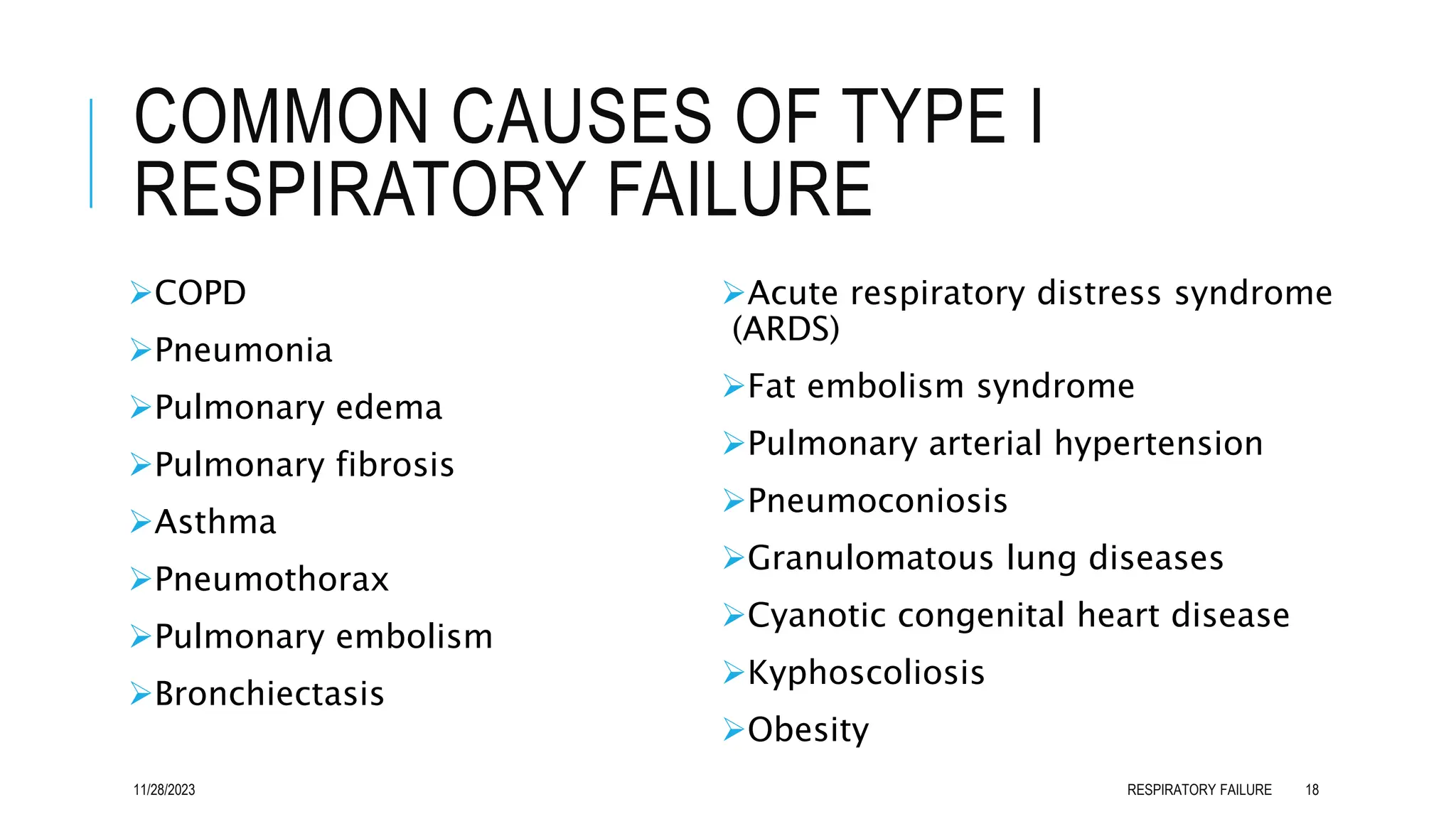
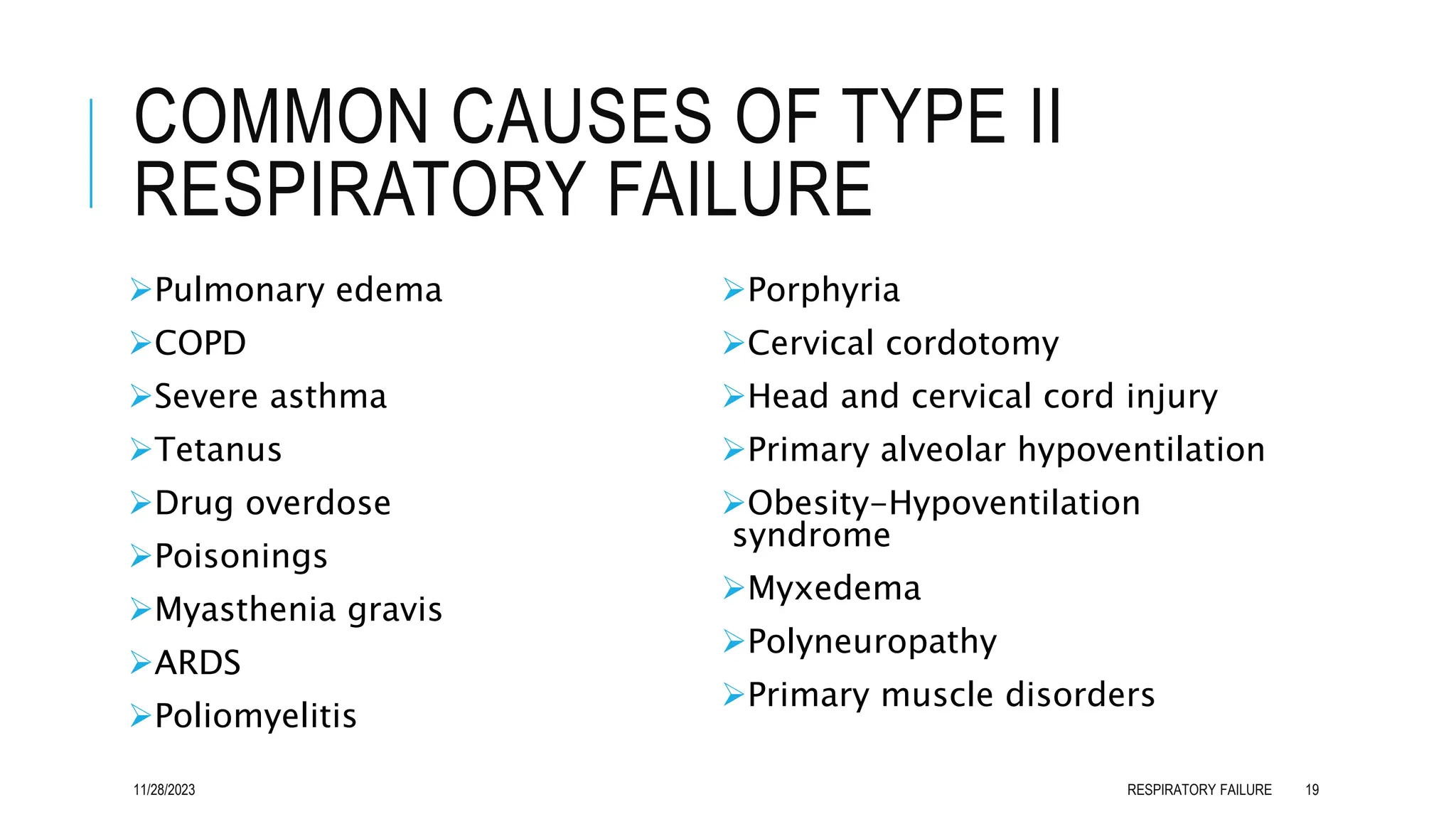
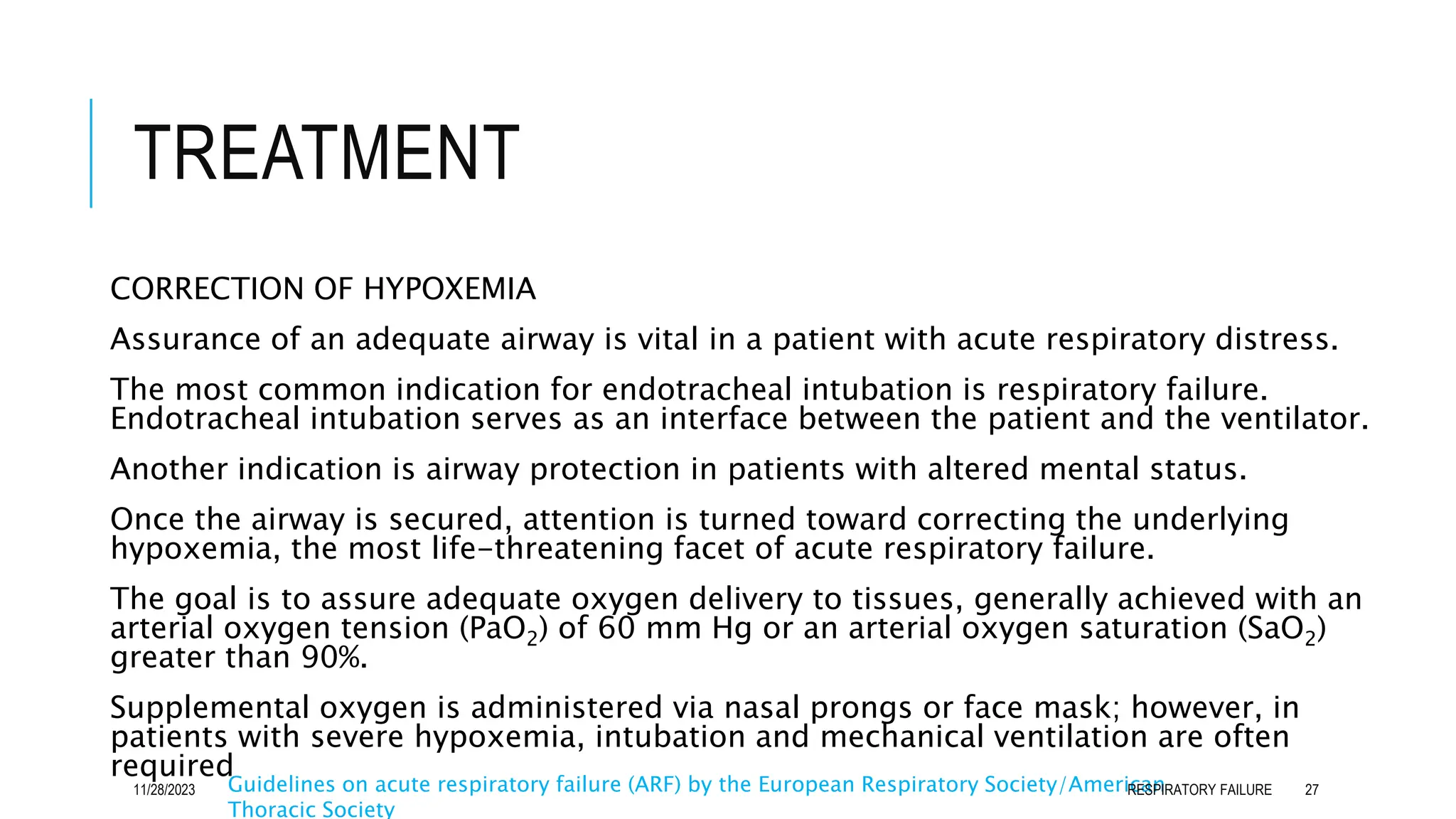
Respiratory failure is a syndrome characterized by the inability of the respiratory system to adequately exchange gases, classified into hypoxemic (Type I) and hypercapnic (Type II) forms. Common causes include acute lung diseases and underlying conditions affecting the central nervous system, respiratory muscles, and airways. Effective management involves identifying and treating the underlying cause, with severe cases often requiring mechanical ventilation and intensive care support.















![ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS
SYNDROME(ARDS)
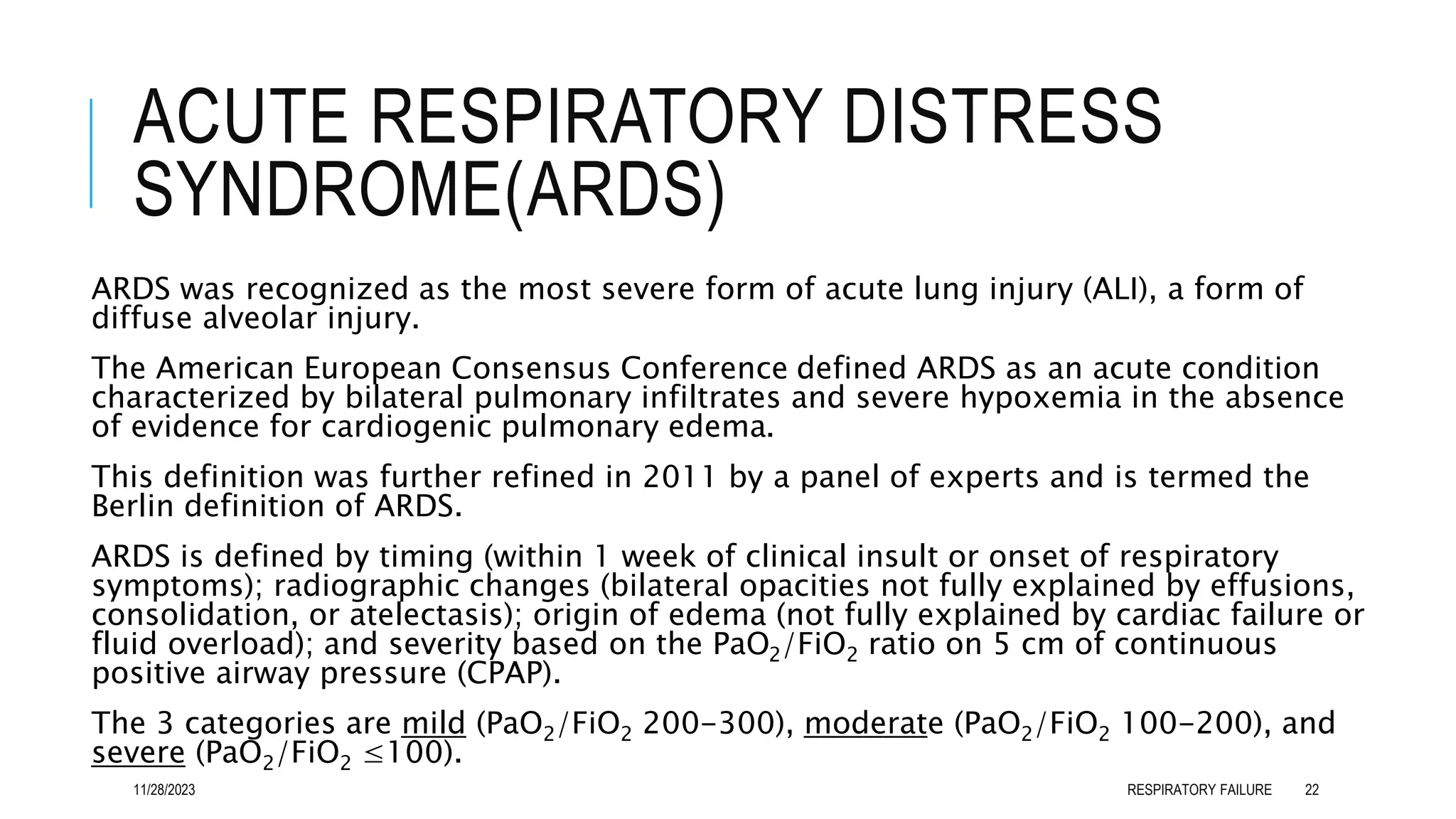
Criteria for the diagnosis of ARDS include the following:
