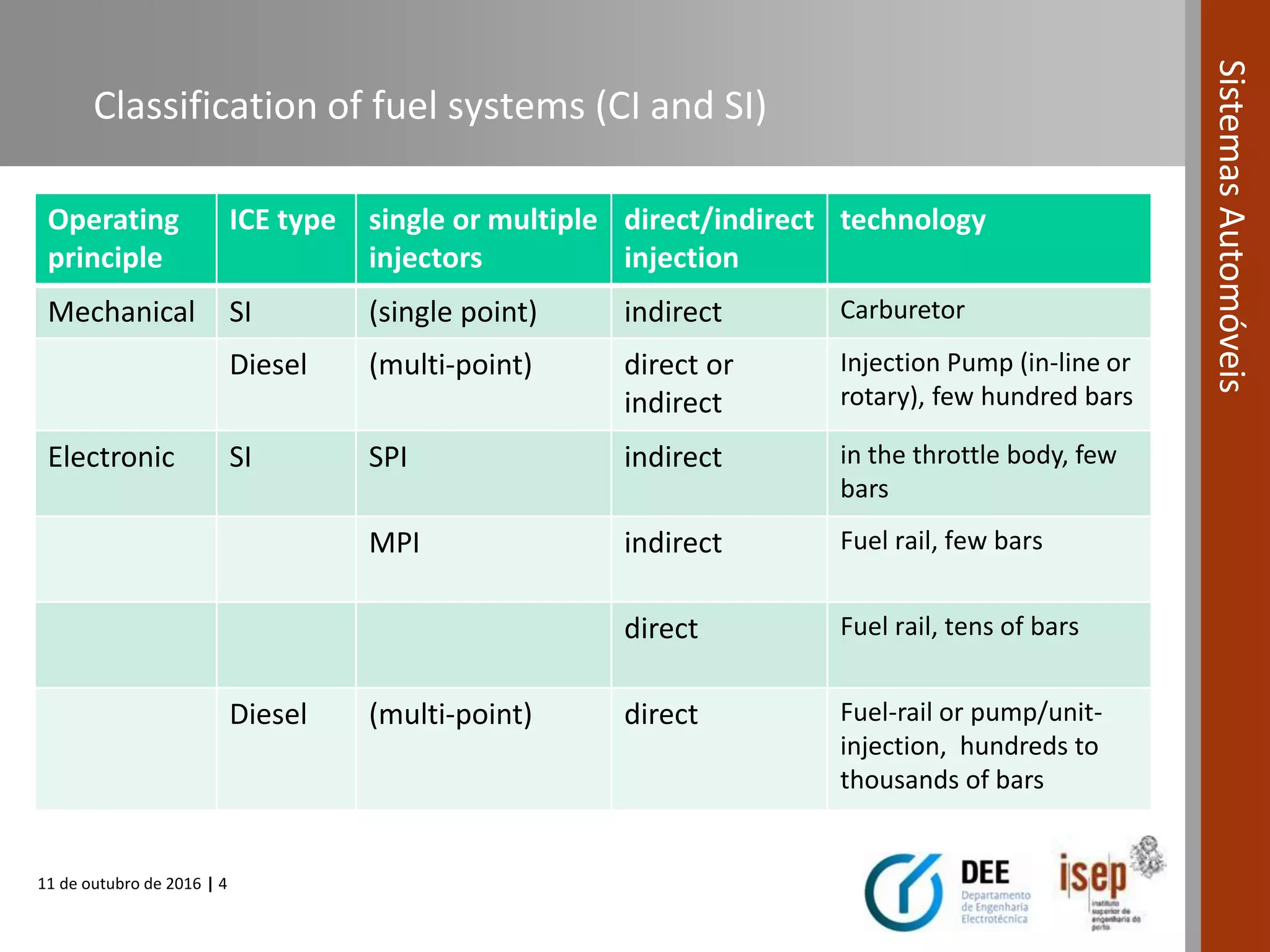
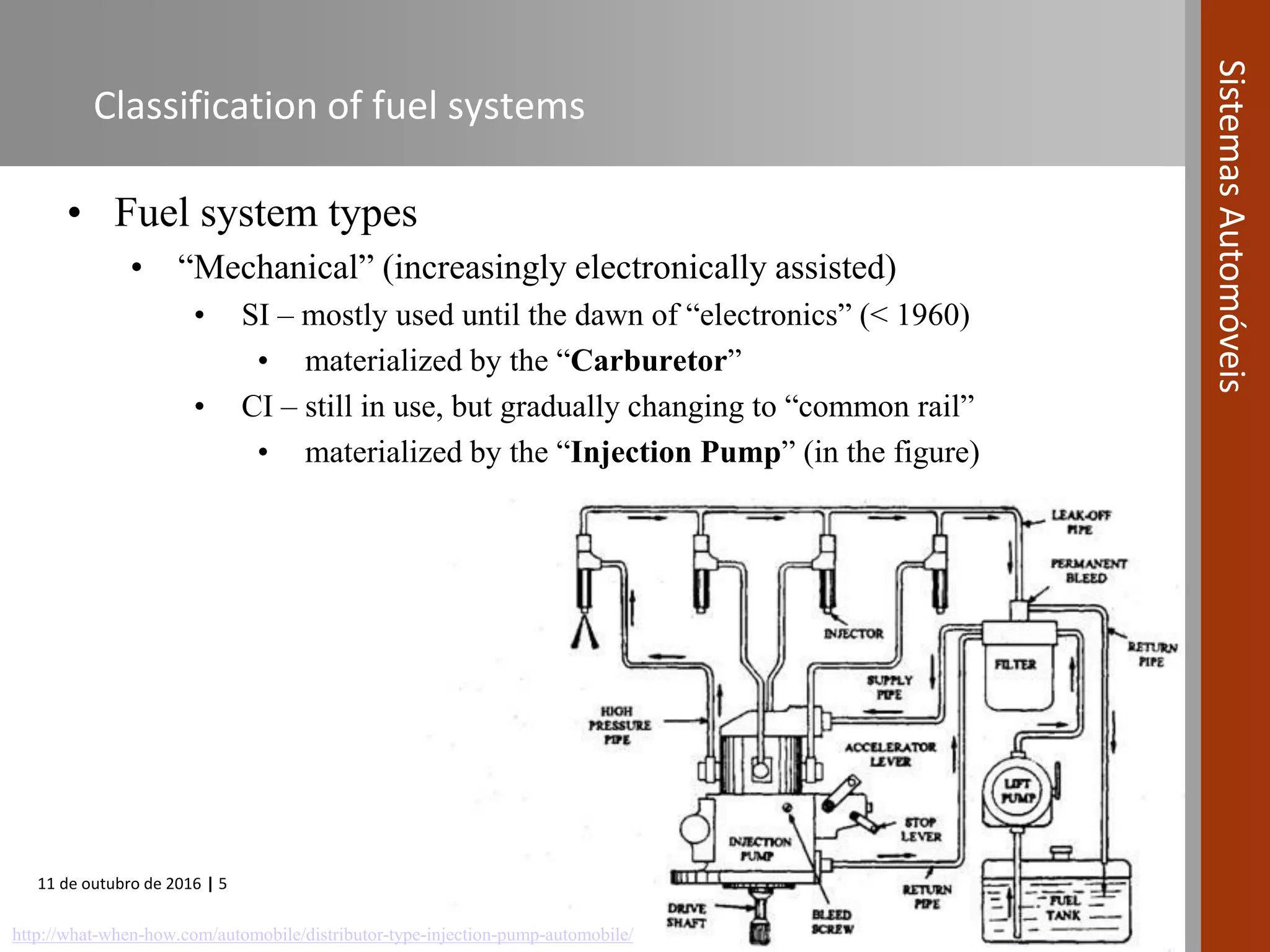
