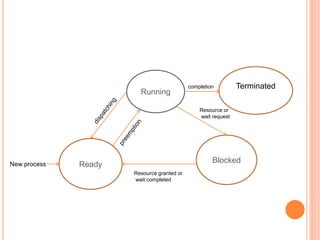
This document discusses processes and process states in operating systems. It defines a process as a program in execution that can exist in different states. The main states are new, ready, running, blocked, and terminated. A process can transition between these states, such as moving from ready to running when assigned CPU resources or from running to blocked when waiting for a required resource. An additional suspended state is used when a process is swapped out of memory. The document provides detailed descriptions of each state and the transitions between them.