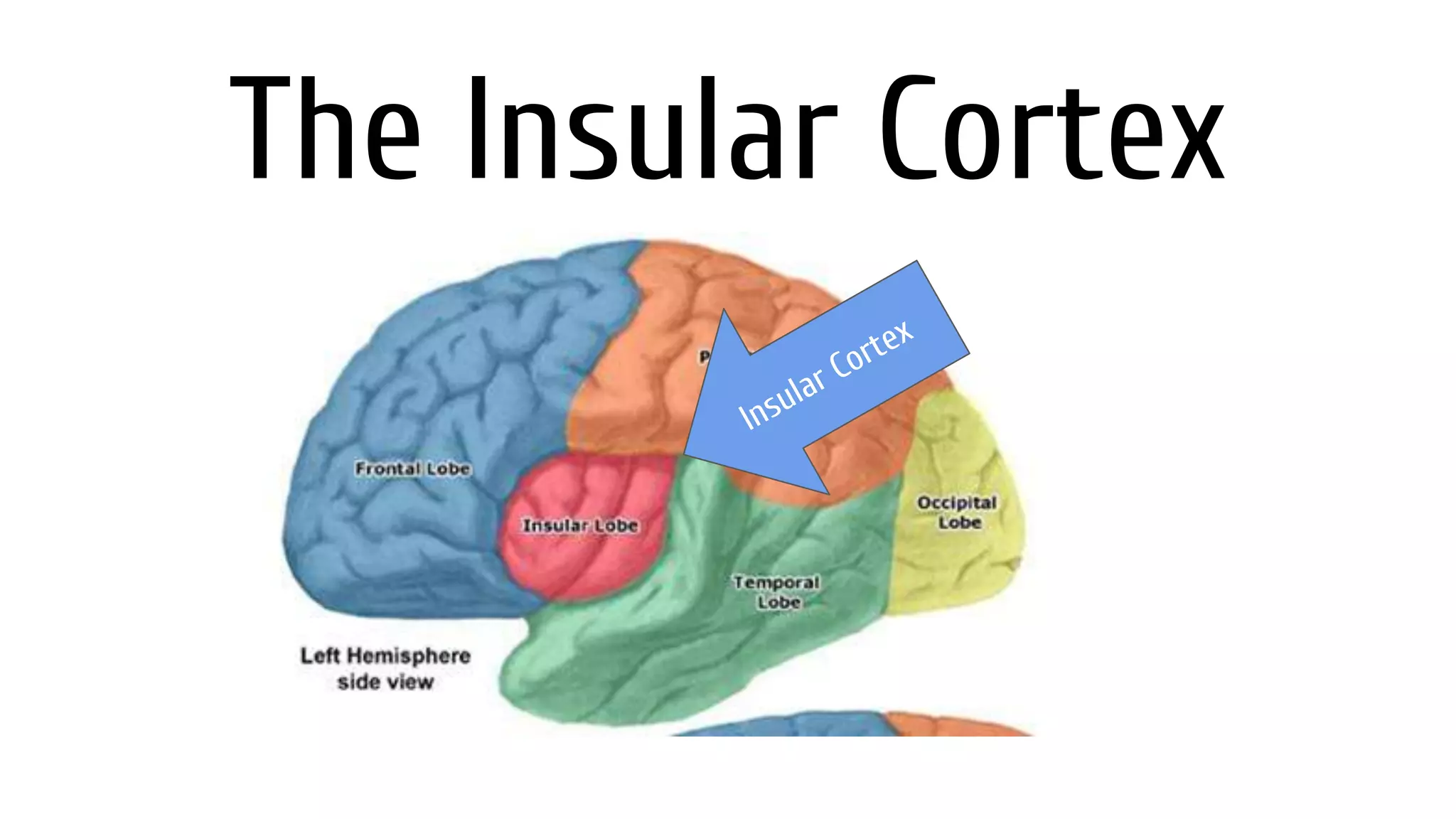
The insular cortex is located deep within the brain nestled between the frontal and temporal lobes. It has several functions including decision making, empathy, detecting bodily states, and regulating disgust. A key study showed that activating the insular cortex by having subjects hold warm objects made them rate others more positively and act more generously compared to activating it with cold objects. Dysfunctions in the insular cortex are implicated in various mood, anxiety, and psychotic disorders.