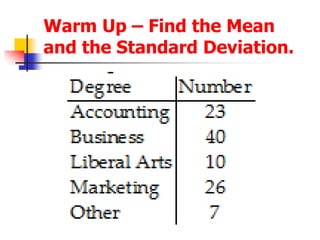
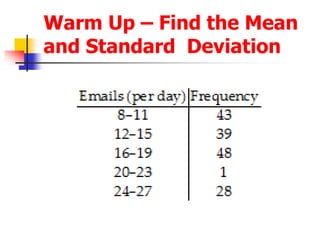
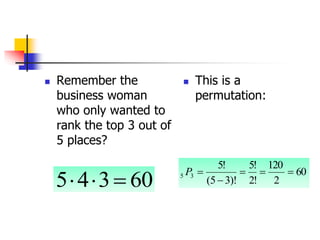
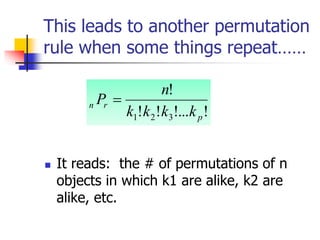
This document provides examples and definitions for permutations and combinations. It begins by defining a permutation as an arrangement of objects in a specific order where order matters. A combination is a selection of objects without regard to order. The key rules are explained: for permutations, "n objects taken r at a time" is calculated as nPr = n!/(n-r)!, and for combinations "n objects taken r at a time" is calculated as nCr = n!/r!(n-r)!. Several examples are worked through for both permutations and combinations problems to illustrate how to set them up and calculate the number of possible outcomes. Special cases like repeating objects are also addressed.