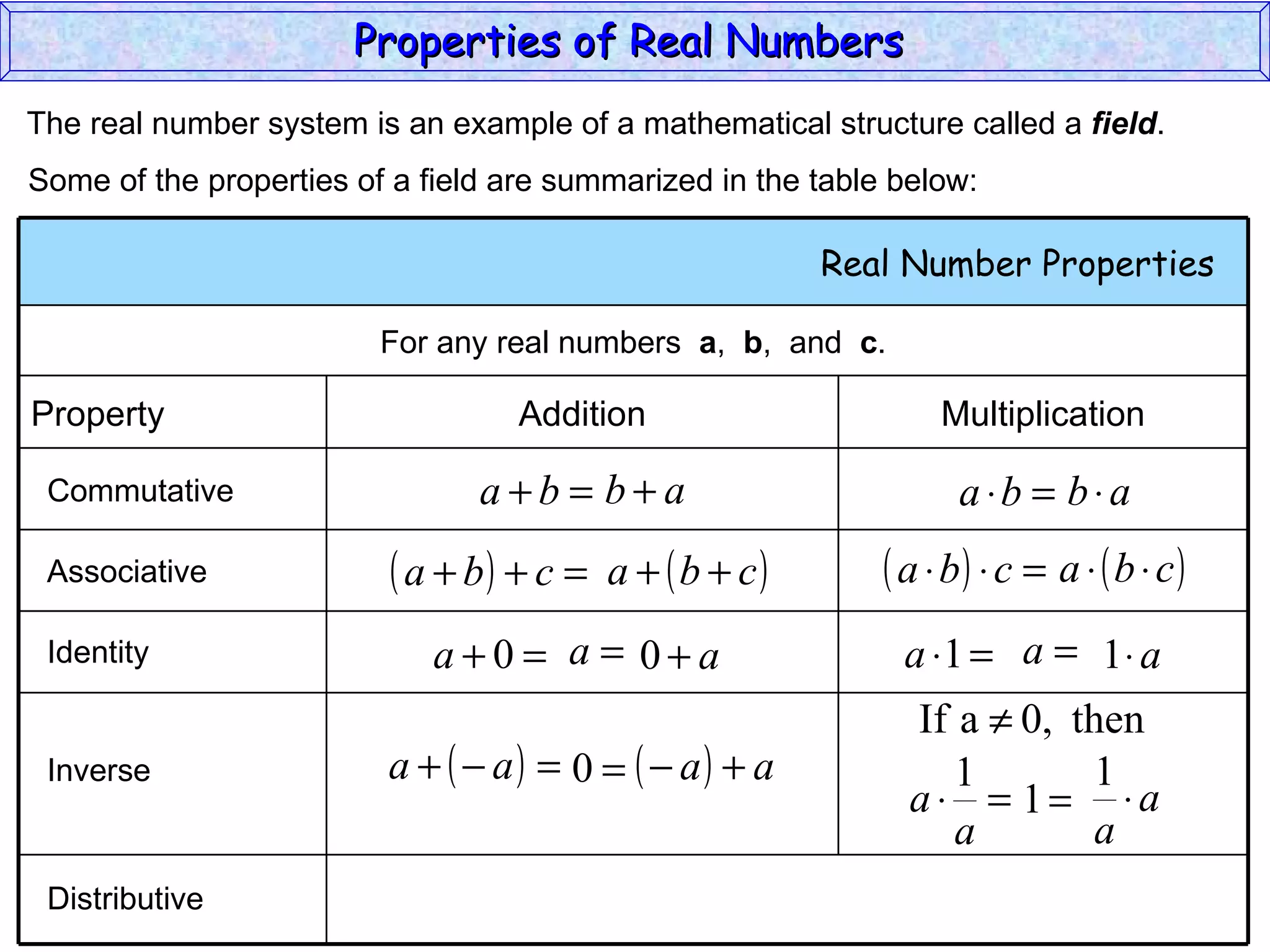
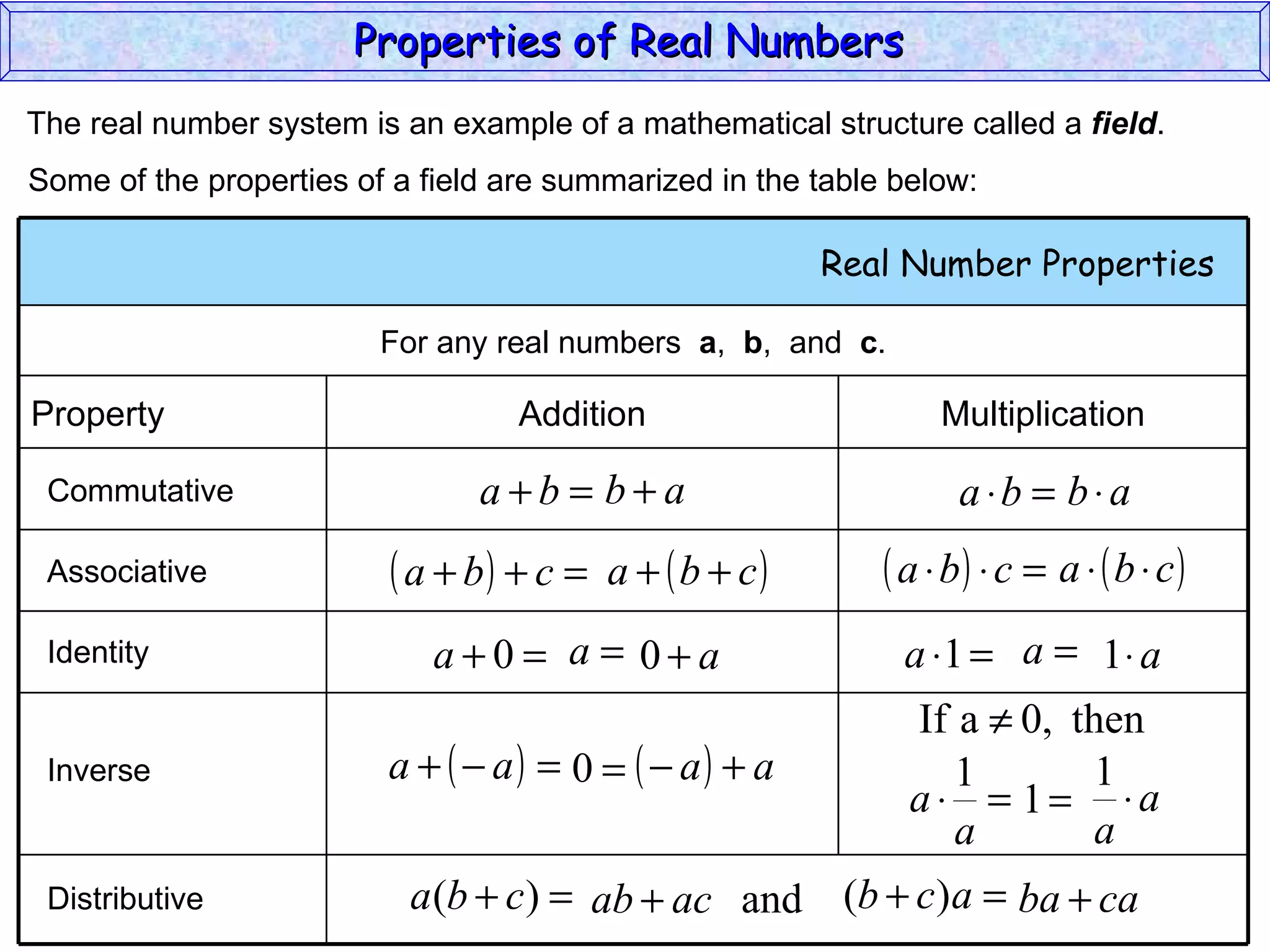
The document summarizes key properties of real numbers. It defines real, rational, and irrational numbers and discusses how they relate to each other and the number line. Rational numbers can be written as ratios of integers, and their decimals terminate or repeat. Irrational numbers have non-terminating, non-repeating decimals. The real number system forms a field with properties like commutativity and distributivity for addition and multiplication.