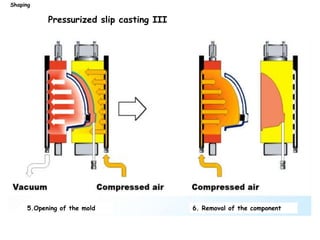
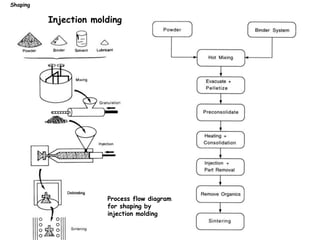
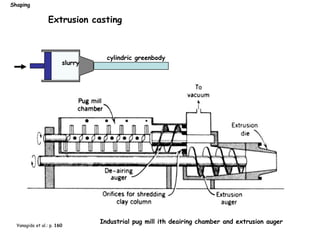
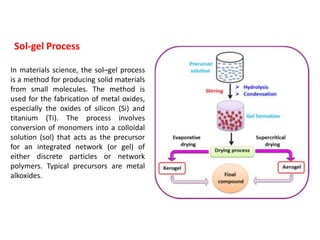
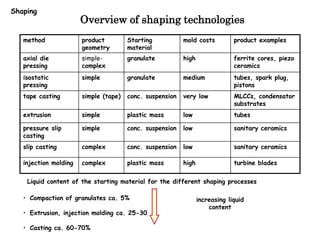
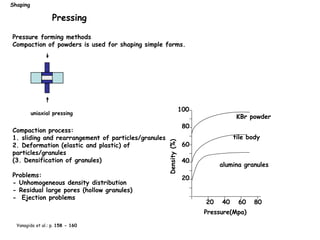
The document discusses various processing methods for ceramics, including the sol-gel process, slip casting, tape casting, extrusion, injection molding, and drying of green bodies. The sol-gel process involves the conversion of monomers into a colloidal solution that acts as a precursor for an integrated network or gel. Slip casting involves pouring a slurry into a plaster mold where the liquid is absorbed, depositing powder particles. Tape casting uses a doctor blade to spread a slurry onto a film at controlled thickness. Drying of green bodies occurs through boundary layer and pore processes, with shrinkage and defects occurring if not done uniformly.





















![A doctor blade assembly. The ceramic
slurry is held in the reservoir behind
the blade [middle of the micrograph].
The twin micrometers [right] control the
blade height above the carrier film.
More sophisticated versions feature
double blades and pumped metered
slurry flow to keep the height of the
slurry reservoir constant.
Example of a tape drying on the Mistler
laboratory-scale batch tape caster.
Industrially the process is often continuous
with the tape being force dried prior to
removal from the carrier, dicing and
further processing.
Tape casting II
Shaping](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/07-8-lectureprocessing-211110120110/85/07-8-lecture-processing-25-320.jpg)