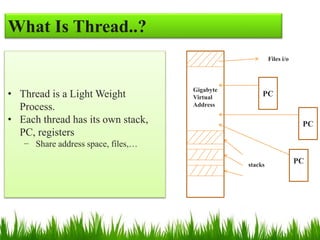
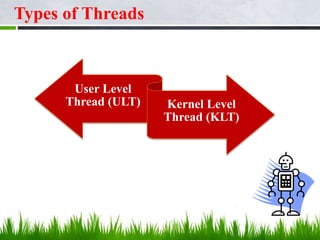
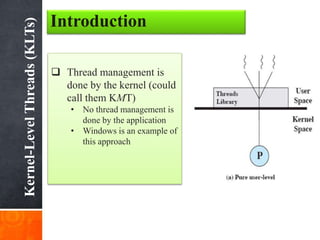
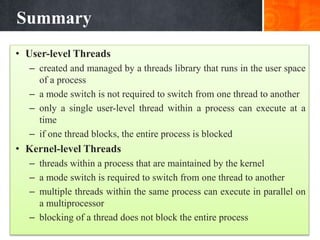
User-level threads (ULTs) are managed by a user-level threads library and do not require a kernel context switch when switching between threads. However, if one ULT blocks, the entire process is blocked. Kernel-level threads (KLTs) are managed by the kernel, allowing true parallelism within a process on multiprocessors. A mode switch is required to switch KLTs but blocking a single KLT does not block the entire process. Threads provide benefits over processes like lower overhead for creation, termination, and context switching.