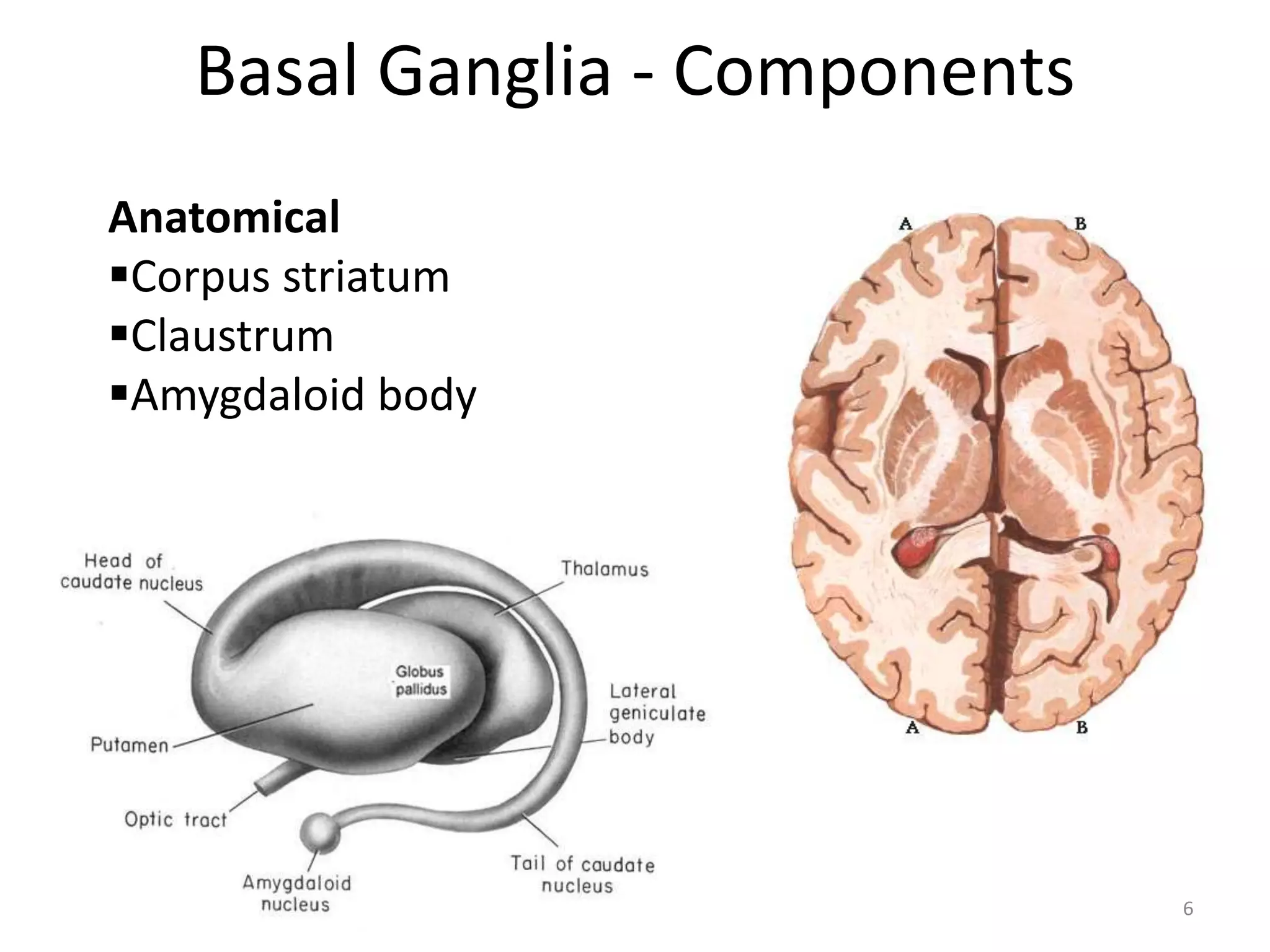
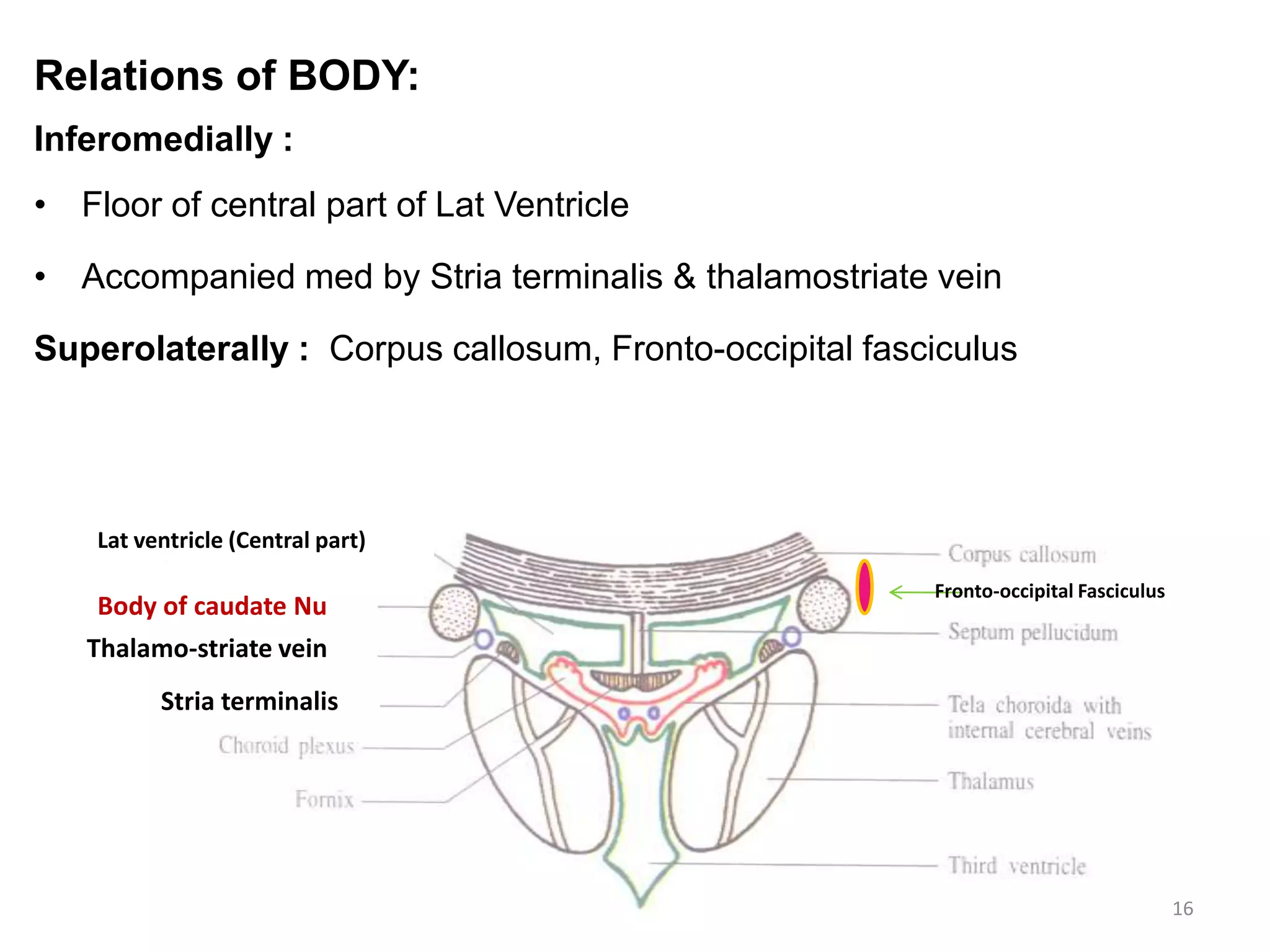
The basal ganglia are a group of subcortical nuclei that help regulate motor control and learning. They modulate movements through neuronal circuits and help produce purposeful movements while suppressing unwanted ones. Damage to different parts of the basal ganglia can result in either hypokinetic or hyperkinetic movement disorders. Parkinson's disease involves degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, leading to reduced excitation of motor cortex and hypokinesia. Other disorders like athetosis, hemiballism, chorea, and Wilson's disease each involve damage to specific basal ganglia structures and circuits.