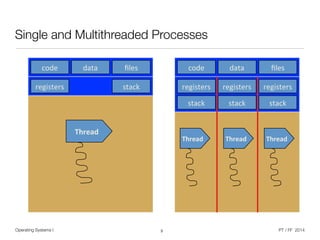
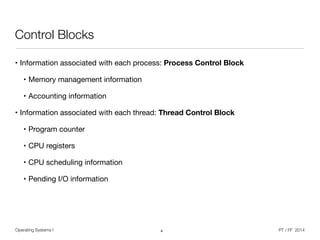
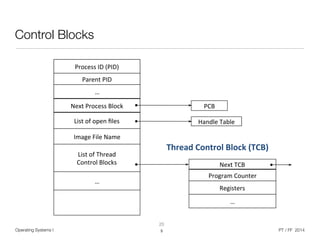
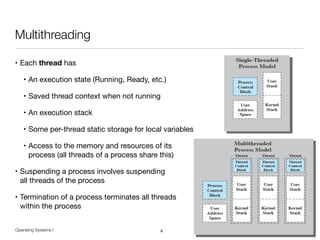
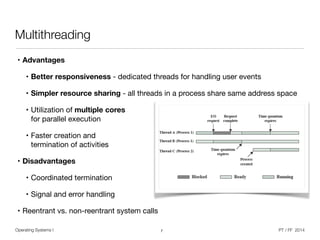
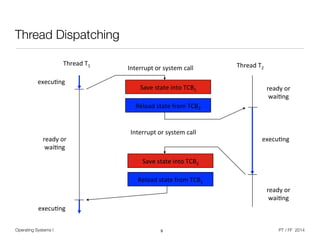
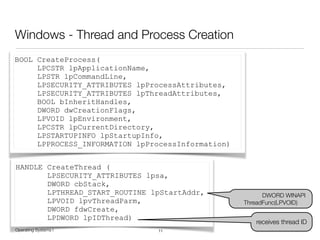
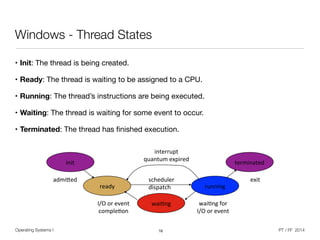
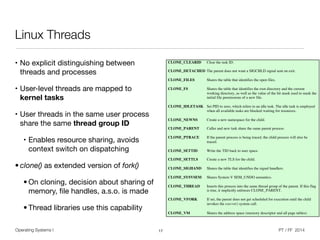
The document discusses processes and threads in operating systems. It describes how processes contain multiple threads that can run concurrently on multicore systems. Each thread has its own execution state and context stored in a thread control block. When a thread is not actively running, its context is saved so it can resume execution later. The document provides examples of how threads are implemented in Windows and Linux operating systems.









![20
#include <pthread.h>!
#include <stdio.h>!
#include <string.h>!
#include <unistd.h>!
!
void * hello_thread( void *arg ) {!
! printf( "hello " ); return( 0 ); }!
!
void * world_thread( void *arg ) {!
int n;!
! pthread_t!tid!= (pthread_t) arg;!
! if ( n = pthread_join( tid, NULL ) ) {!
! ! fprintf( stderr, "pthread_join: %sn", strerror( n ) );!
! ! return( NULL ); }!
! printf( "worldn" );!
! pthread_exit( 0 ); }!
!
int main( int argc, char *argv[] ) {!
! int!n;!
! pthread_t!htid, wtid;!
! if ( n = pthread_create( &htid, NULL, hello_thread, NULL ) ) {!
! ! fprintf( stderr, "pthread_create: %sn", strerror( n ) );!
! ! return( 1 ); }!
!
! if ( n = pthread_create( &wtid, NULL, world_thread, (void *) htid ) ) {!
! ! fprintf( stderr, "pthread_create: %sn", strerror( n ) );!
! ! return( 1 ); }!
!
! if ( n = pthread_join( wtid, NULL ) ) {!
! ! fprintf( stderr, "pthread_join: %sn", strerror( n ) );!
! ! return( 1 ); }!
! return( 0 ); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twuhnllr12jd8ncuumdv-signature-31e86b4e6484b81e4b5bd78d4baddbd59d710461bb150a035e879c3c5237bcb9-poli-150108021406-conversion-gate01/85/Operating-Systems-1-7-12-Threads-20-320.jpg)