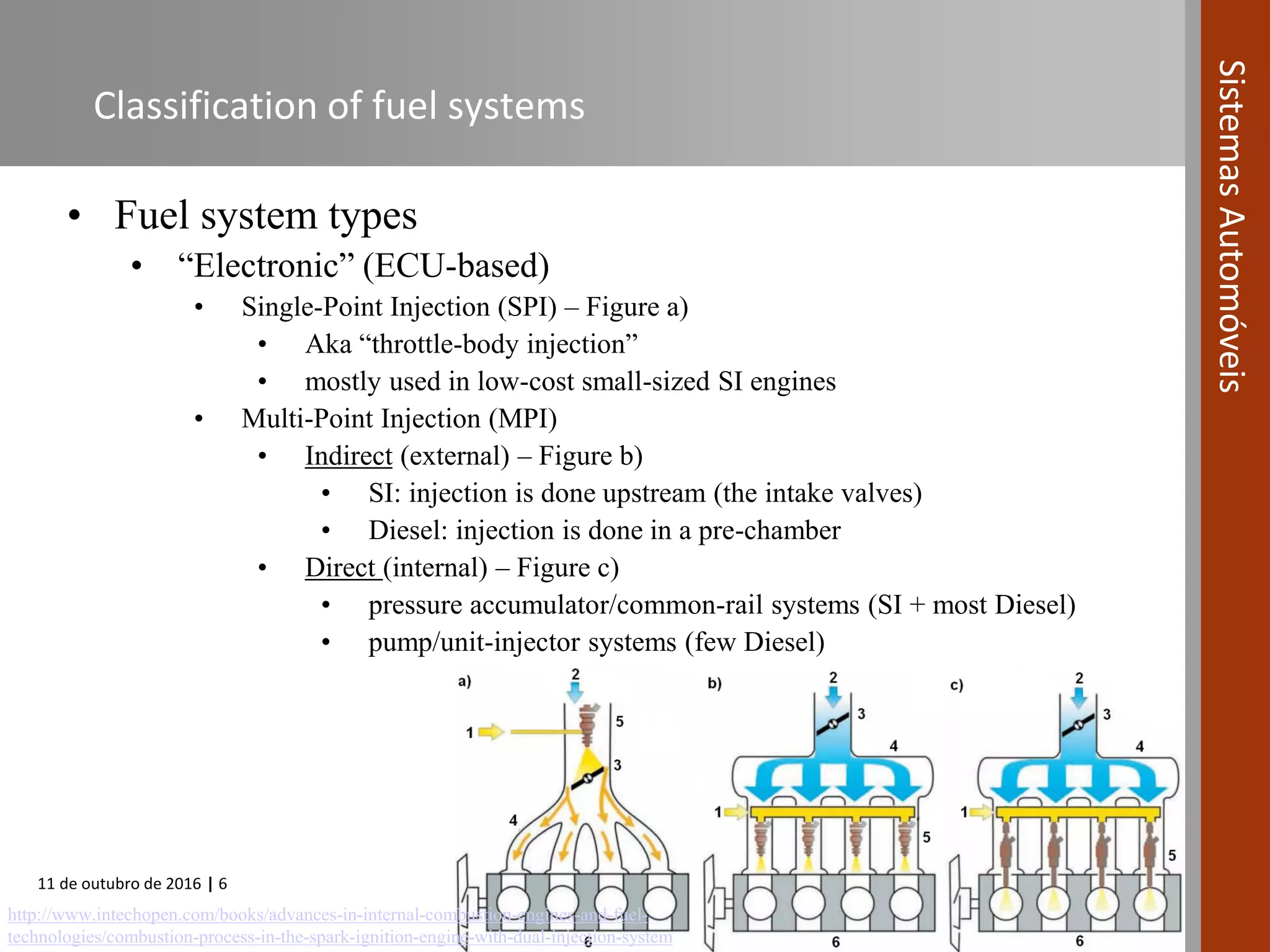
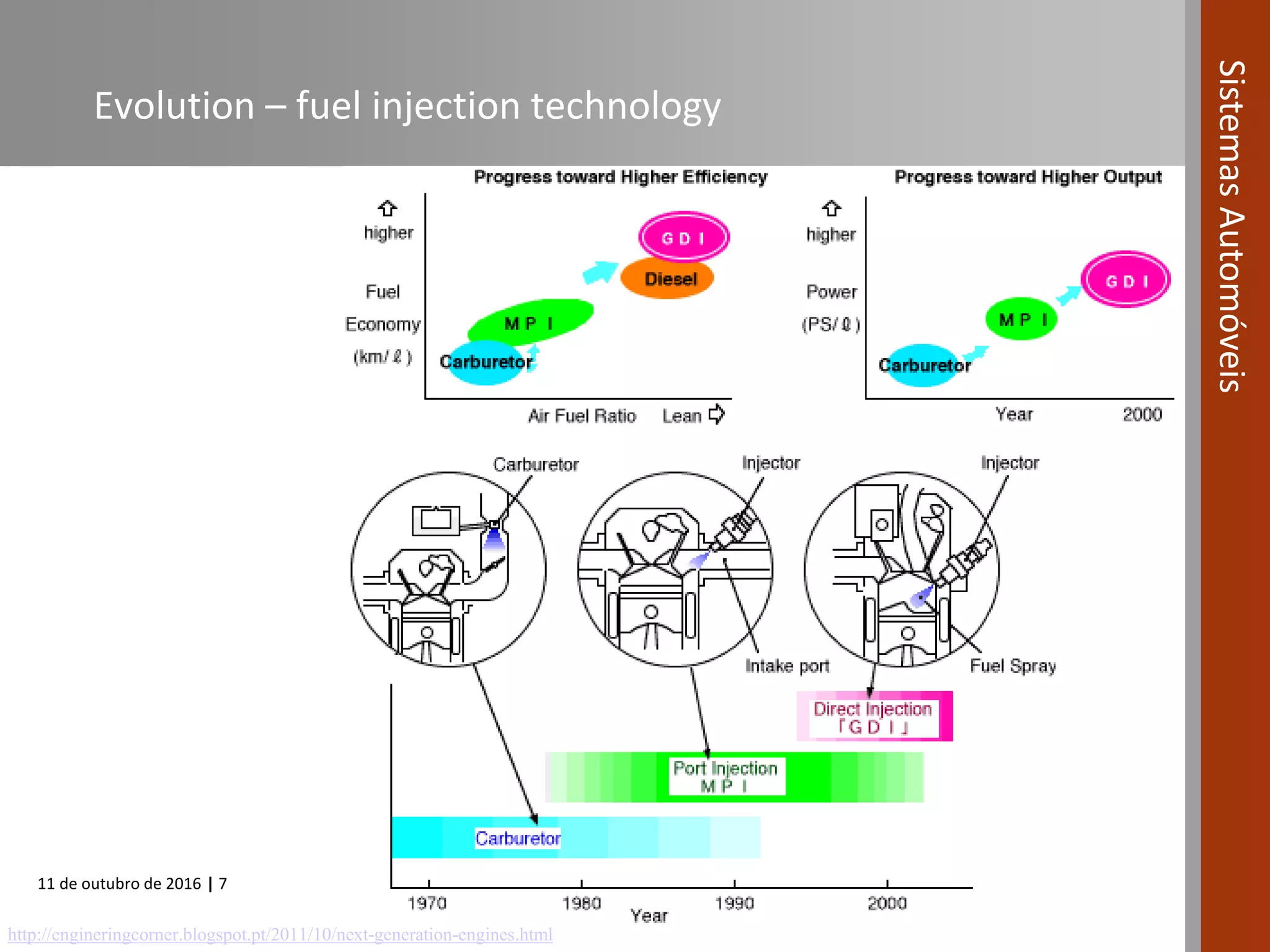
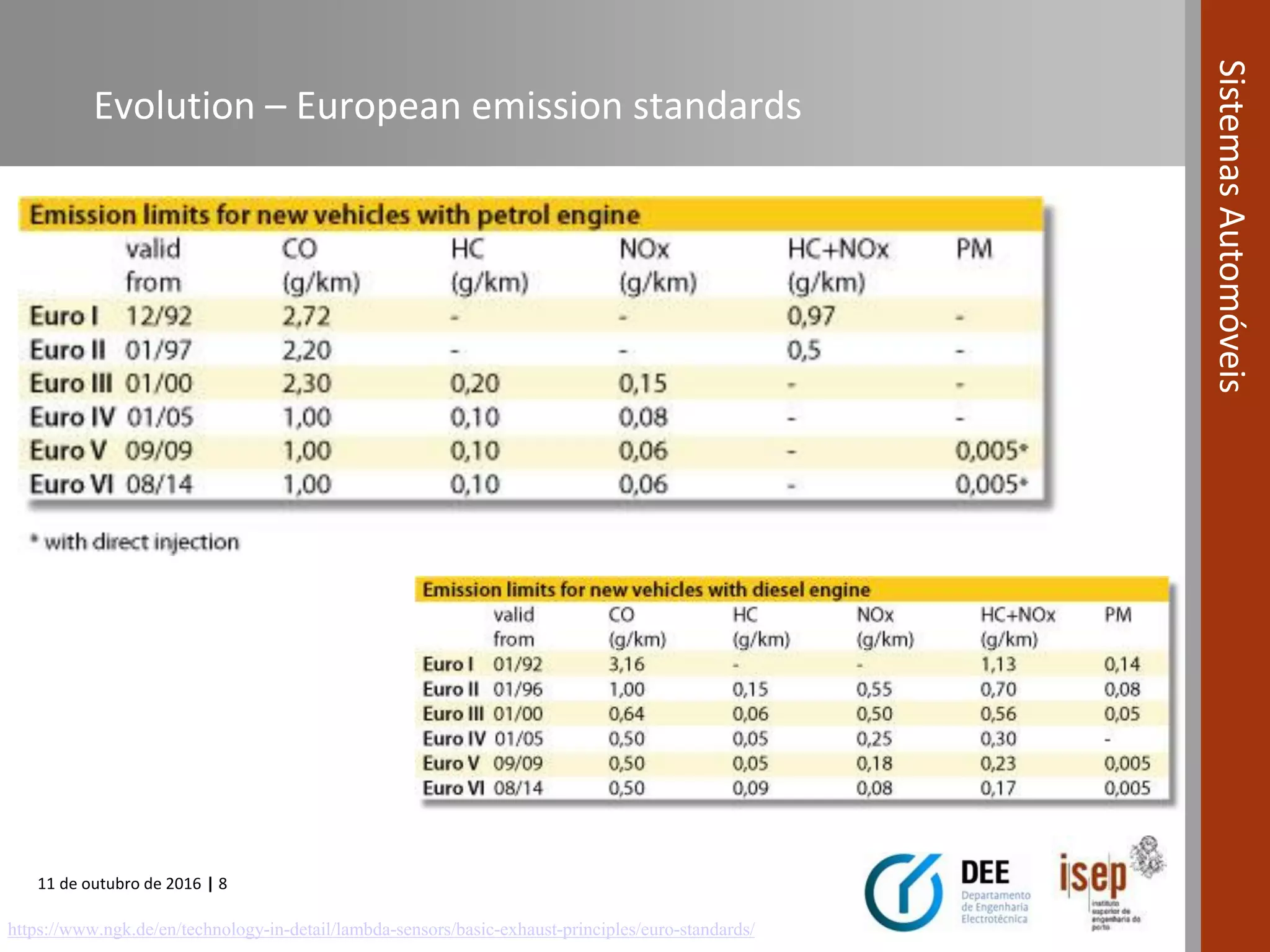
