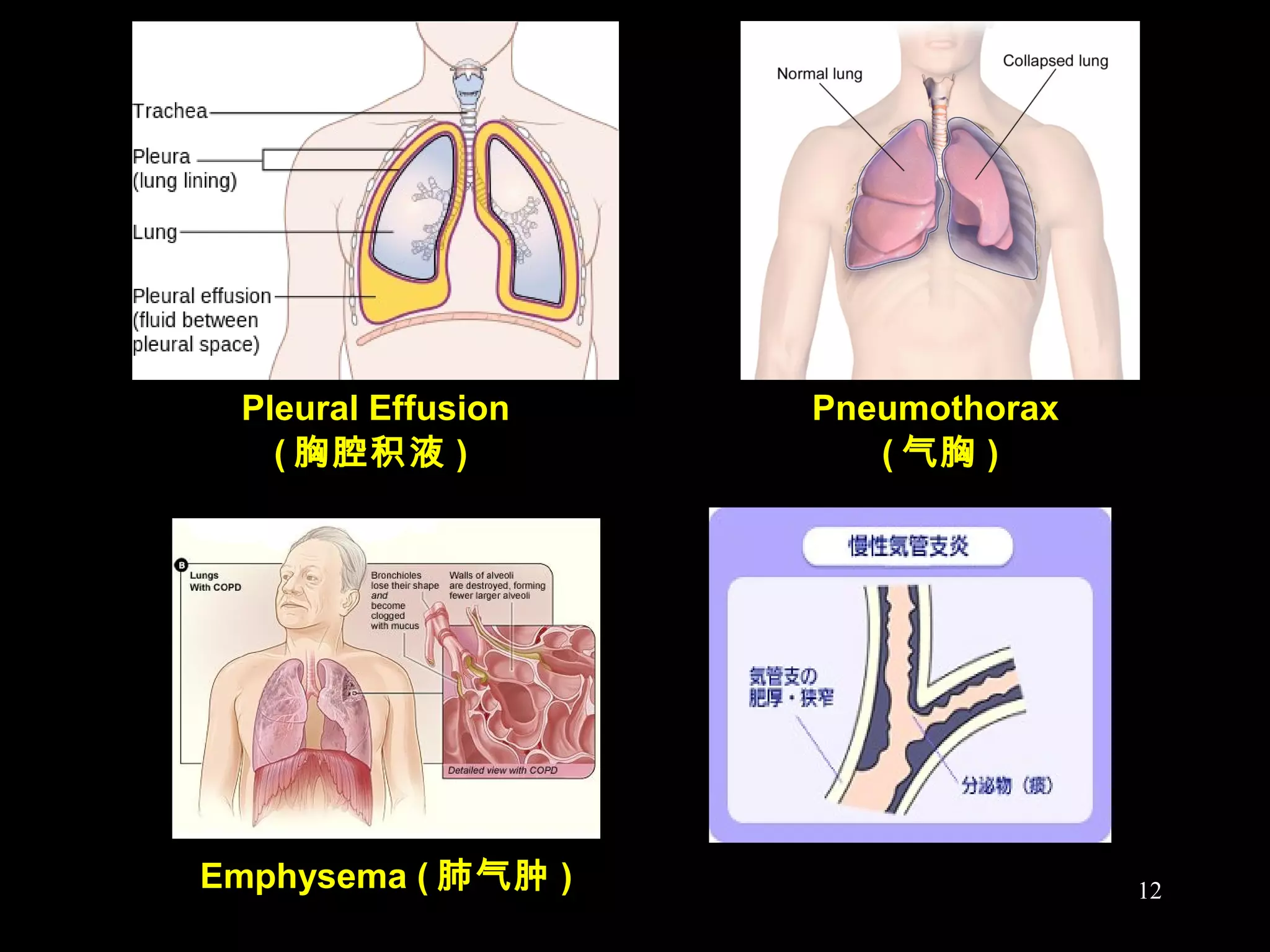
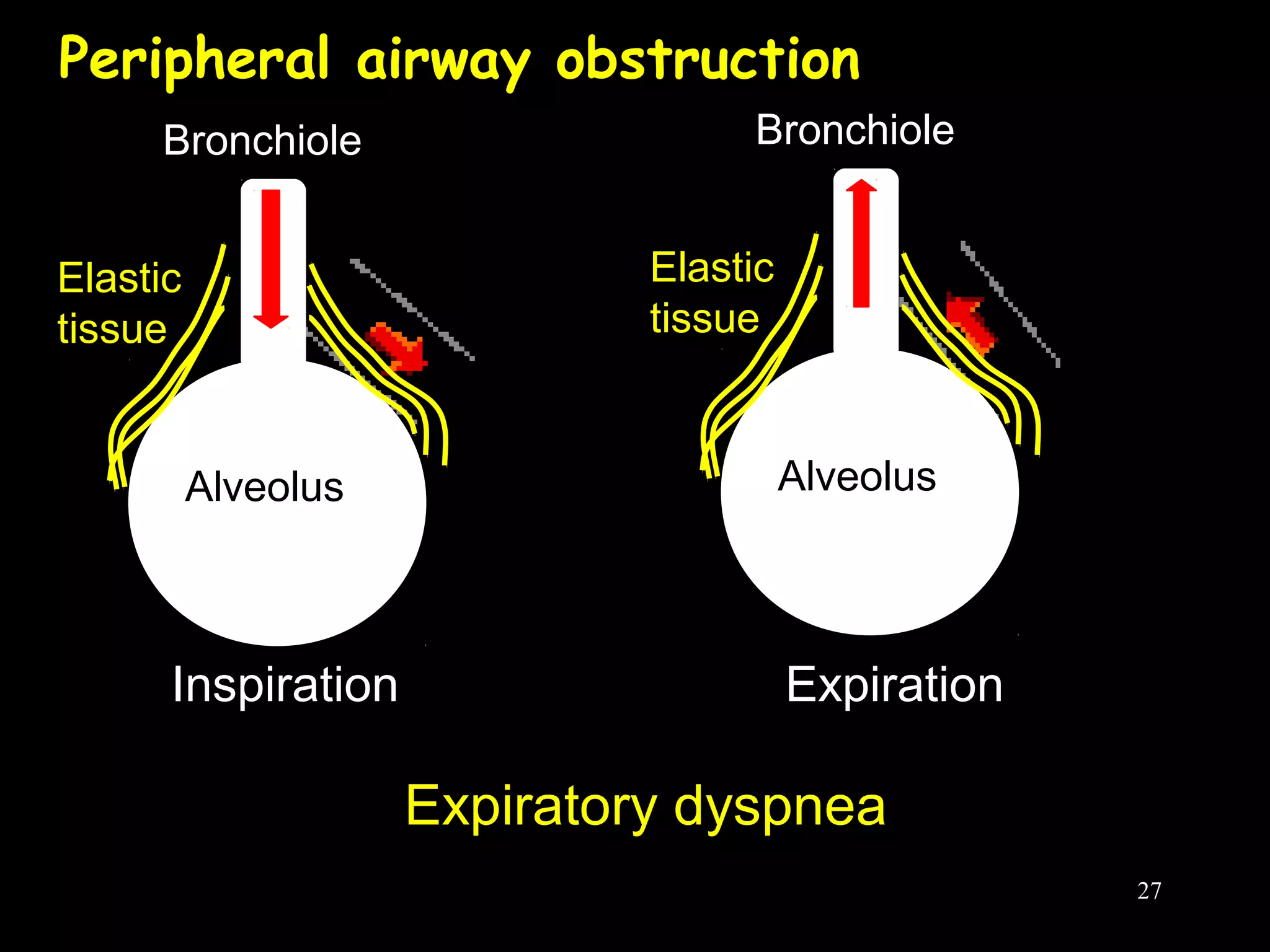
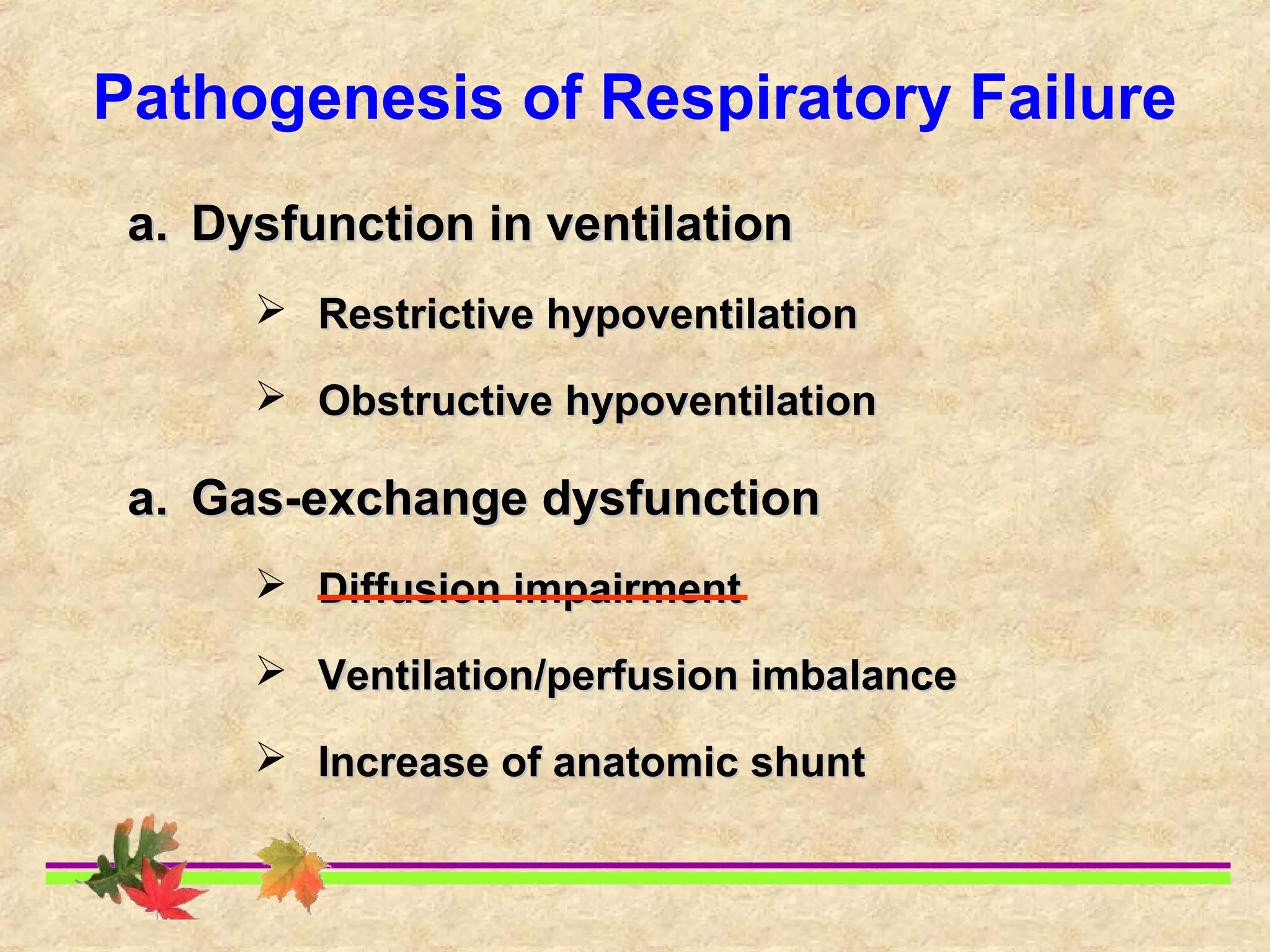
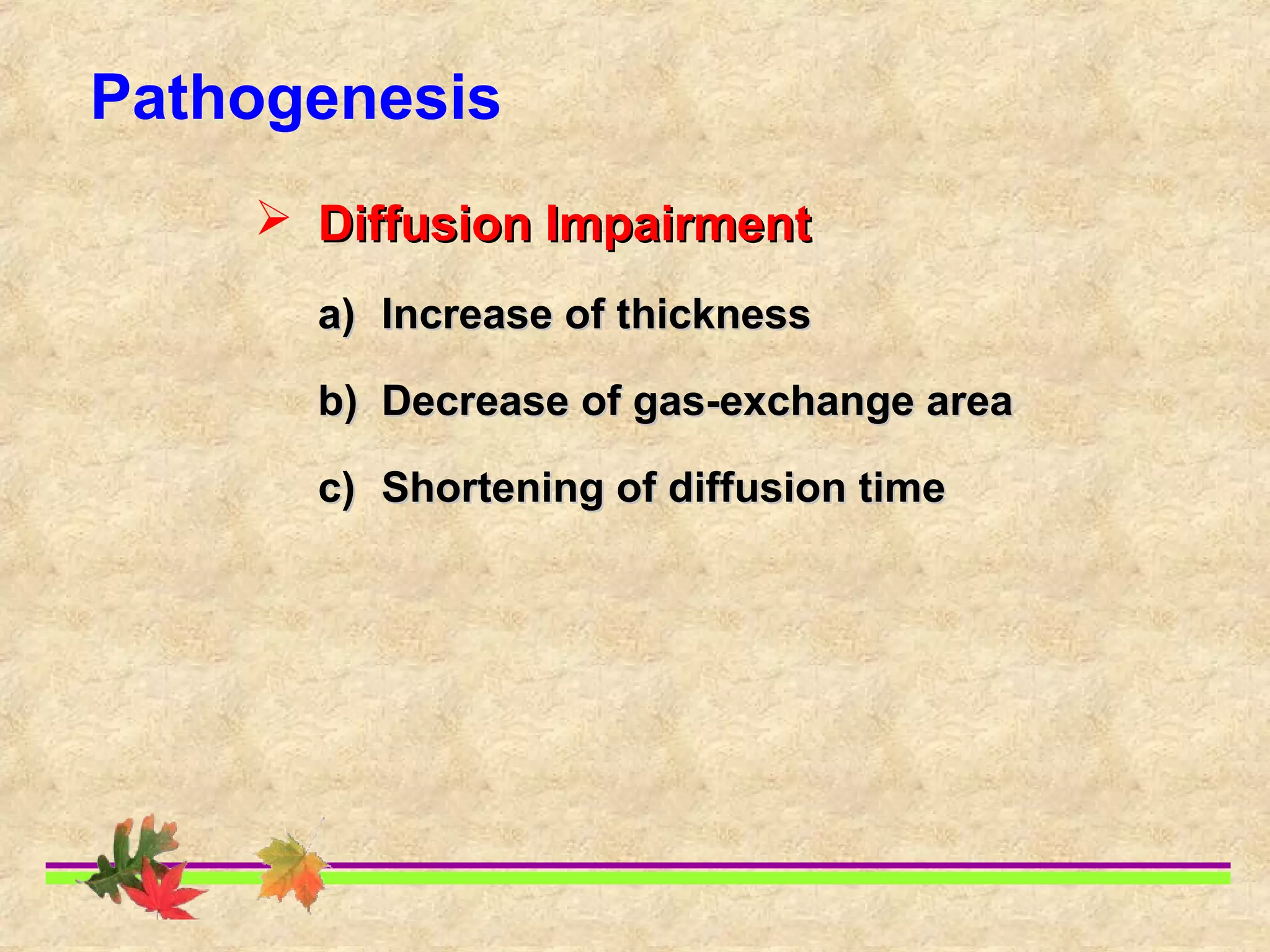
