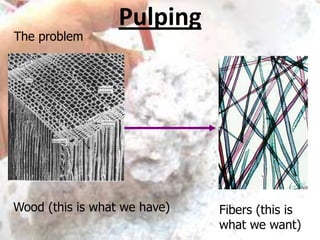
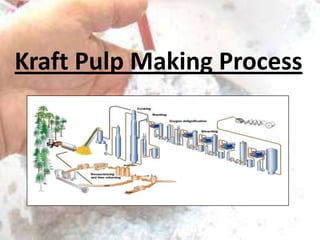
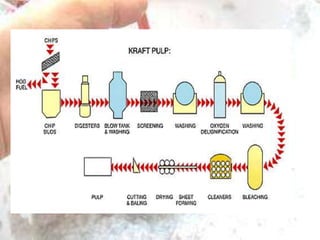
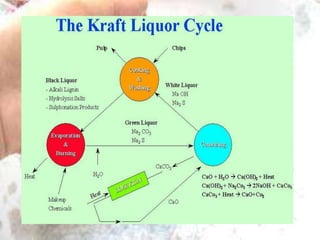
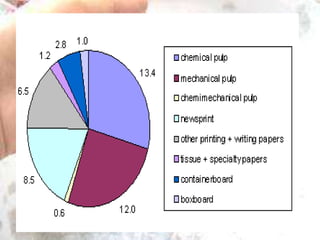
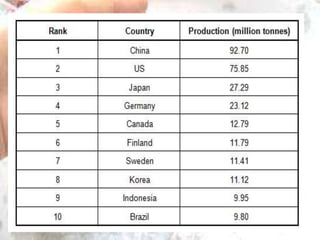
The kraft process, also known as the sulfate process, is an industrial process that converts wood into pulp consisting mainly of pure cellulose fibers. It involves treating wood chips with a mixture of sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide known as liquor. This breaks the bonds linking lignin to the cellulose. The process includes impregnating chips with white liquor, cooking them to remove lignin, recovering chemicals from the spent liquor, screening and washing the pulp, and sometimes bleaching it to produce high brightness pulp. The kraft process was invented in the 1870s and is now the dominant pulping process worldwide.