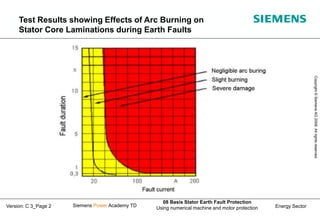
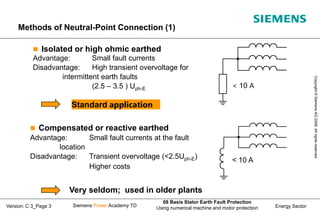
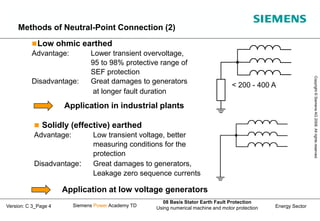
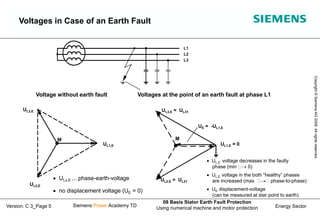
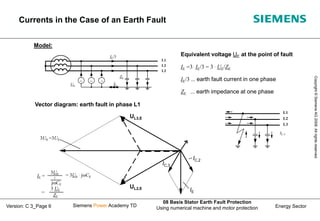
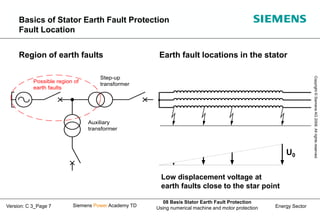
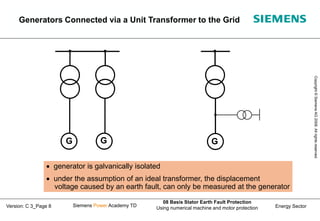
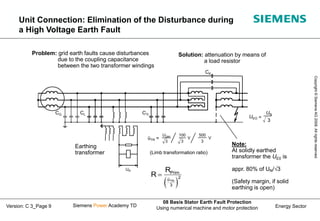
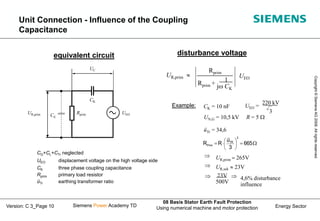
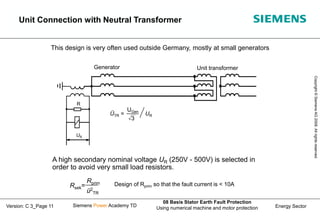
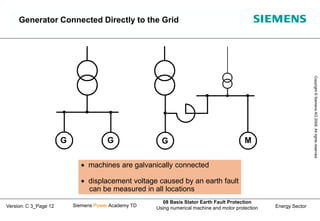
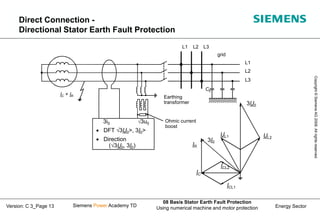
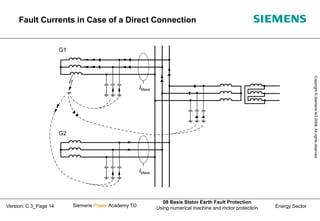
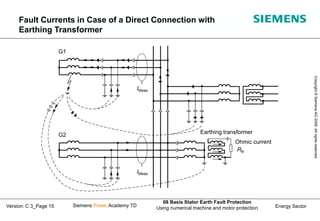
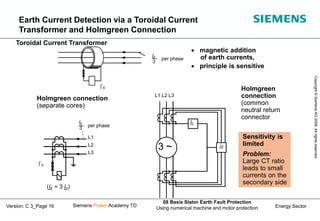
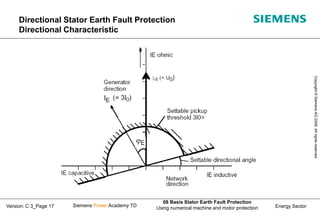
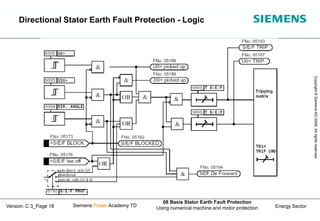
This document discusses methods for stator earth fault protection in generators. It presents:
1) Different methods of neutral point grounding and their advantages/disadvantages.
2) How earth fault voltages and currents behave depending on the fault location for different generator connections.
3) Techniques for measuring earth fault currents including use of a toroidal current transformer and Holmgreen connection.