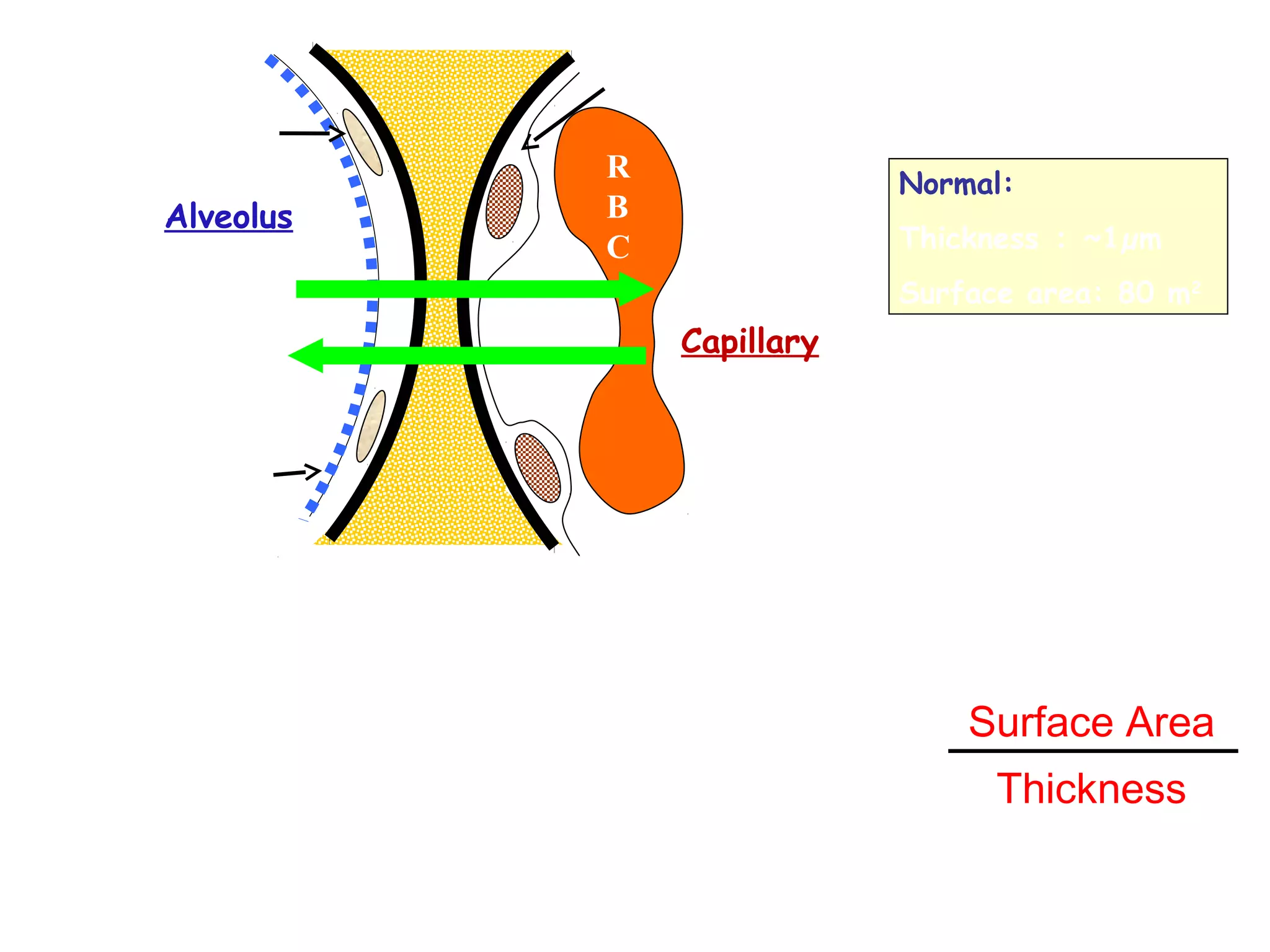
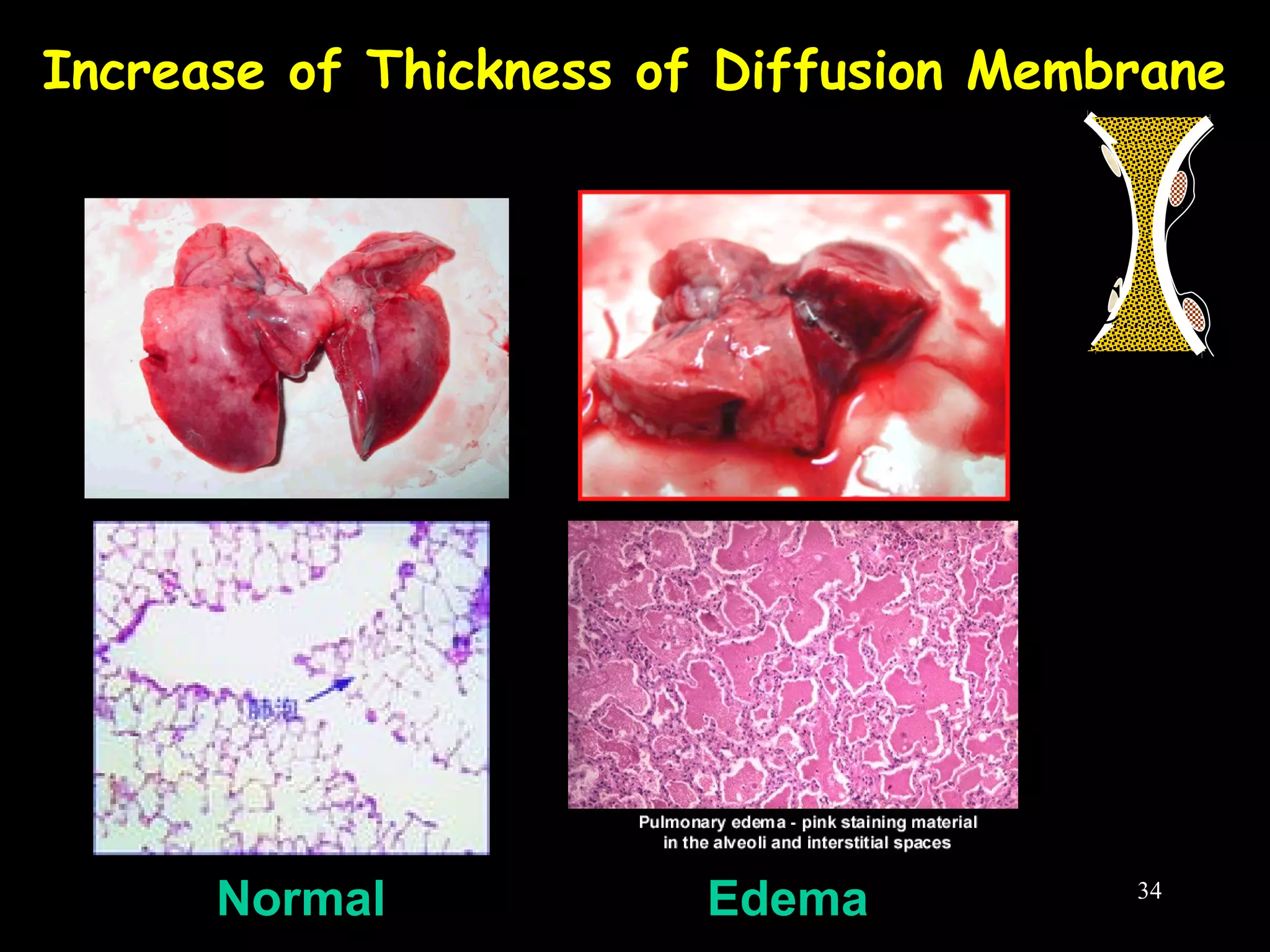
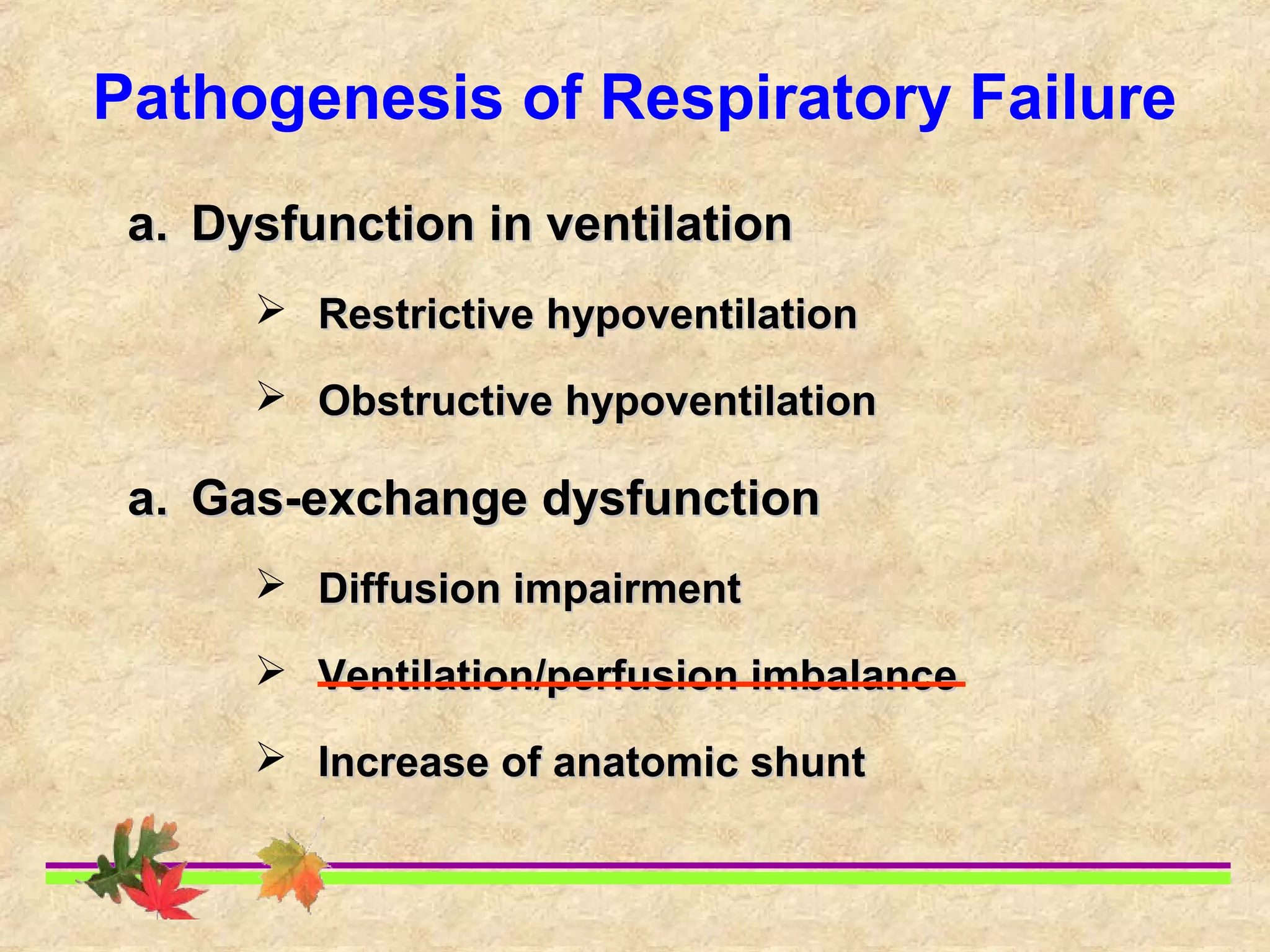
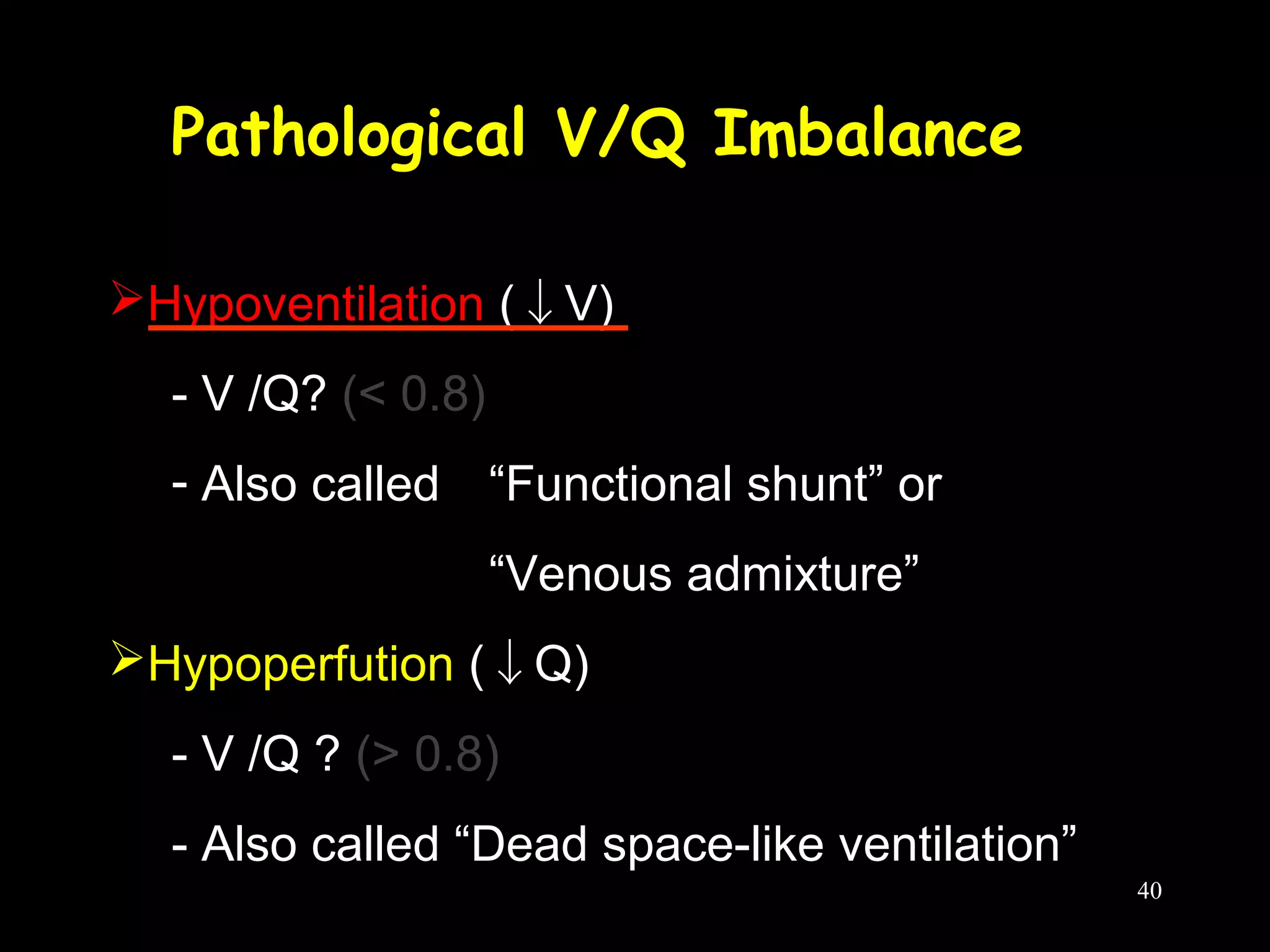
