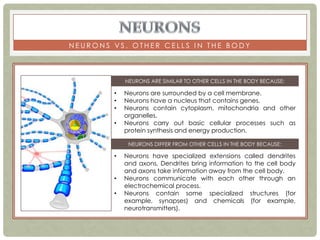
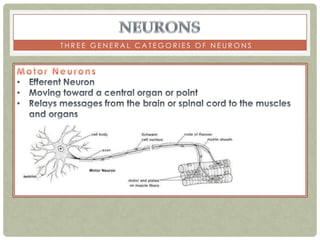
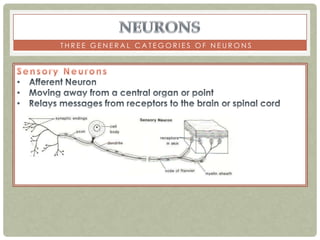
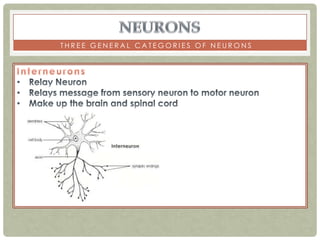
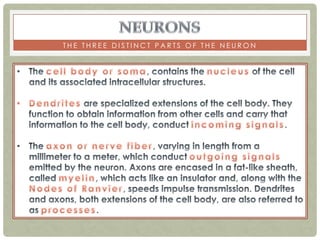
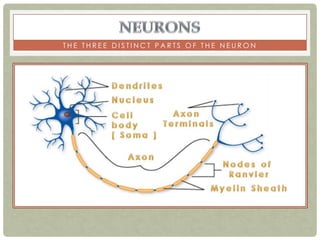
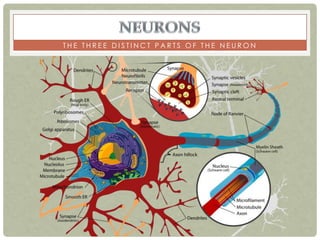
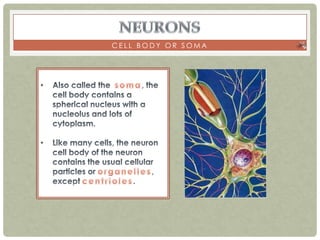
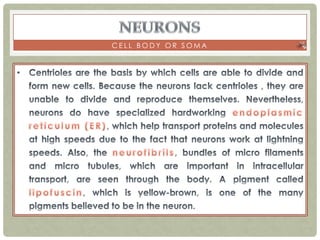
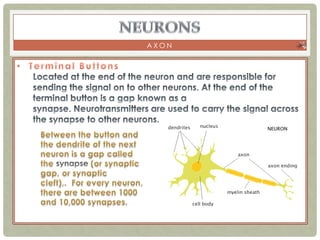
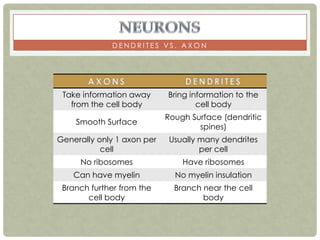
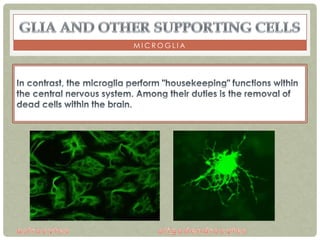
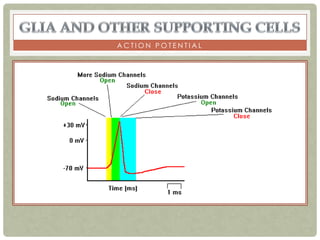
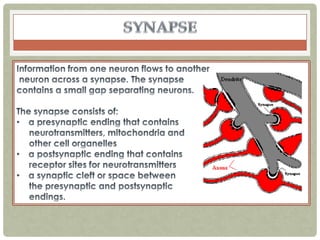
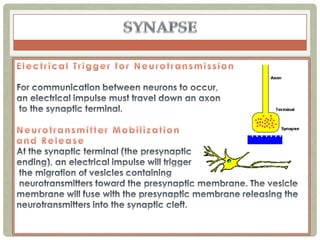
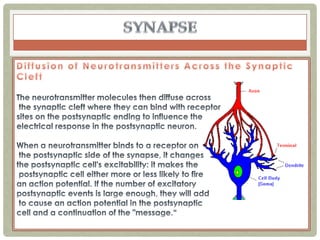
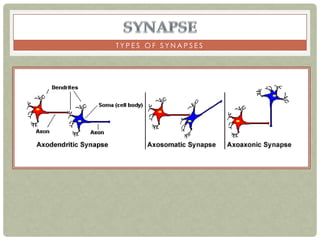
There are three main categories of neurons: sensory neurons, which conduct impulses to the spinal cord; interneurons, which interconnect sensory and motor neurons; and motor neurons, which conduct impulses from the spinal cord to effectors like muscles. Neurons are similar to other cells but have specialized extensions called dendrites and axons that allow them to communicate electrochemically. The three main parts of a neuron are the cell body, dendrites that receive signals, and a single axon that transmits signals. Glial cells support neurons and include oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, Schwann cells, and microglia. An action potential is the electrochemical signal transmitted along the axon.