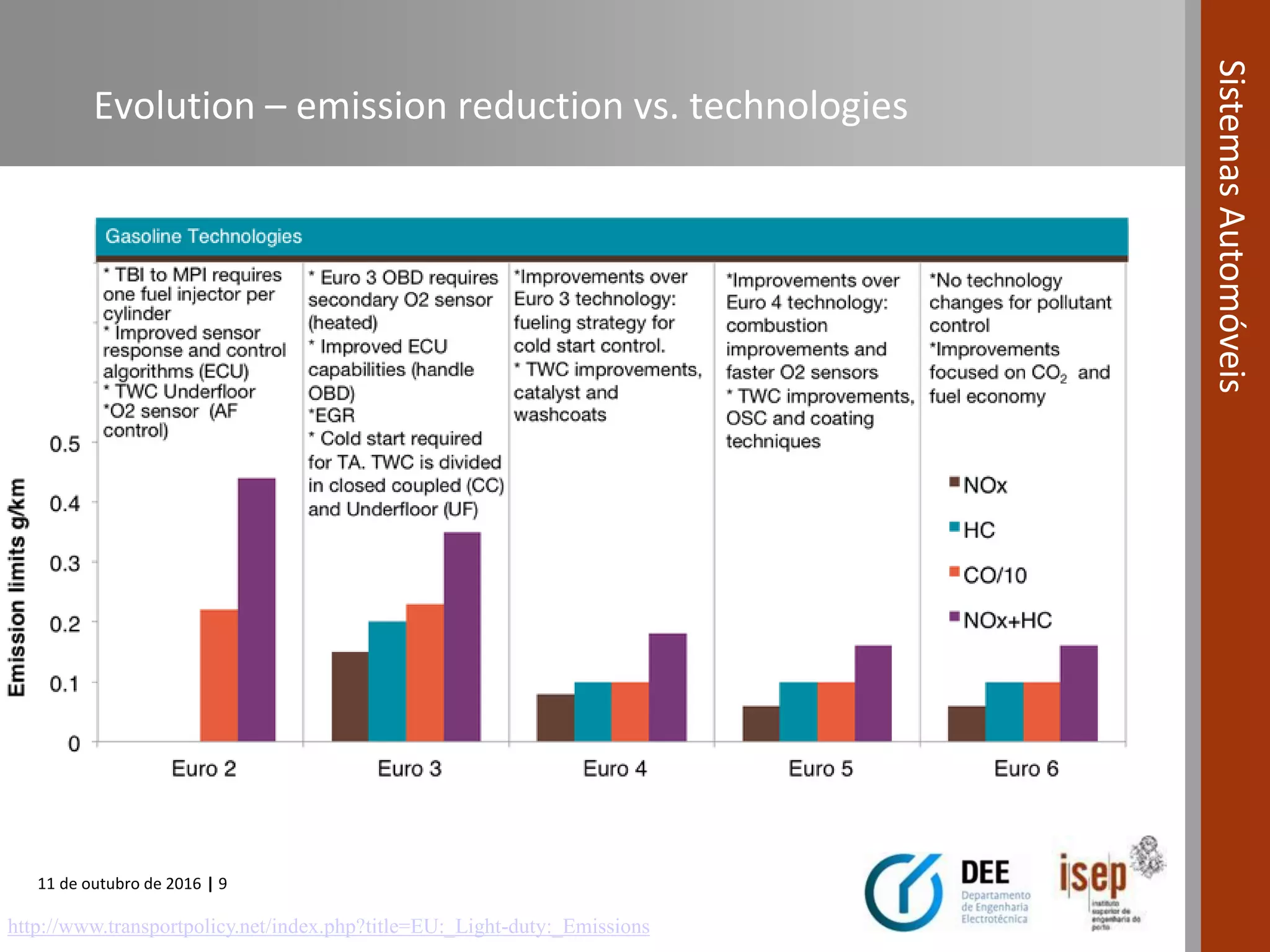
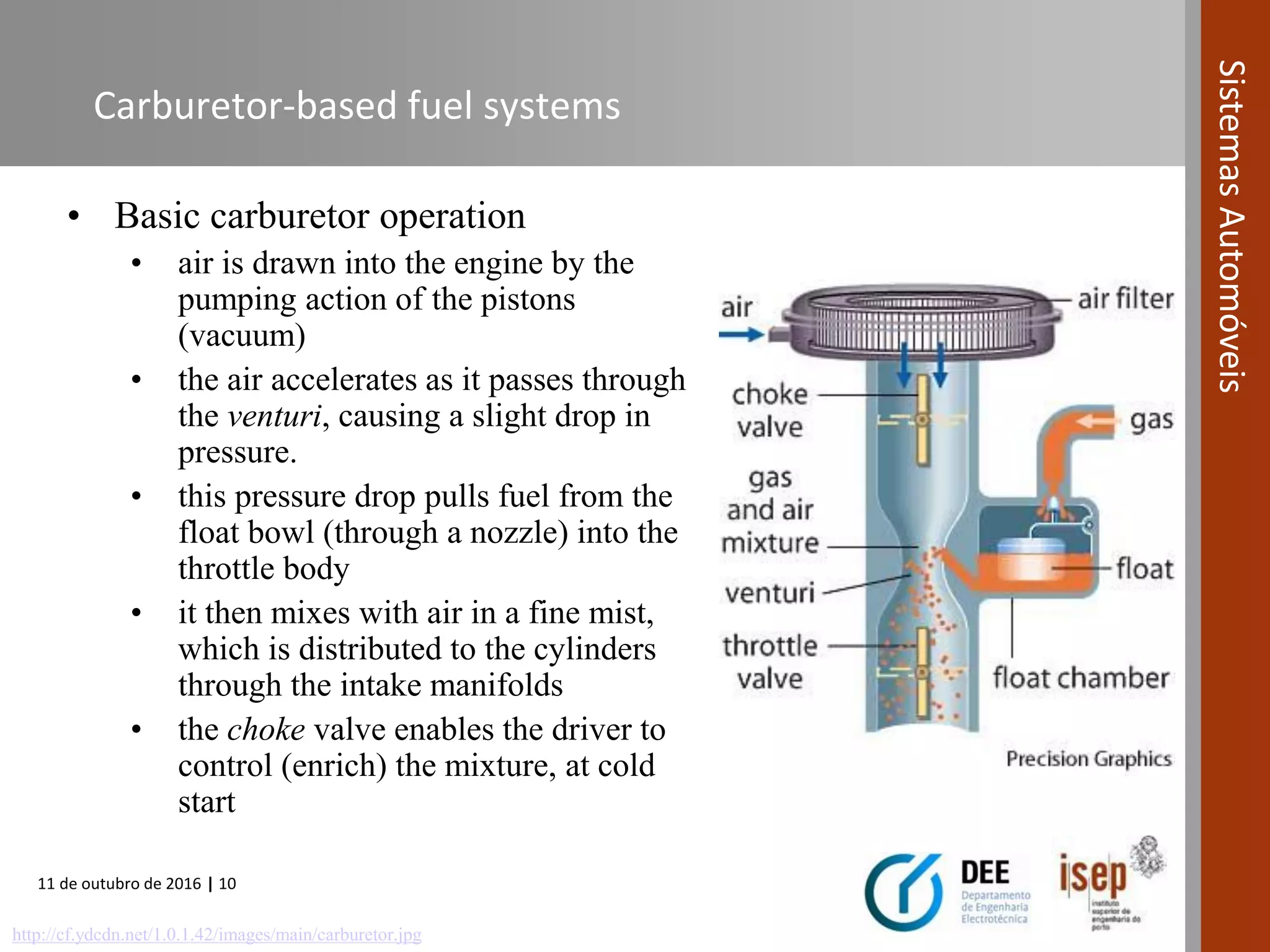