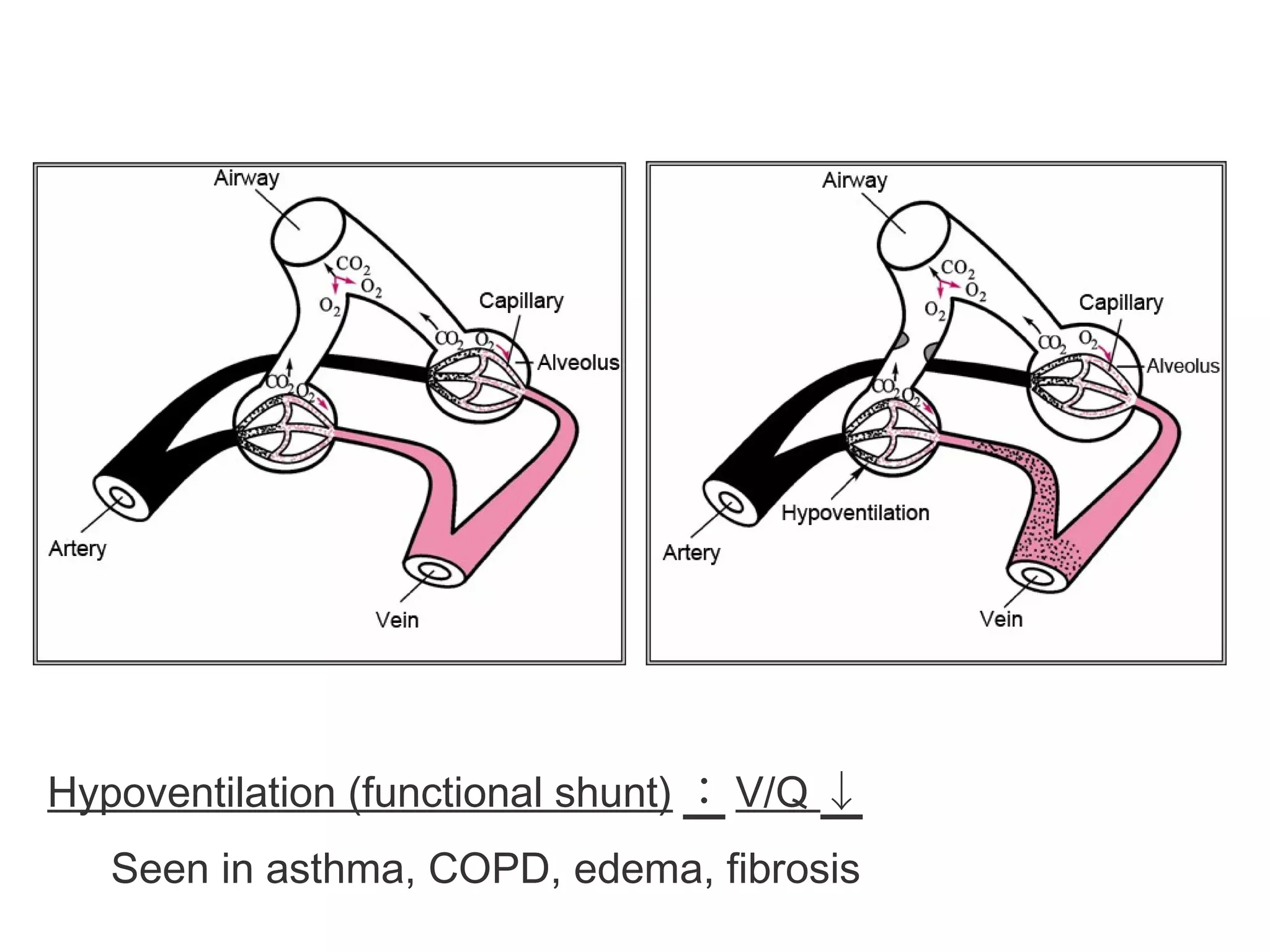
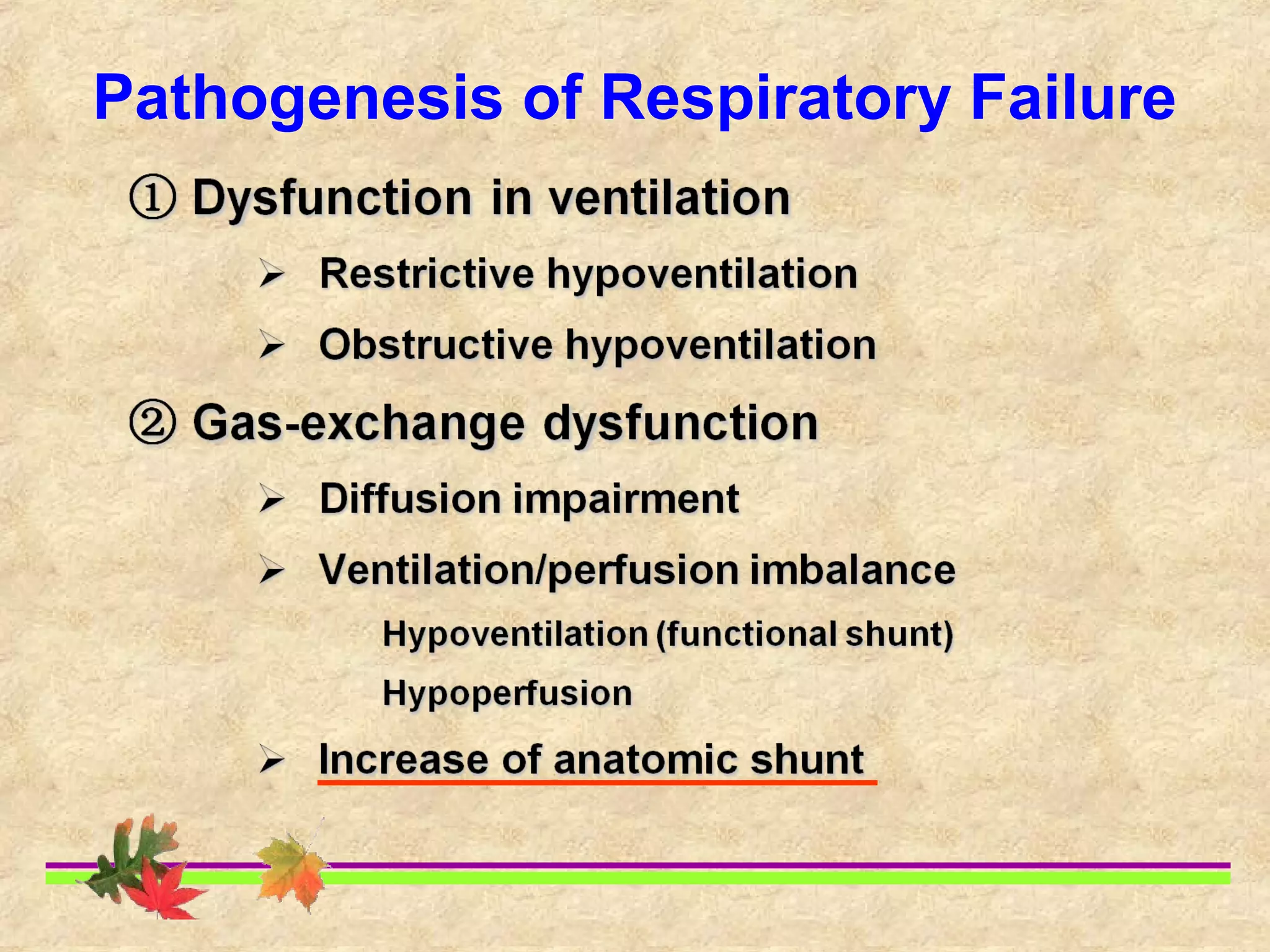
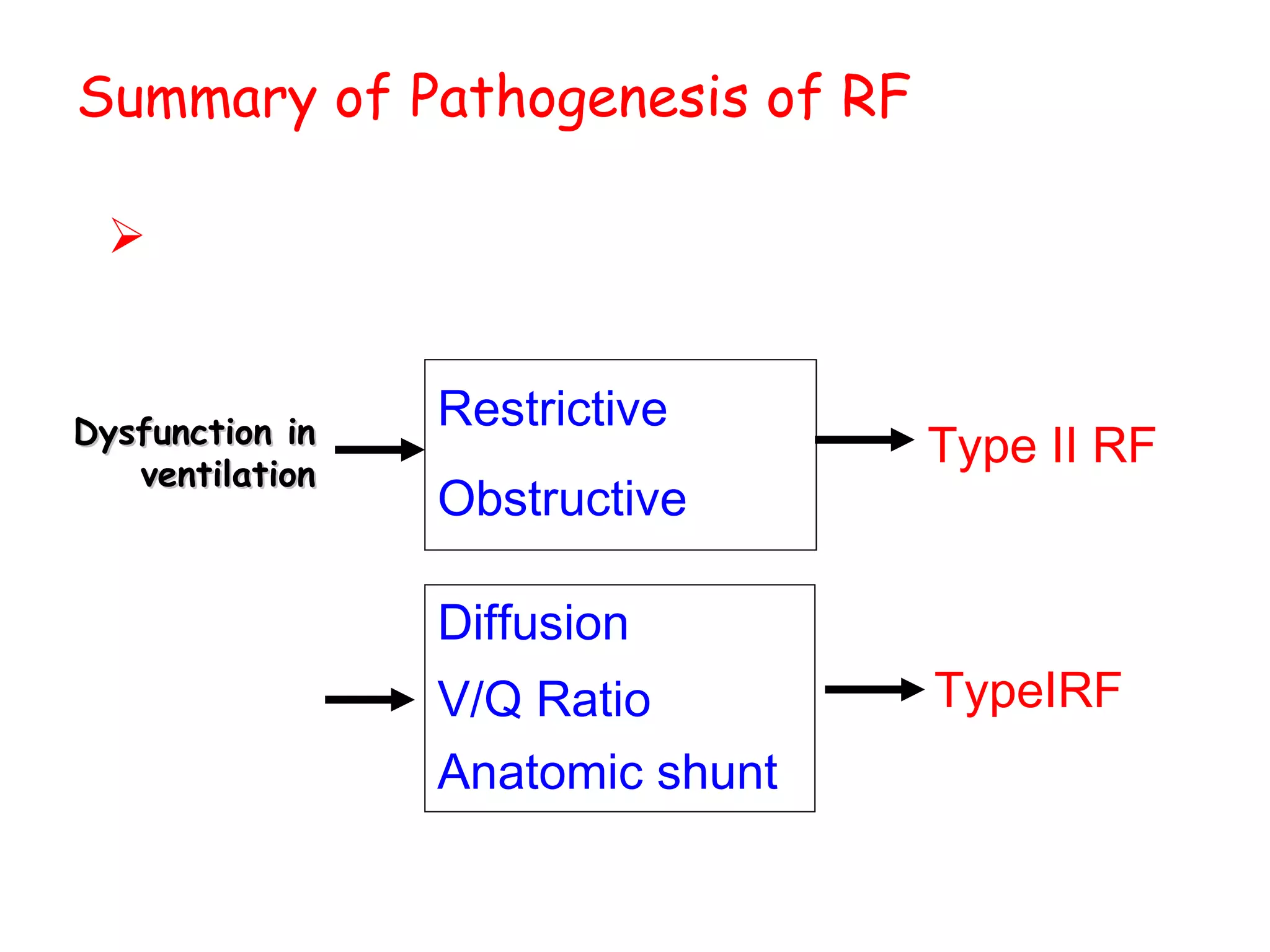
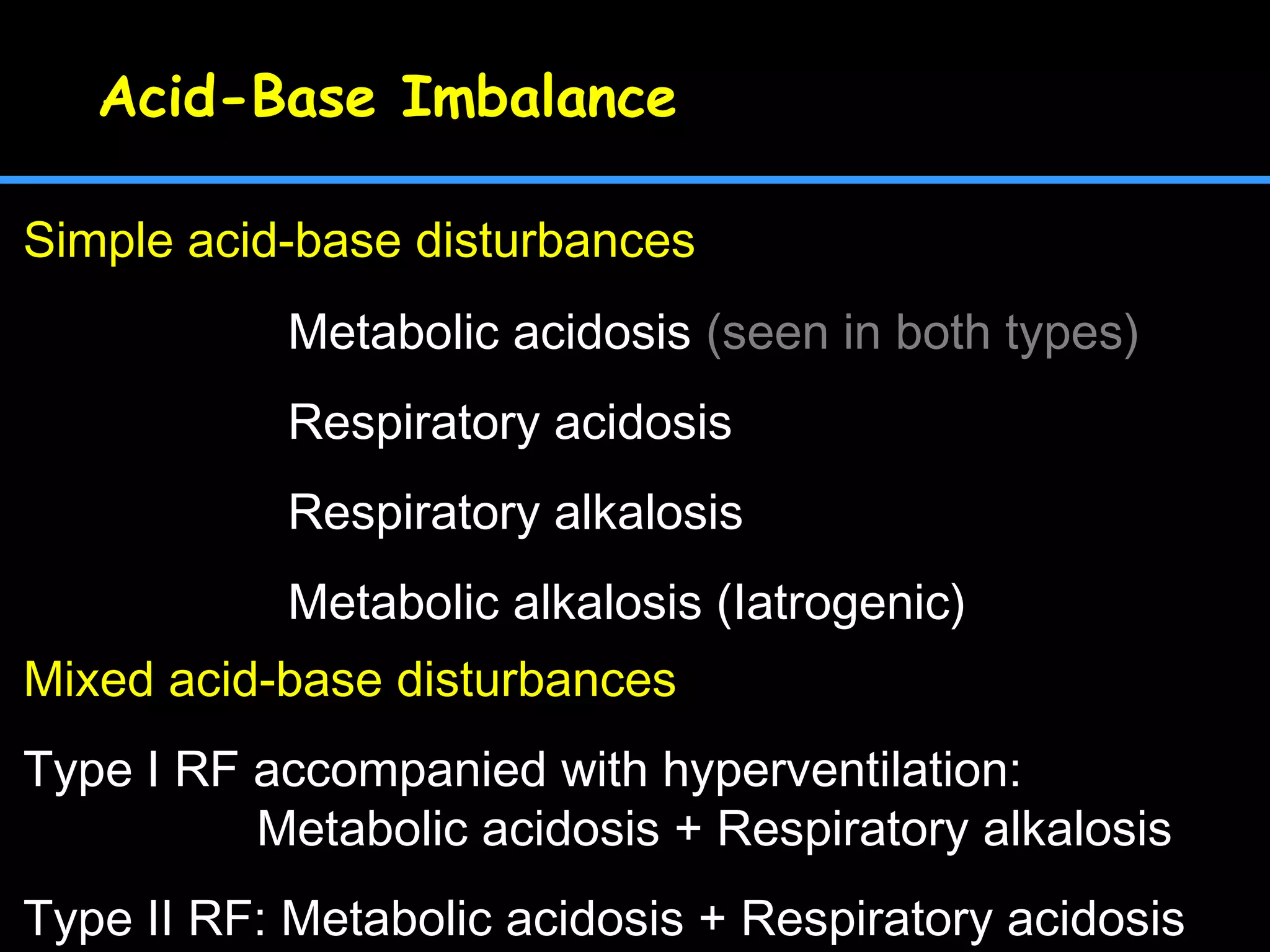
