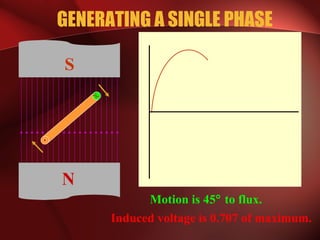
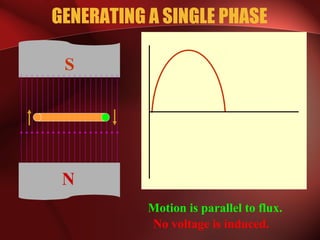
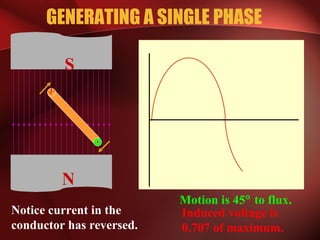
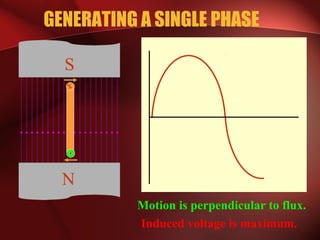
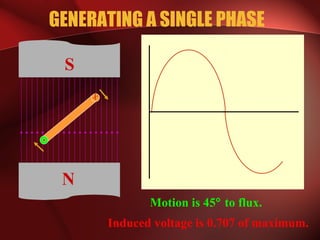
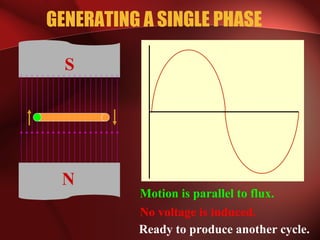
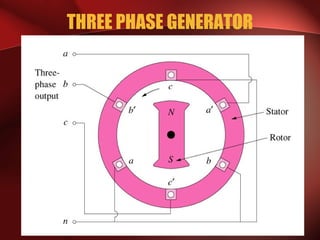
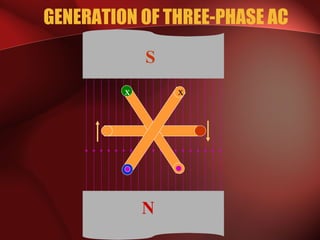
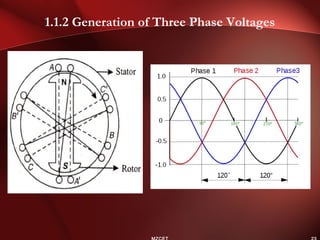
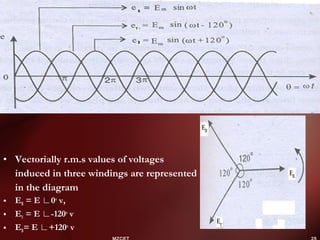
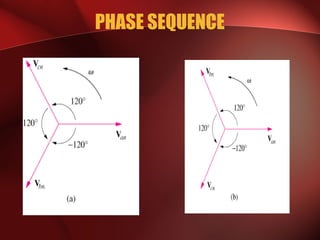
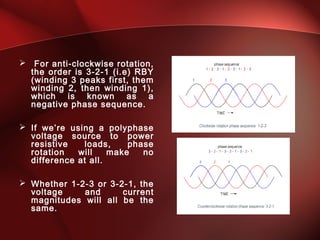
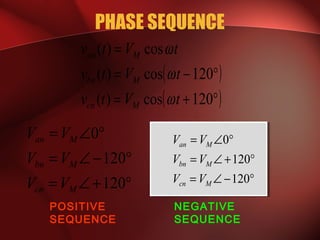
Three phase power systems have several advantages over single phase systems:
1) They provide uniform power transmission with less vibration in three phase machines due to the constant instantaneous power.
2) They are more economical since they require less wiring to transmit the same amount of power over the same distance and power loss.
3) Large power motors prefer the steady torque produced by the rotating magnetic field generated by three phase systems.