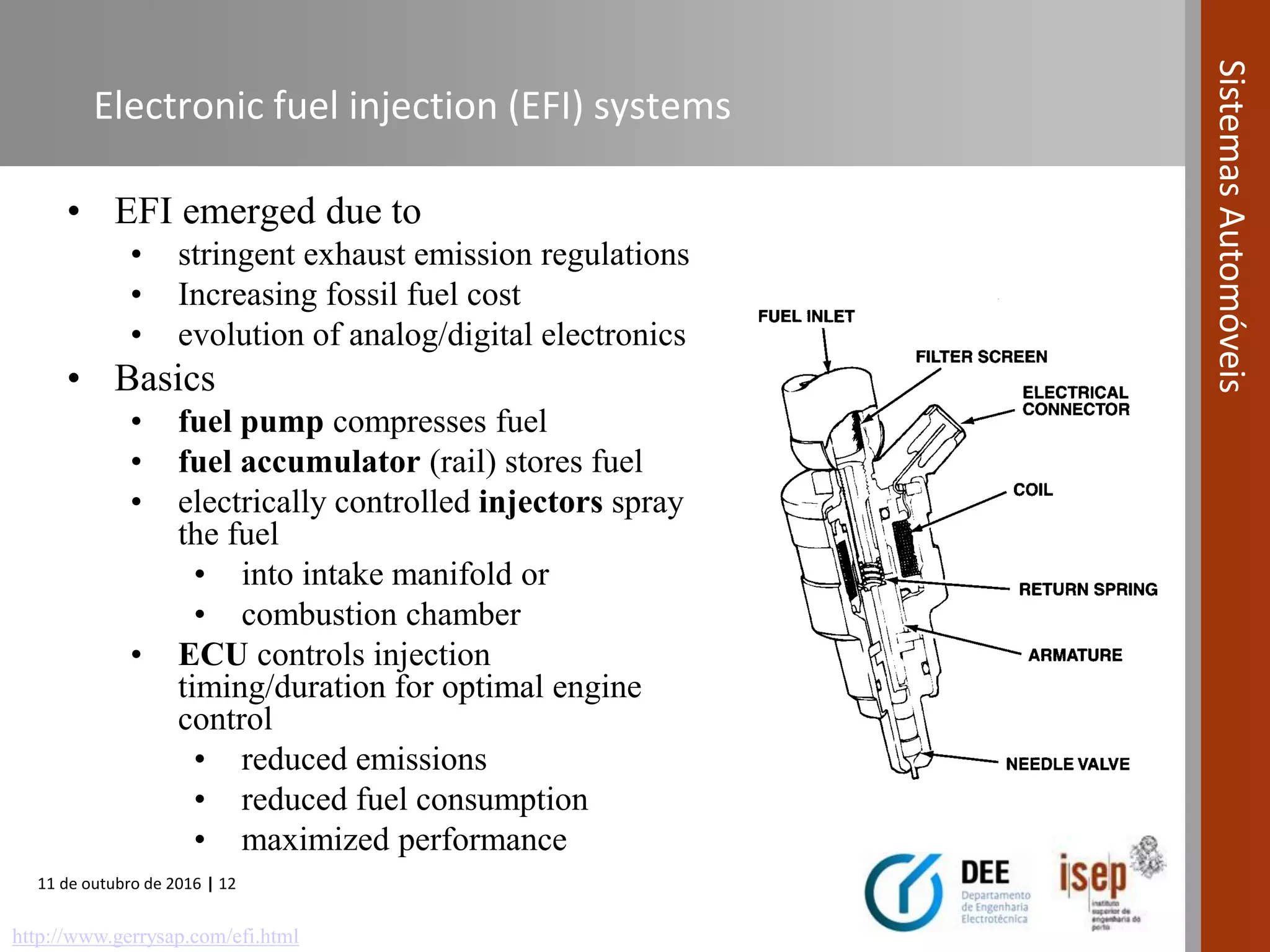
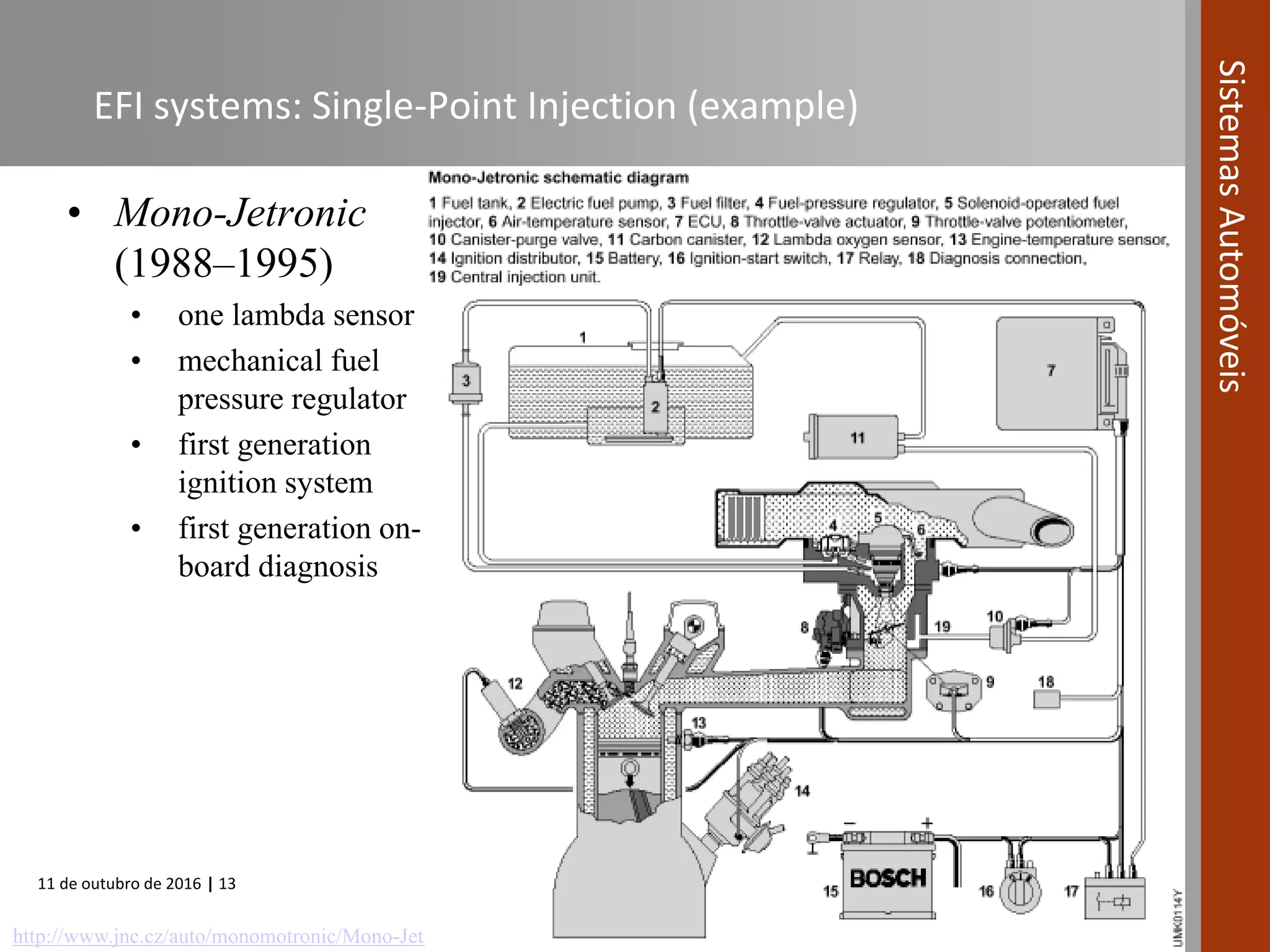
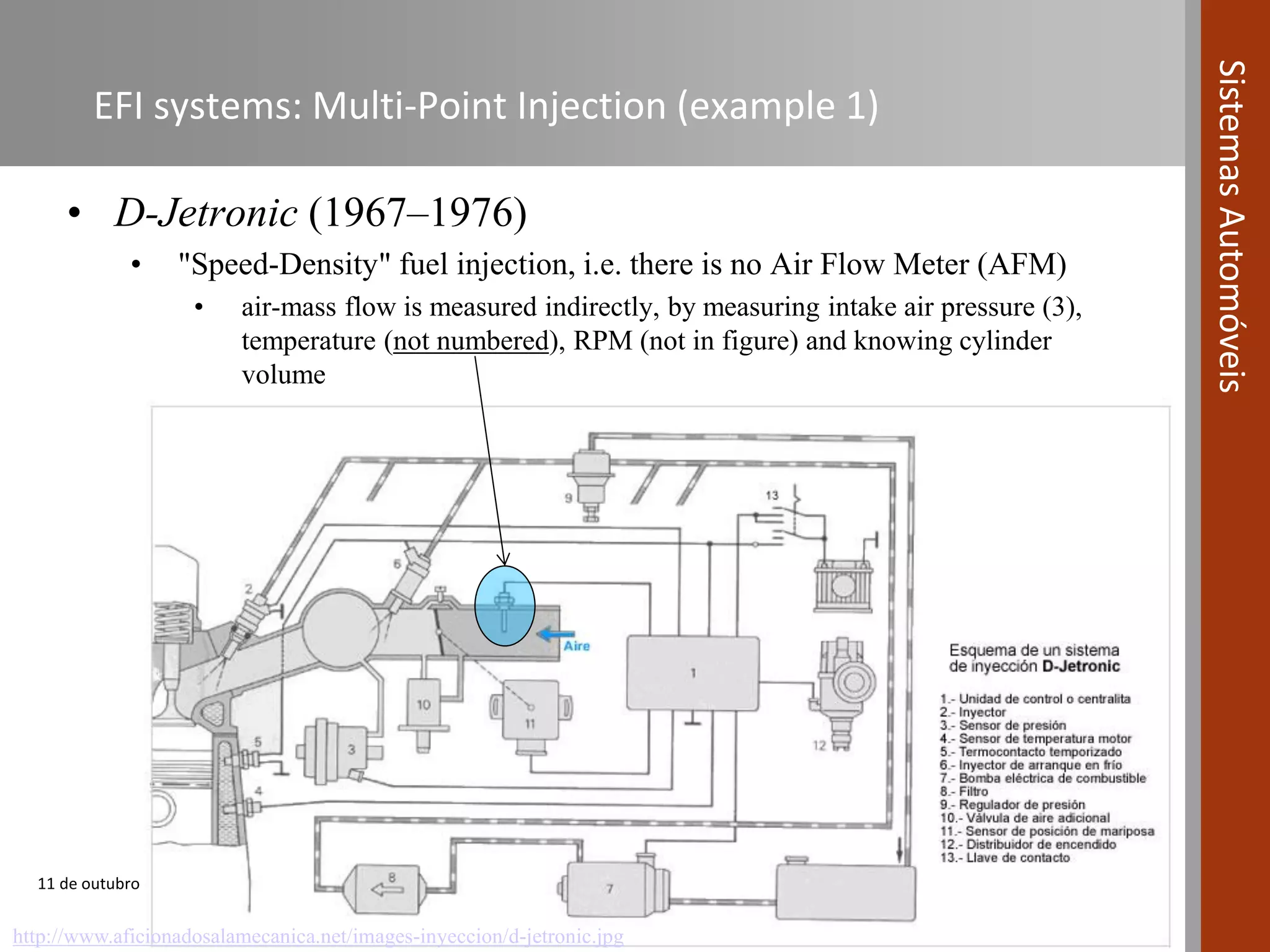
