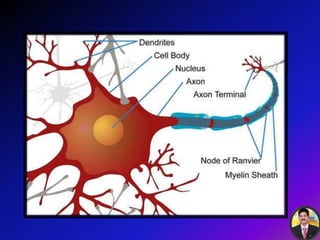
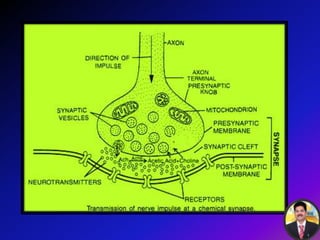
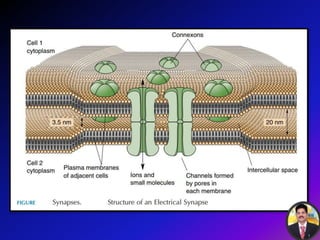
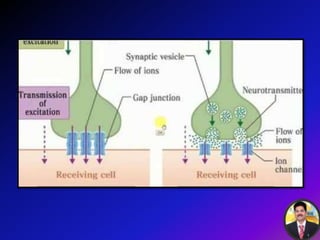
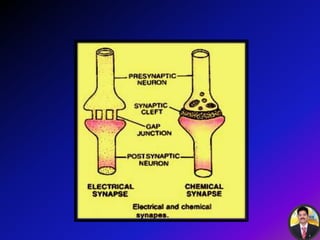
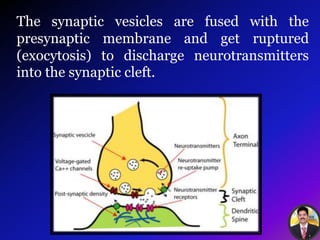
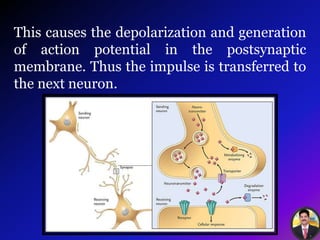
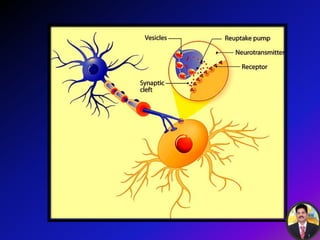
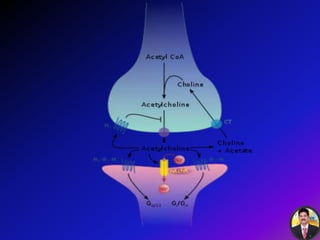
The transmission of nerve impulses occurs via electrical or chemical synapses. At an electrical synapse, there is direct continuity between neurons via gap junctions that allow the free movement of ions, allowing for very fast impulse transmission. At a chemical synapse, neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic neuron into the synaptic cleft upon an action potential arrival. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, causing ion channels to open and potentially triggering another action potential. Common neurotransmitters include acetylcholine, norepinephrine, GABA, and others.