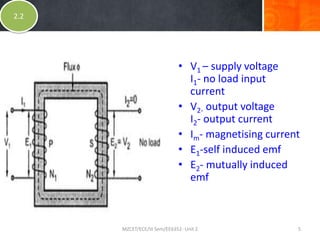
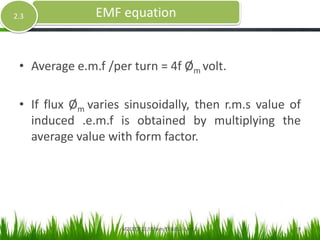
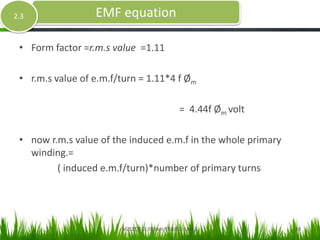
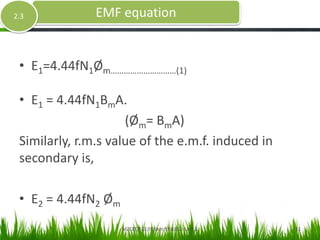
- The document discusses the ideal transformer model and equations for calculating induced voltages. It assumes zero leakage flux, windings with no resistance, an infinitely permeable core with negligible magnetizing current, and a lossless core with no hysteresis or eddy currents.
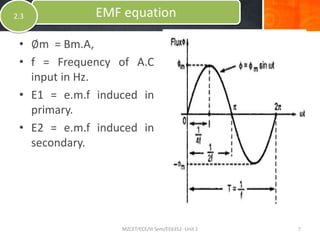
- Equations shown for the induced voltages E1 and E2 in the primary and secondary windings respectively, with E1/N1 = E2/N2 = 4.44fφm, where f is the frequency, N1 and N2 are the number of turns, and φm is the maximum magnetic flux in the core.
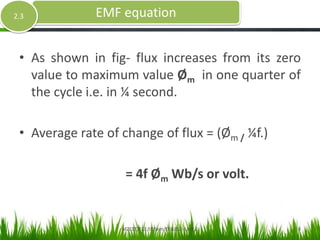
- The derivation considers the average and RMS rates of change of the sinusoidally varying flux to determine