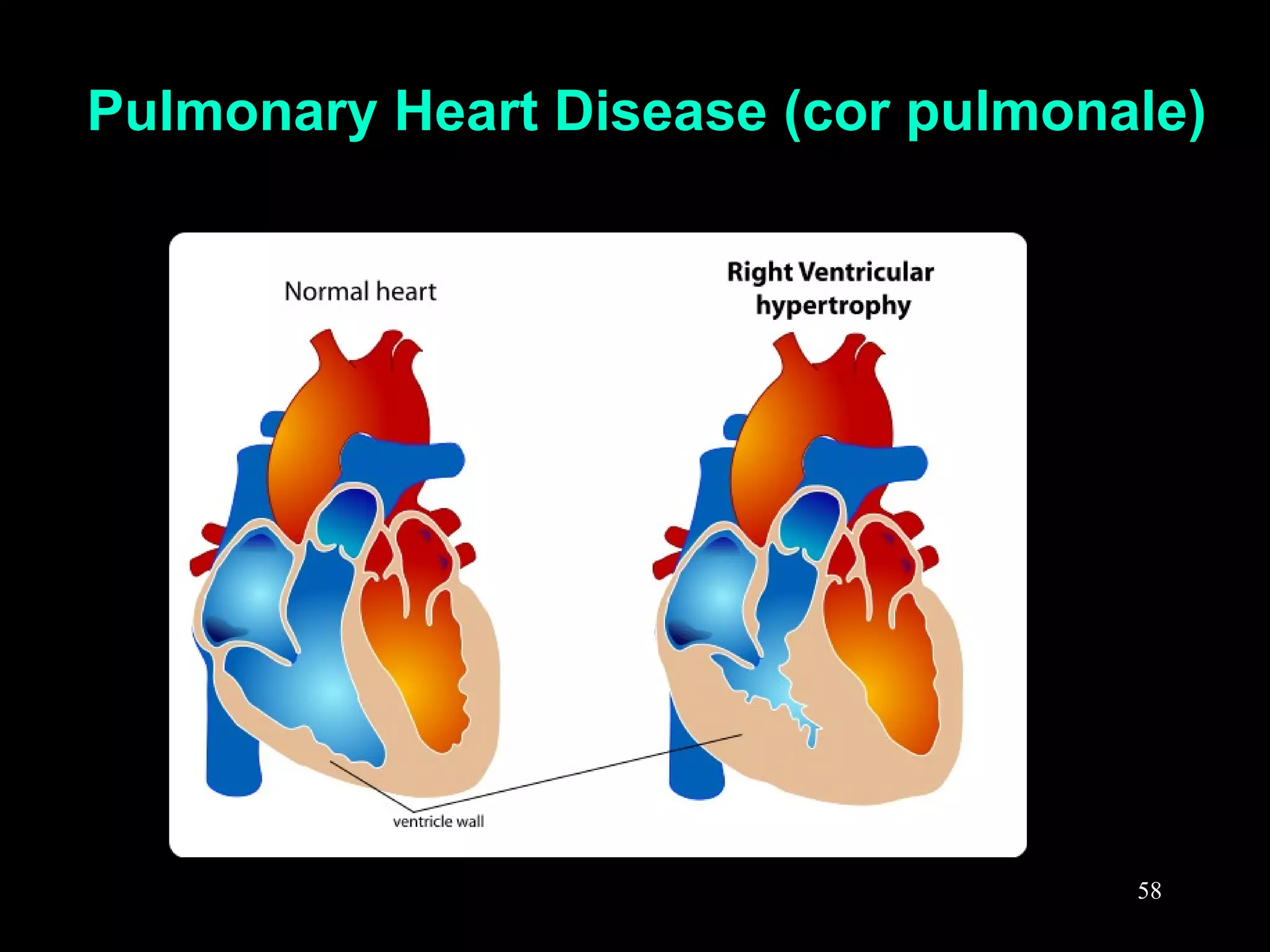
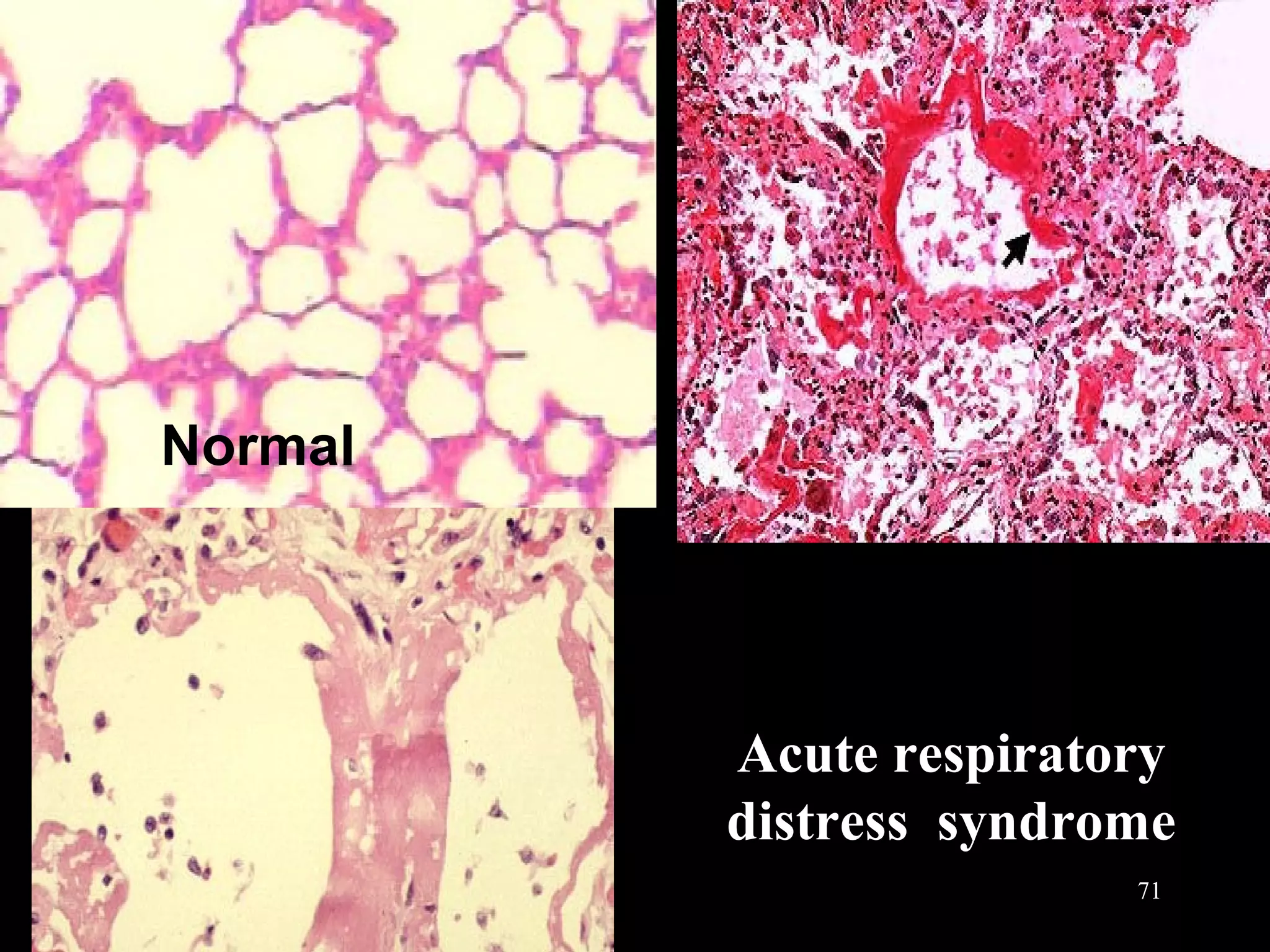
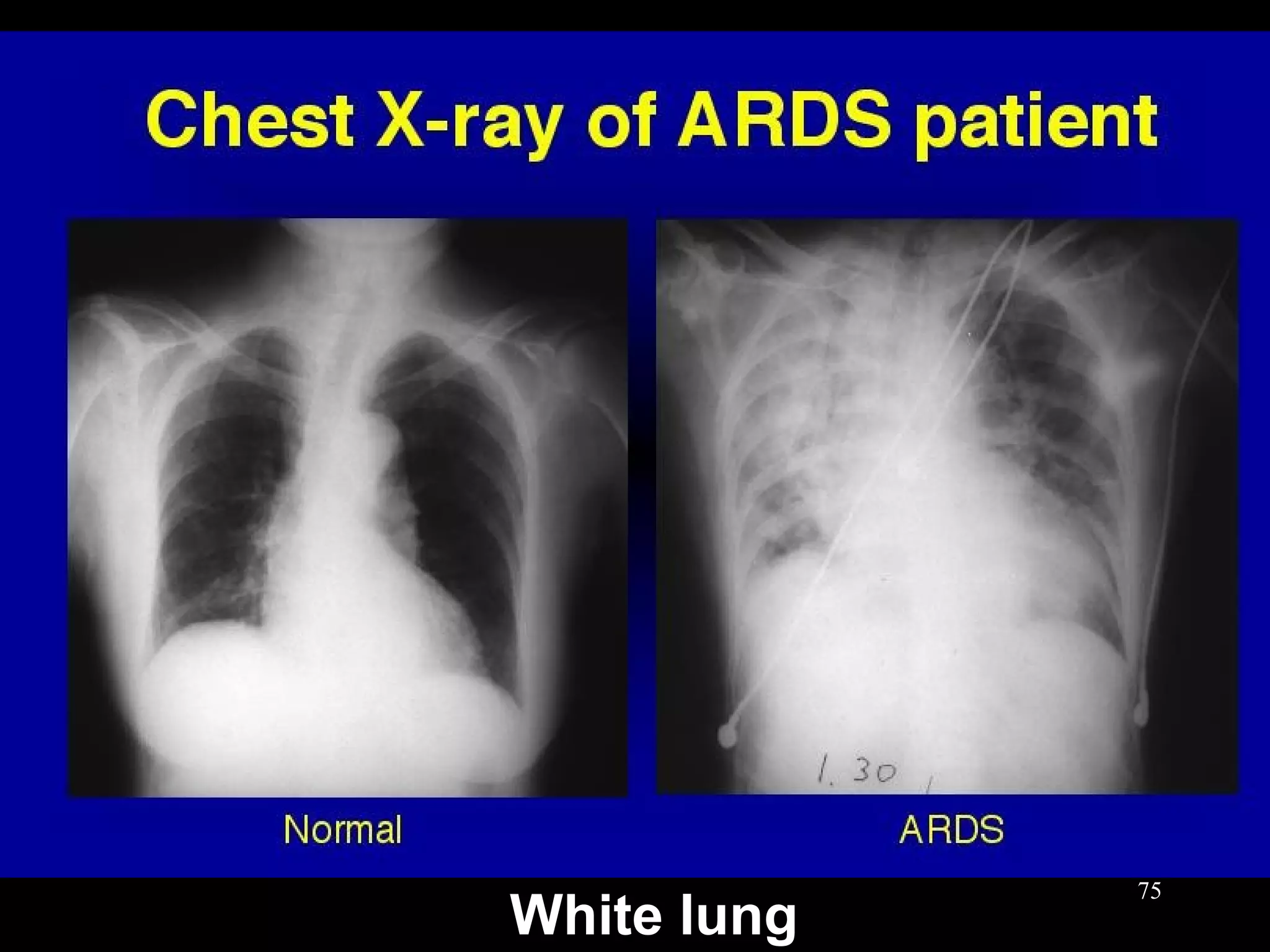
This document discusses respiratory failure, including its definition, causes, classification, pathogenesis, and effects on organ systems. Respiratory failure is defined as inadequate oxygenation of venous blood due to low PaO2 levels and potentially high PaCO2 levels. It can be caused by issues affecting ventilation like restrictive lung disease or obstructive airway diseases. The pathogenesis involves dysfunction of ventilation leading to hypoventilation, as well as gas exchange issues from diffusion impairment, ventilation/perfusion mismatching, or anatomic shunts. Respiratory failure leads to acid-base imbalances, electrolyte disturbances, and dysfunction of organ systems like the lungs, heart, brain, kidneys and gastrointestinal tract.