The document presents a paper on power quality analysis of a grid-connected wind farm. It discusses modeling and simulating the wind farm using MATLAB/Simulink. It shows simulations of the wind farm under normal operation and during events like voltage sags and swells. Data from the simulations investigating current, voltage, power and power quality are presented. The conclusions state that power quality issues for high-penetration grid-connected wind farms have been investigated through modeling and simulations in MATLAB/Simulink.


![
I. INTRODUCTION
Renewable Energy & Its Importance[1]
DG Solution against load shedding in rural area of
Maharashtra, India.[2]
Electrical Power Quality.[3]
Integrating renewable into grids and Power
Quality issues.[4]
Heavy Penetration of Renewable Wind Energy
affect Power Quality.[5]
11/12/2013
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/105kisore-131211042124-phpapp01/85/105-kisore-3-320.jpg)
![II SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT & ITS
DESCRIPTION
Integrated wind farm is used and power
quality analysis is performed.[6]
The integration of big wind farm will create
new problems regarding the power quality.[7]
Technical details of Wind farm.[8]
The simulation model implemented in the
MATLAB/SIMULINK. [9]
11/12/2013
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/105kisore-131211042124-phpapp01/85/105-kisore-4-320.jpg)
![ Renewable Energy Source (RES) integrated at
distribution level is termed as Distributed
Generation(DG).[10]
high penetration level of wind energy in
distribution systems, as it may pose a threat to
network is terms of Power Quality(PQ) issues ,
voltage regulation and stability. [11]
wind energy system integration issues
associated PQ problems are discussed.
and
As per the modeling and simulation of a case
study, the power quality of the grid connected
wind farm has been investigated at different
wind velocity. [12]
11/12/2013
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/105kisore-131211042124-phpapp01/85/105-kisore-5-320.jpg)
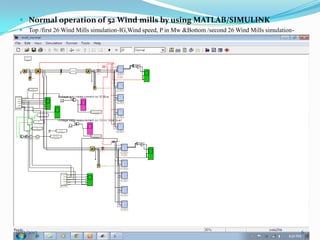
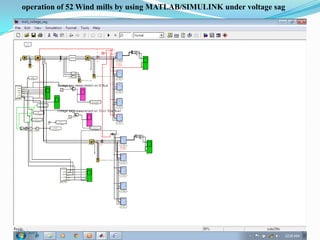
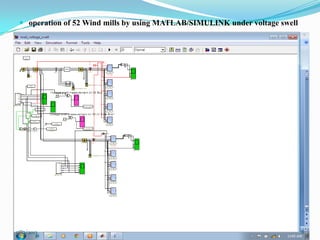
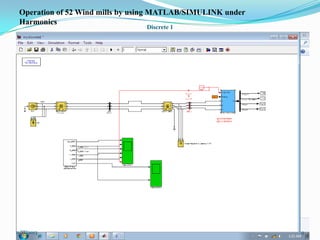
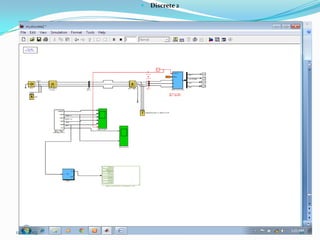
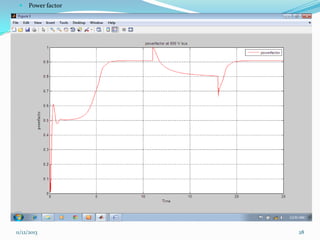
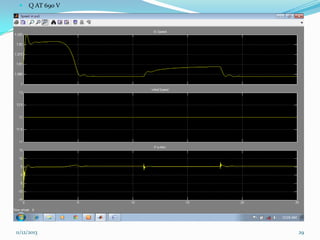
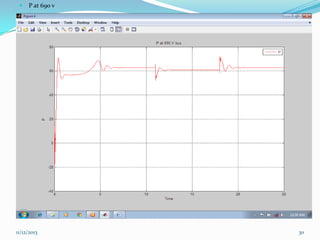
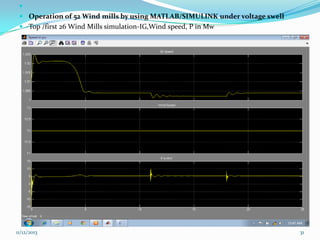
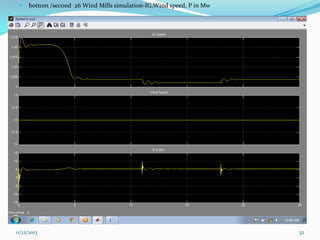
![ III SIMULATION AND MODELLING
Wind turbines cause significant impacts on the
power quality of their connected grid.
Voltage fluctuations produced by wind turbines
are usually due to wind speed variations, power
and voltage fluctuations.
This case presents simulations for numerical
models of two wind turbine schemes, fixed and
variable
speed
types,
by
using
MATLAB/SIMULINK.[12]
In order to investigate the power system impact of
wind turbines, it is essential to use accurate
dynamic simulation models of wind turbines and
power system.