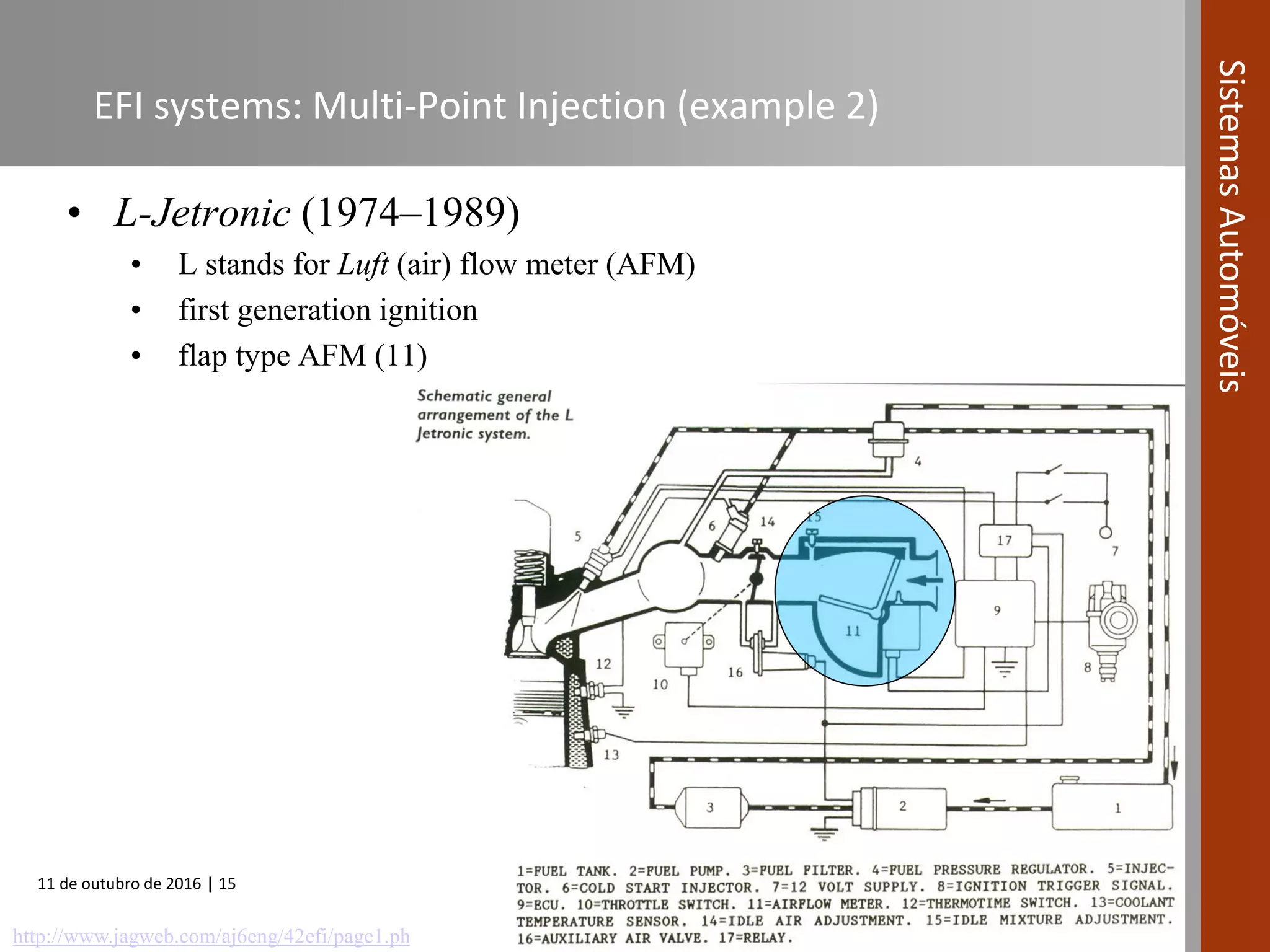
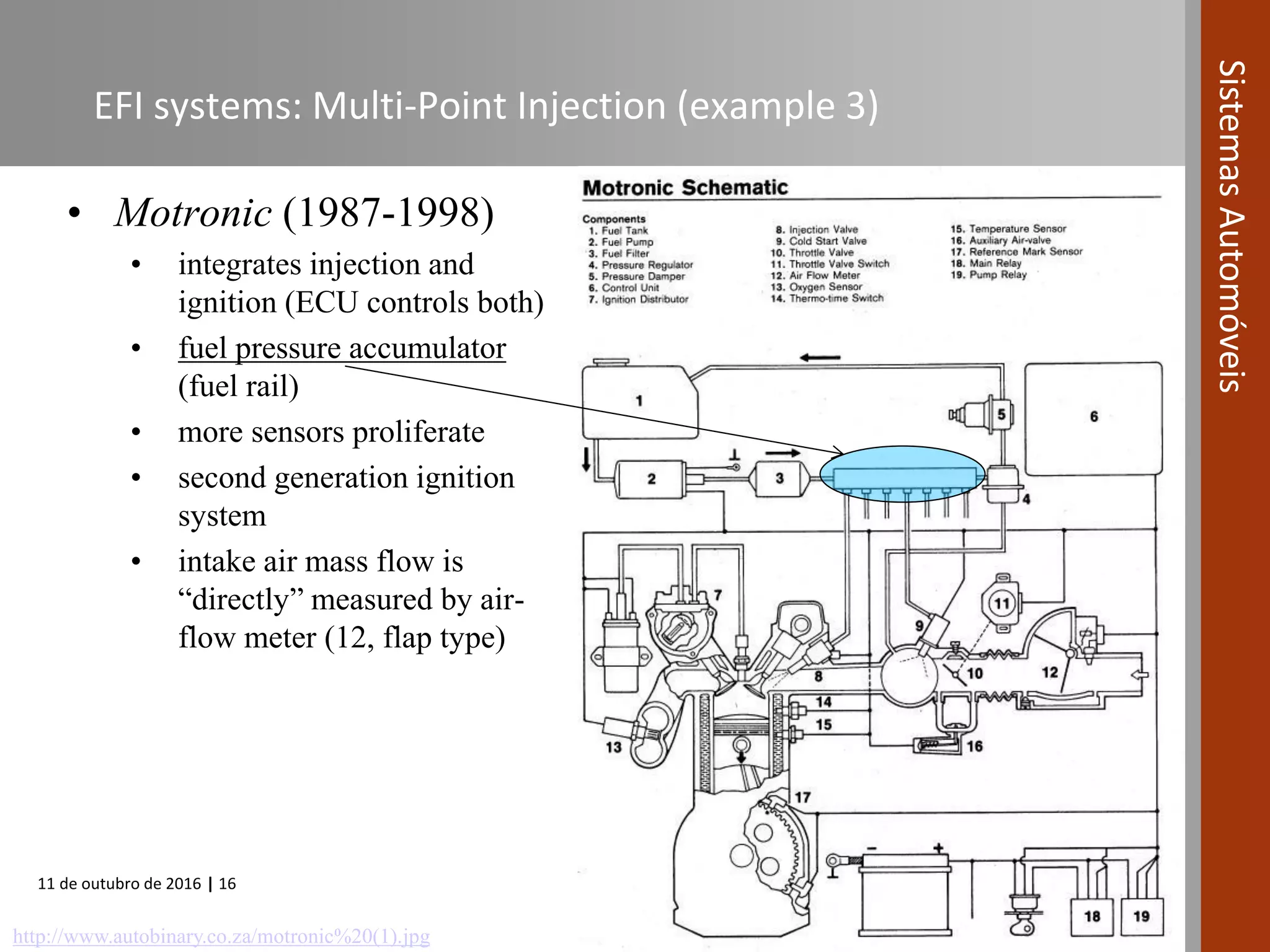
