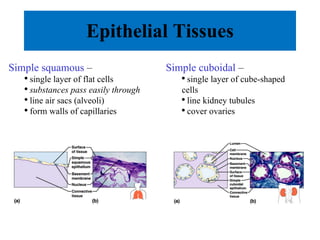
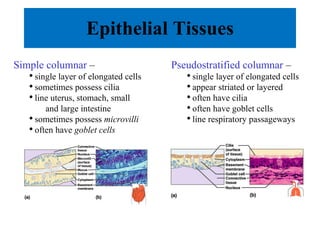
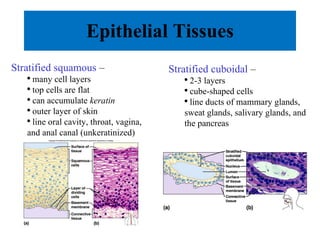
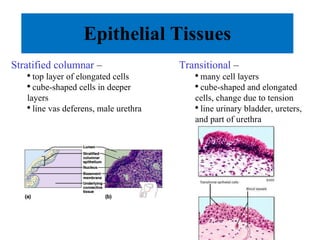
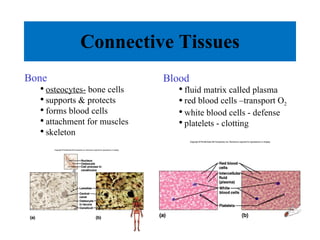
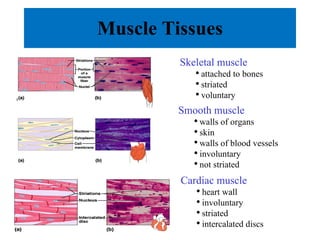
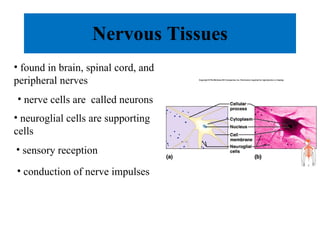
The document summarizes the four major tissue types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. It provides details on the characteristics and classifications of epithelial tissues, including the different cell shapes and number of cell layers. It also describes the general characteristics and major cell types of connective tissues, including fibers, and examples of loose, dense, cartilage and bone connective tissues. Finally, it outlines the characteristics of the three muscle tissue types - skeletal, smooth and cardiac - and notes that nervous tissue is found in the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves.