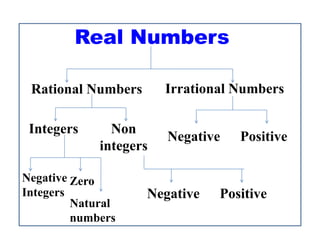
The real numbers consist of rational numbers like integers, fractions, and repeating decimals as well as irrational numbers like square roots and pi. Real numbers have the properties that between any two real numbers there are an infinite number of real numbers, and real numbers are closed under addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division except by zero. Rational numbers can be written as fractions of integers, while irrational numbers cannot be written as fractions.