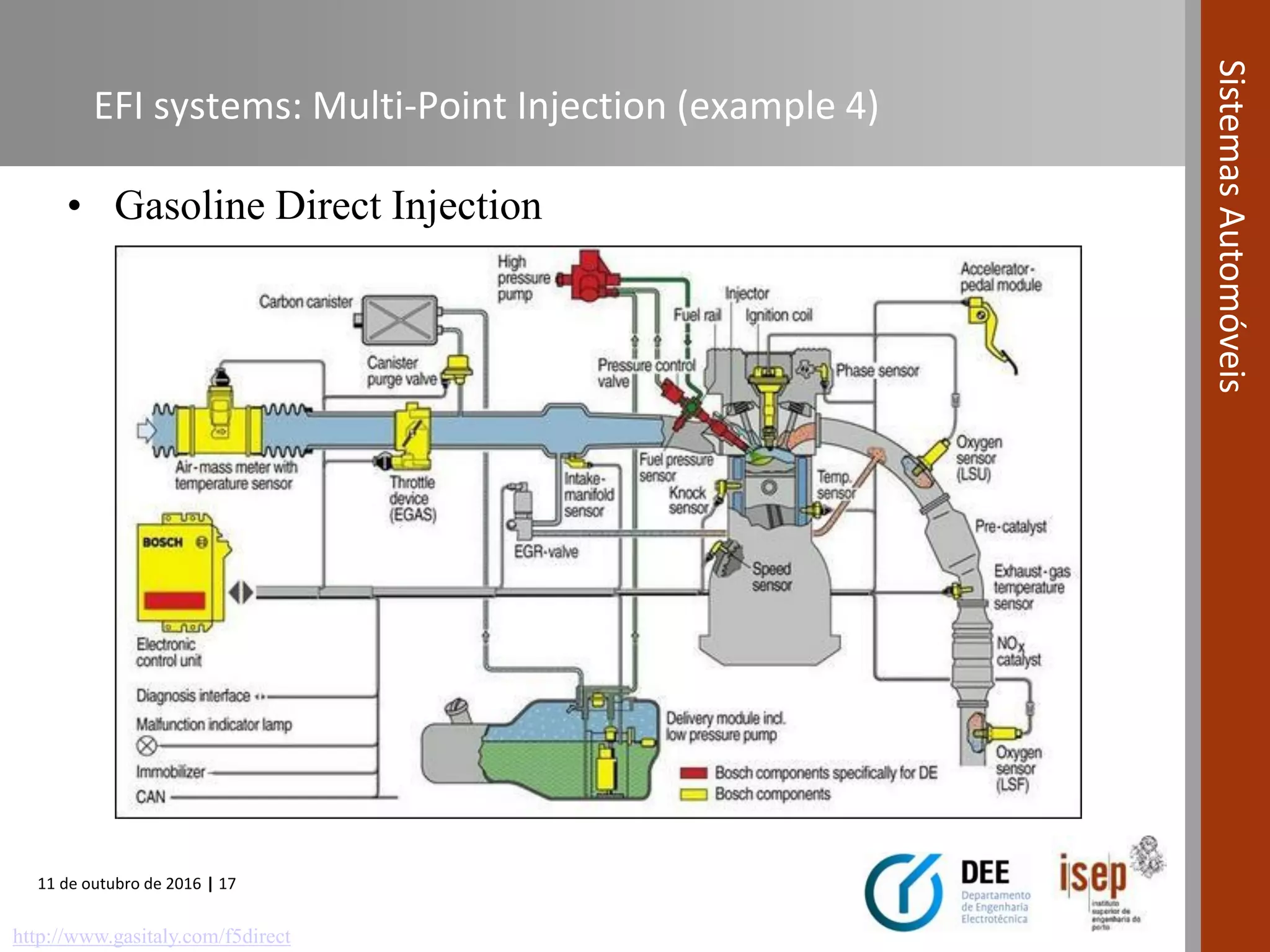
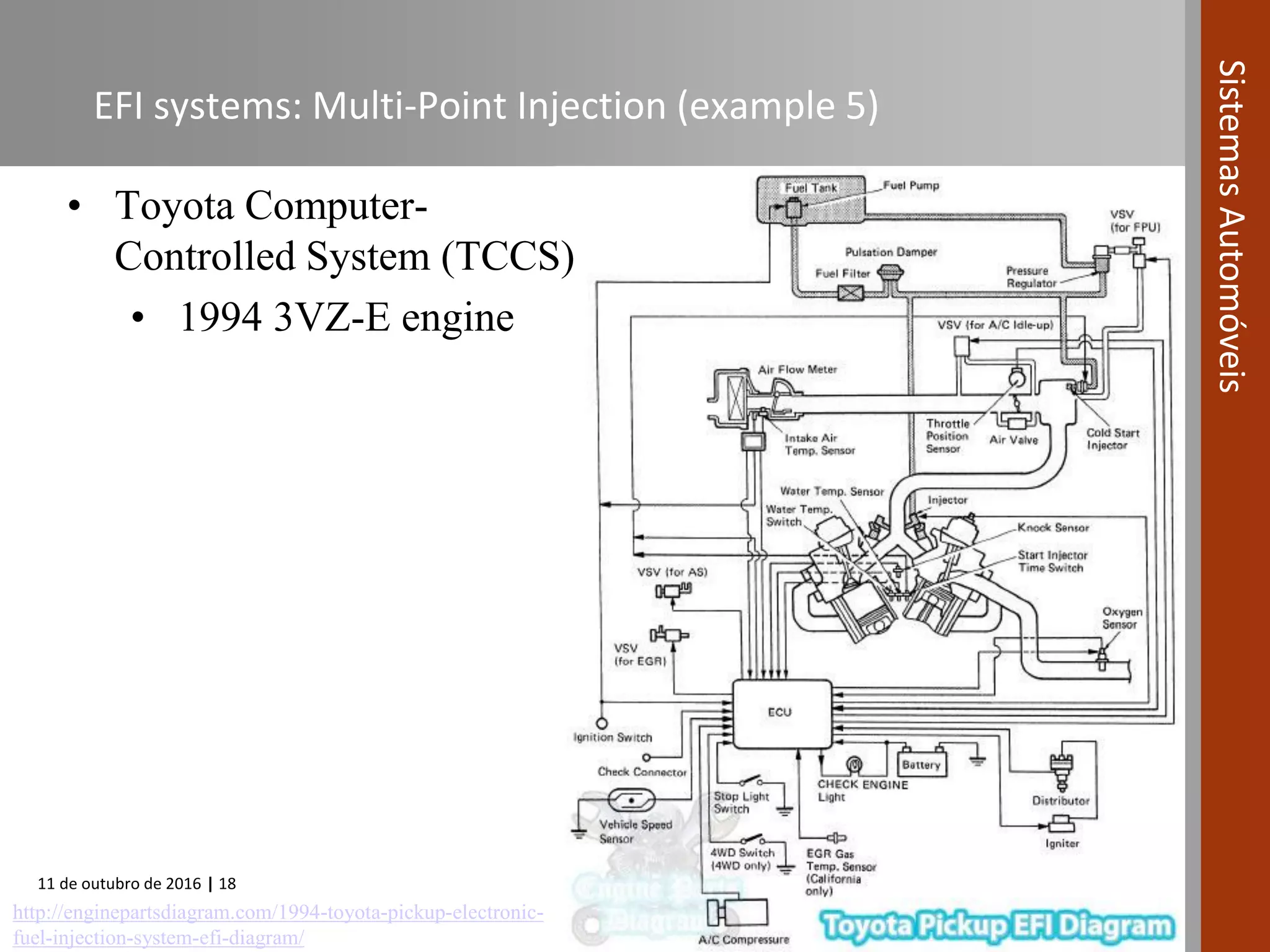