11/12/2013
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/105kisore-131211042124-phpapp01/85/105-kisore-12-320.jpg)
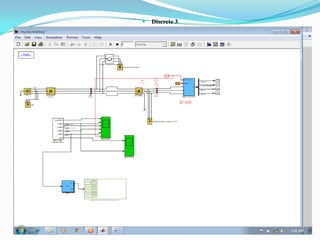
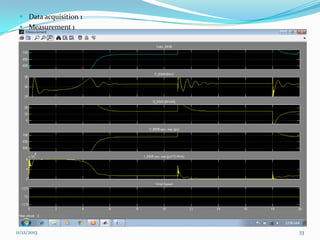
![ The models must correctly represent the dynamic
behavior of the wind turbines in order to predict
critical operation conditions at the one hand and to
improve their dynamic performance at the other
hand.
Hence, those wind turbine models have to be
developed and implemented in dedicated power
system simulation tools in order to facilitate study
on the wind turbines interaction with the power
system. MATLAB software tools build the basis
for power system simulations .[13]
11/12/2013
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/105kisore-131211042124-phpapp01/85/105-kisore-13-320.jpg)
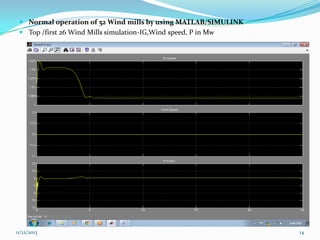
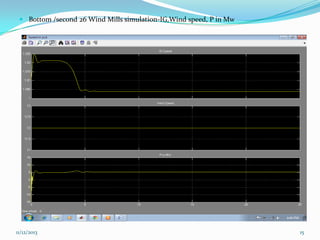
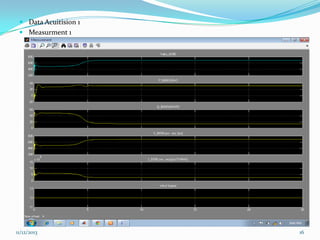
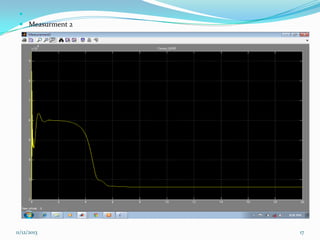
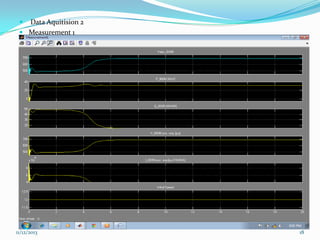
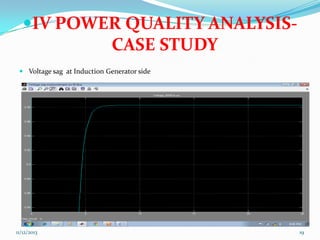

![
References
[1] E. Muljadi, C.P. Butterfield,J. Chacon,H. Romanowitz ,” POWER QUALITY ASPECTS IN A WIND
POWER PLANT”,IEEE 2006
[2] Gabriele Michalke, Department for Renewable Energies Institute of Electrical power system,”
Variable Speed Wind Turbines - Modelling, Control, and Impact on Power Systems “, pp.1-228, 2008
[3} Nguyen Tung Linh ,Electric Power University, “Power Quality Investigation of Grid Connected
Wind Turbines”, ICIEA 2009, pp.2018-2022, IEEE 2009
[4] SU Shi-ping ,QIN Zhi-qing ,” Study on Transient Power Quality Detection of Grid-Connected
Wind Power Generation System Based on Wavelet Transform”, DOI 10.1109/ICEET.2009.213,PP.861864,IEEE computer society.
[5] H. J. Su, H. Y. Huang, and G. W. Chang,” Power Quality Assessment of Wind Turbines by
Matlab/Simulink”, IEEE 2010.
[6] O. A. Giddani, G. P. Adam, O. Anaya-Lara, G. Burt and K. L. Lo, ” Enhanced performance of FSIG
wind farms for Grid Code compliance”, SPEEDAM 2010 International Symposium on Power
Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion, pp.660-665 IEEE 2010.
[7] Zbigniew Leonowicz, ” Assessment of Power Quality in Wind Power Systems”, IEEE 2011
[8] John P. Barton, Simon J. Watson, “Analysis of electrical power data for condition monitoring of a
small wind turbine” , Published in IET Renewable Power Generation, doi: 10.1049/iet-rpg.2012.0326.
[9] Sharad W. Mohod, Member, IEEE, and Mohan V. Aware “Micro wind power generator with battery
storage” IEEE SYSTEMS JOURNAL, VOL. 6, NO. 1, MARCH 2012
[10] S. W. Mohod and M. V. Aware, “Power quality issues & it’s mitigation technique in wind energy
conversion,” in Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. Quality Power & Harmonic, Wollongong, Australia, 2008.
[11] J. J. Gutierrez, J. Ruiz, L. Leturiondo, “Comparison of Different Control Strategies of STATCOM
for Power Quality Improvement of Grid Connected Wind Energy System”, PP.124-131, IEEE 2013
[12] T. Burton, D. Sharpe, N. Jenkins ,E. Bossanyi, “Wind Energy Handbook ”, John Wiley & sons
Ltd. Chichester , 2001
[13] J. F. Manwell , J. G. Mcgowan , A. L.Rogers, “Wind Energy Explained : Theory , Design and
Application ”, John Wiley & sons Ltd. Chichester , 2002.
11/12/2013
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/105kisore-131211042124-phpapp01/85/105-kisore-35-320.jpg)