Clinical presentation - Tachypnea and dyspnea; crackles upon auscultation
Clinical setting - Direct insult (aspiration) or systemic process causing lung
injury (sepsis)
Radiologic appearance - 3-quadrant or 4-quadrant alveolar flooding
Lung mechanics - Diminished compliance (< 40 mL/cm water)
Gas exchange - Severe hypoxia refractory to oxygen therapy (ratio of arterial
oxygen tension to fractional concentration of oxygen in inspired gas
[PaO2/FiO2] < 200)
Normal pulmonary vascular properties - Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
lower than 18 mm Hg
11/28/2023 RESPIRATORY FAILURE 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/respiratoryfailure-kdamuda-231128090440-4814d091/75/MANAGEMENT-OF-RESPIRATORY-FAILURE-23-2048.jpg)









![REFERENCES
IJ Clifton, DAB Ellames, Respiratory Failure in Davidson’s principle and practice of Medicine 24th Ed., Chapt. 17, pp.
483-485
Vincent SM, Eman S, Abdulghani S, Bracken B: Respiratory Failure, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; Jan
2023 accessible at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526127/
Ata Murat Kaynar, Respiratory Failure, Medscape@emedicine.com
Khan NA, Palepu A, Norena M, et al. Differences in hospital mortality among critically ill patients of Asian, Native
Indian, and European descent. Chest. 2008 Dec. 134(6):1217-22.
Moss M, Mannino DM. Race and gender differences in acute respiratory distress syndrome deaths in the United
States: an analysis of multiple-cause mortality data (1979- 1996). Crit Care Med. 2002 Aug. 30(8):1679-85.
Guideline] Rochwerg B, Brochard L, Elliott MW, Hess D, Hill NS, Nava S, et al. Official ERS/ATS clinical practice
guidelines: noninvasive ventilation for acute respiratory failure. Eur Respir J. 2017 Aug. 50 (2)
[Guideline] Alhazzani W, Møller MH, Arabi YM, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: Guidelines on the Management of
Critically Ill Adults with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). European Society of Intensive Care Medicine.
Available at https://www.esicm.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/SSC-COVID19-GUIDELINES.pdf.2020;
11/28/2023 RESPIRATORY FAILURE 35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/respiratoryfailure-kdamuda-231128090440-4814d091/75/MANAGEMENT-OF-RESPIRATORY-FAILURE-35-2048.jpg)