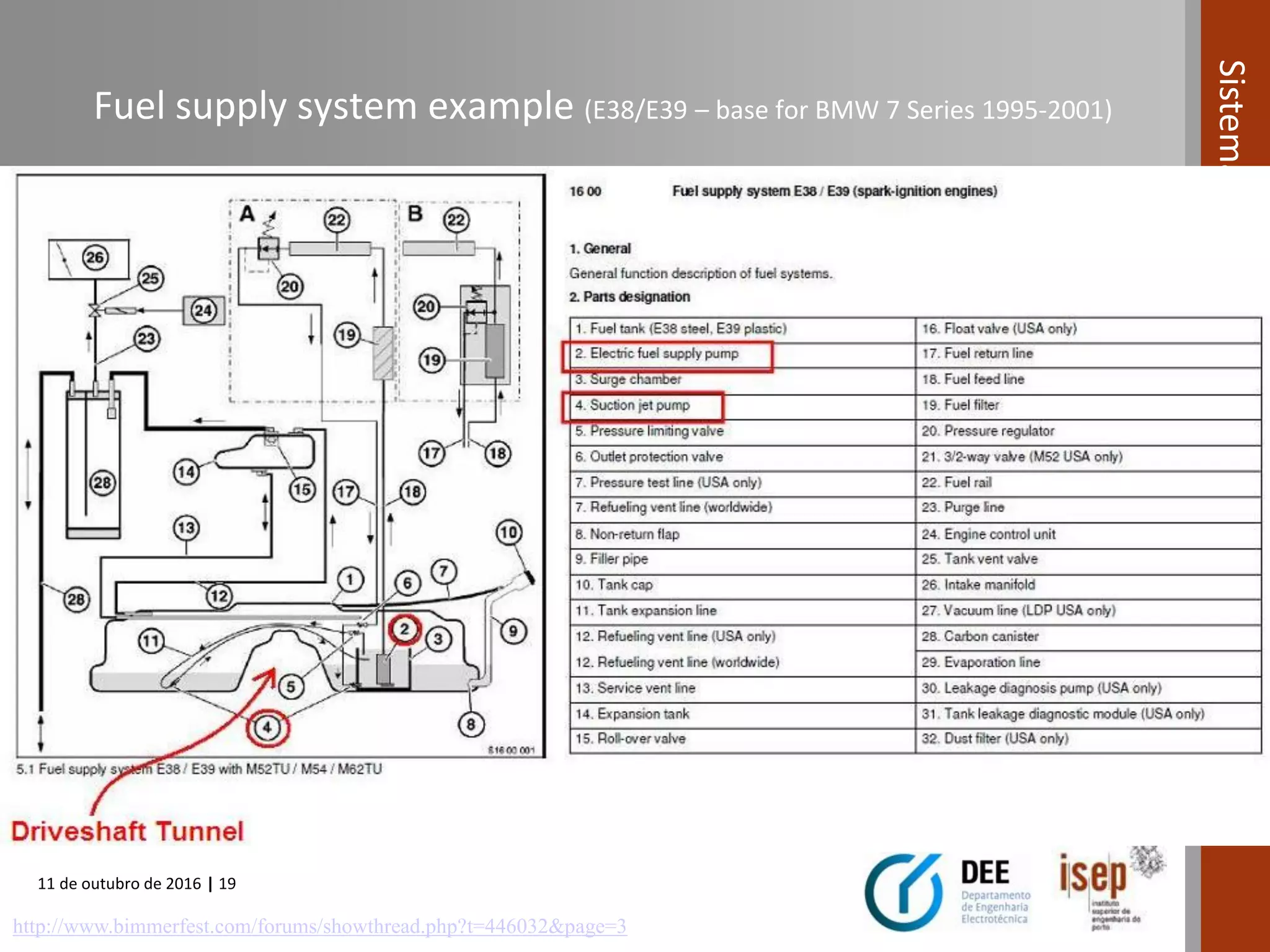
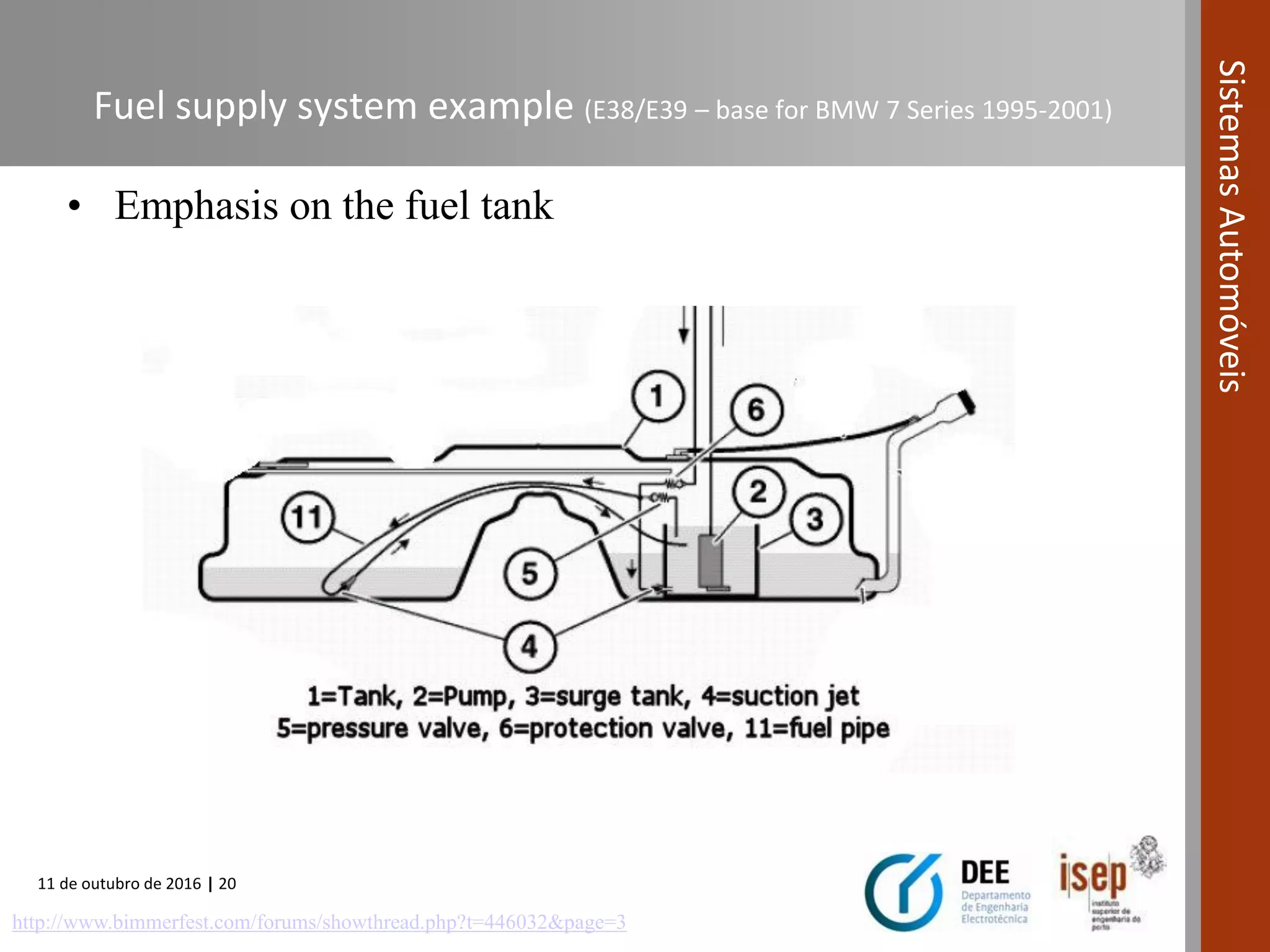
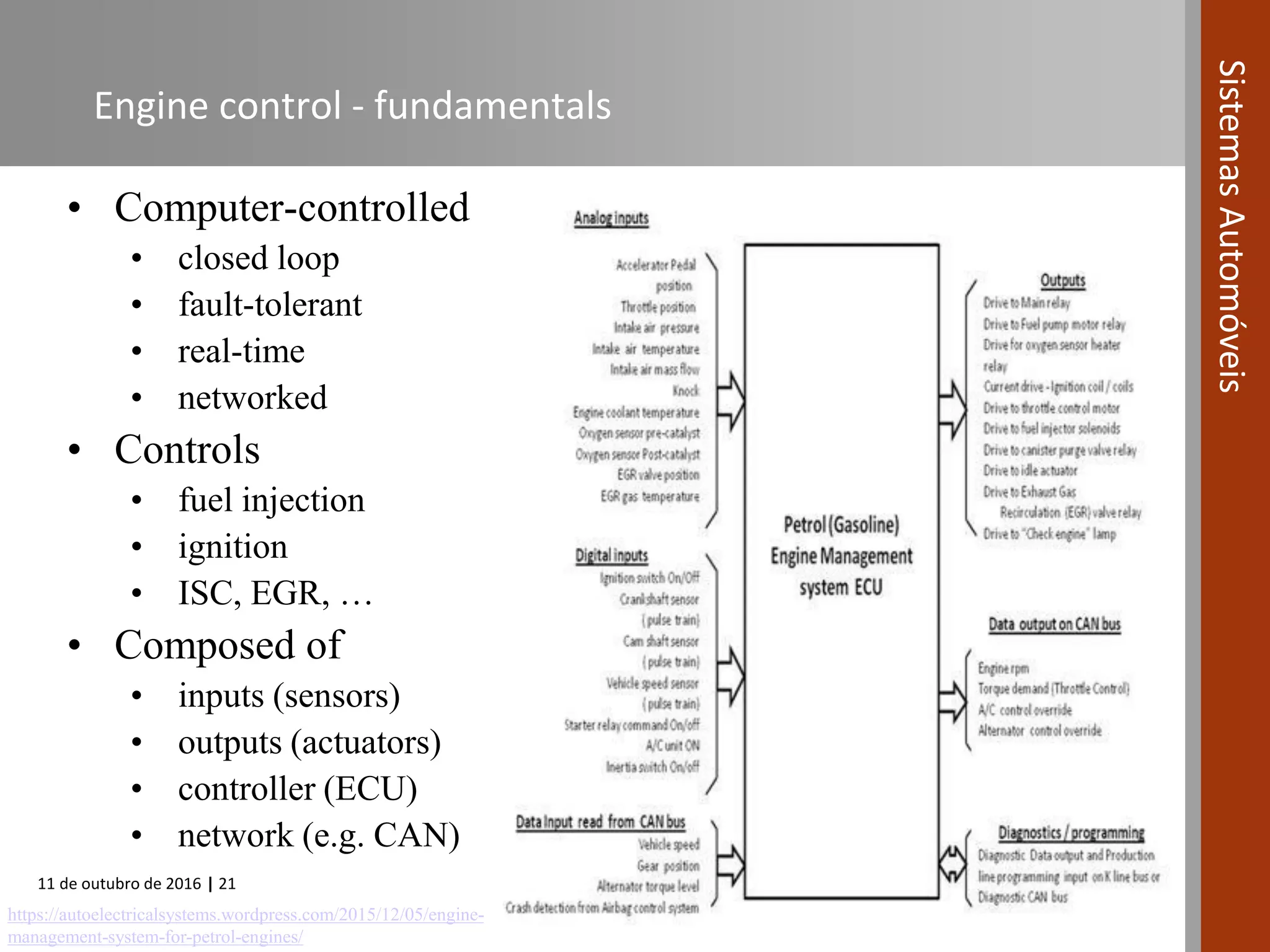
