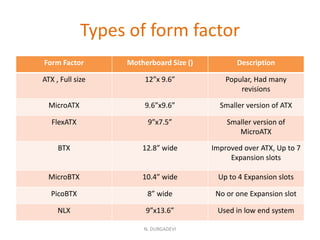
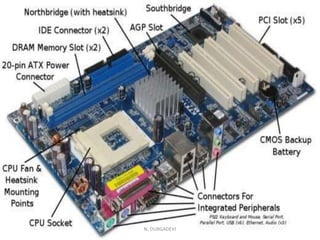
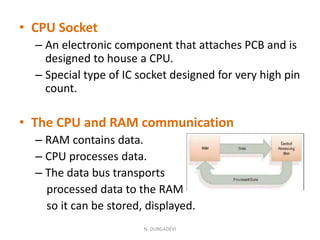
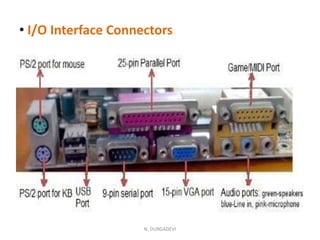
The motherboard is the main circuit board in a computer that holds the central processing unit (CPU) and main components. It allows these components to communicate and work together. Motherboards come in different form factors depending on size and shape to fit cases and components. The most common form factors are ATX, MicroATX, and BTX. The motherboard contains important components like the CPU socket, memory slots, expansion slots, chipset, and connectors for ports, power supply, and drives. It acts as the central hub connecting all the computer's components.