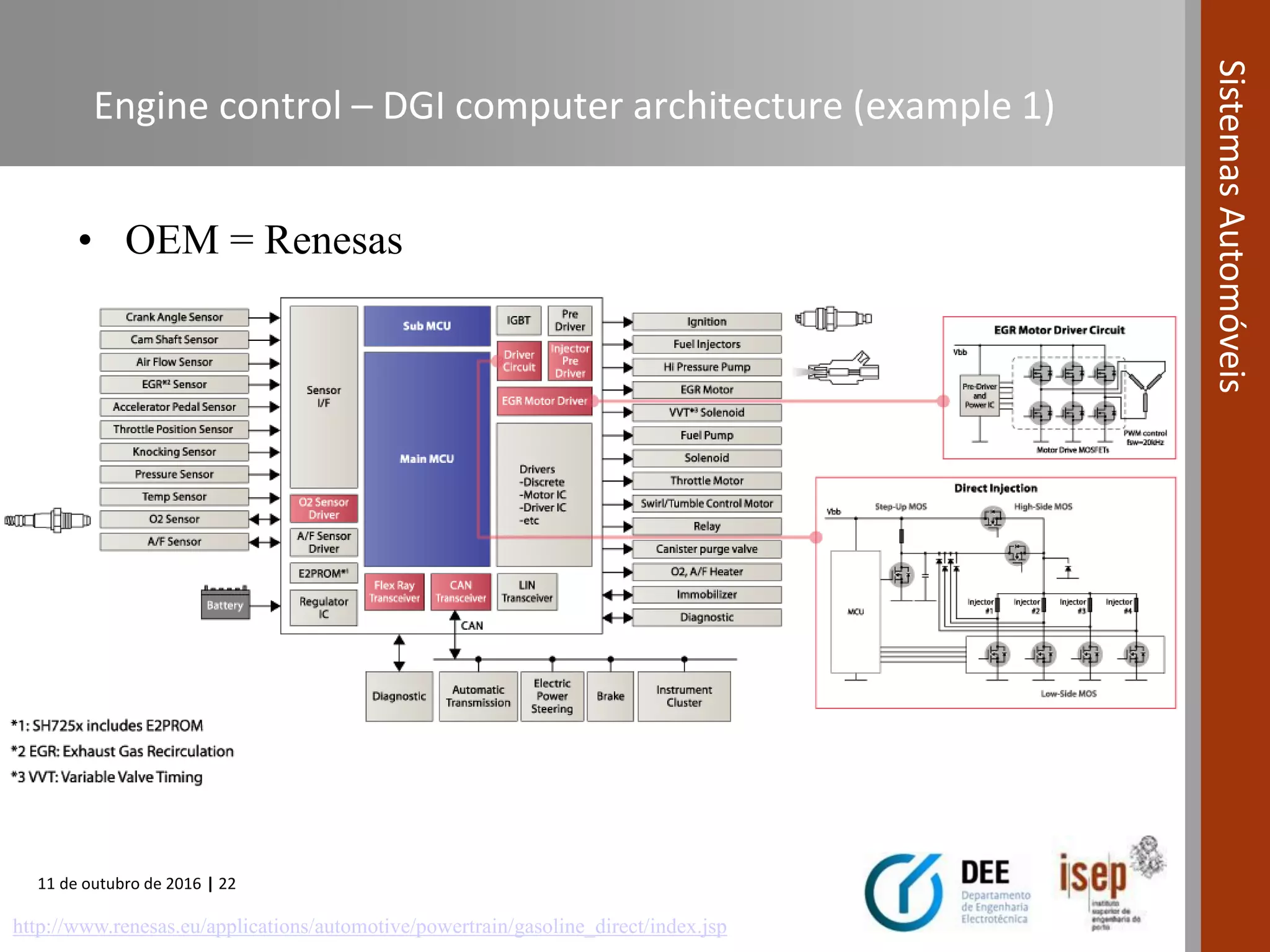
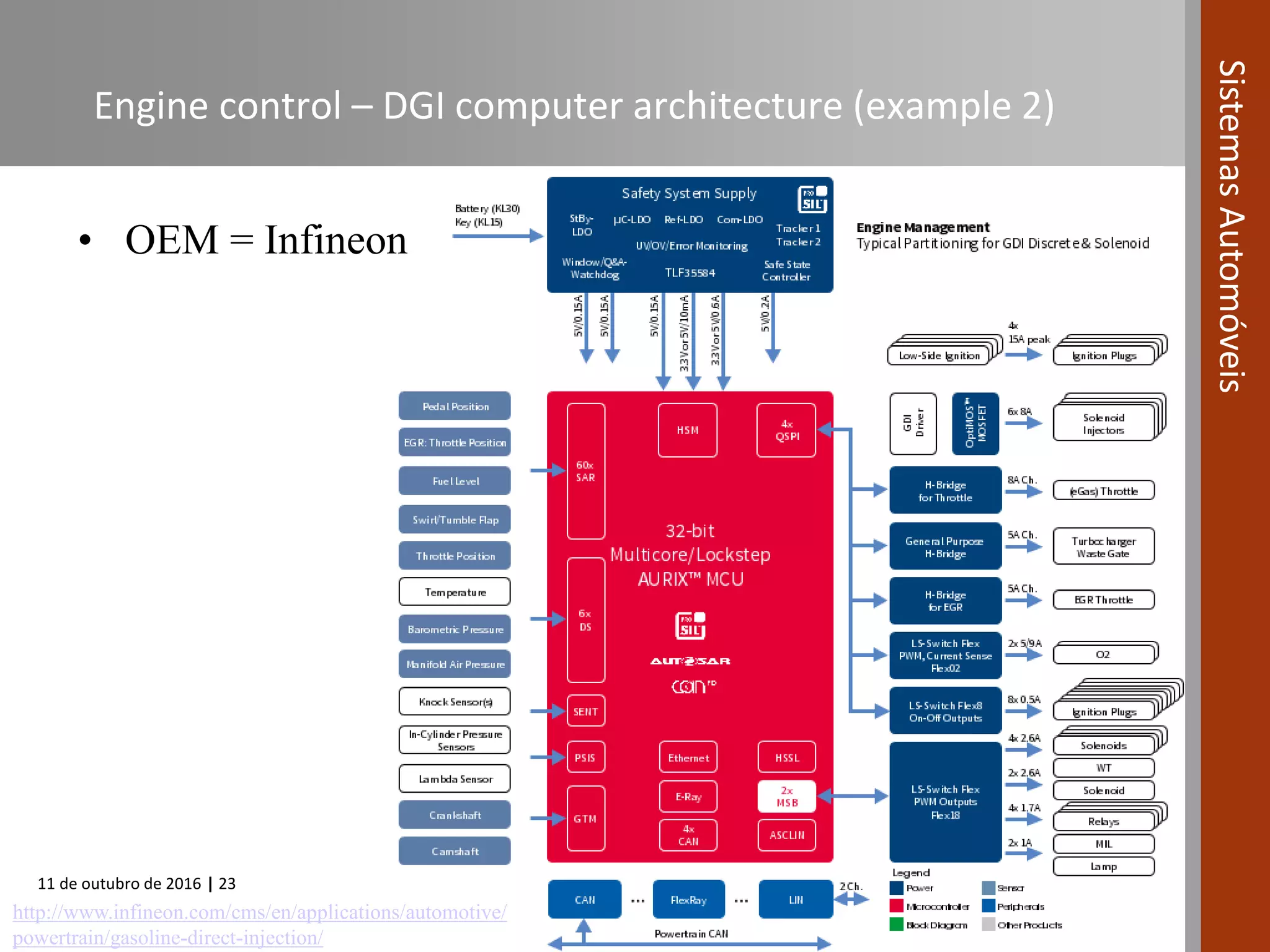
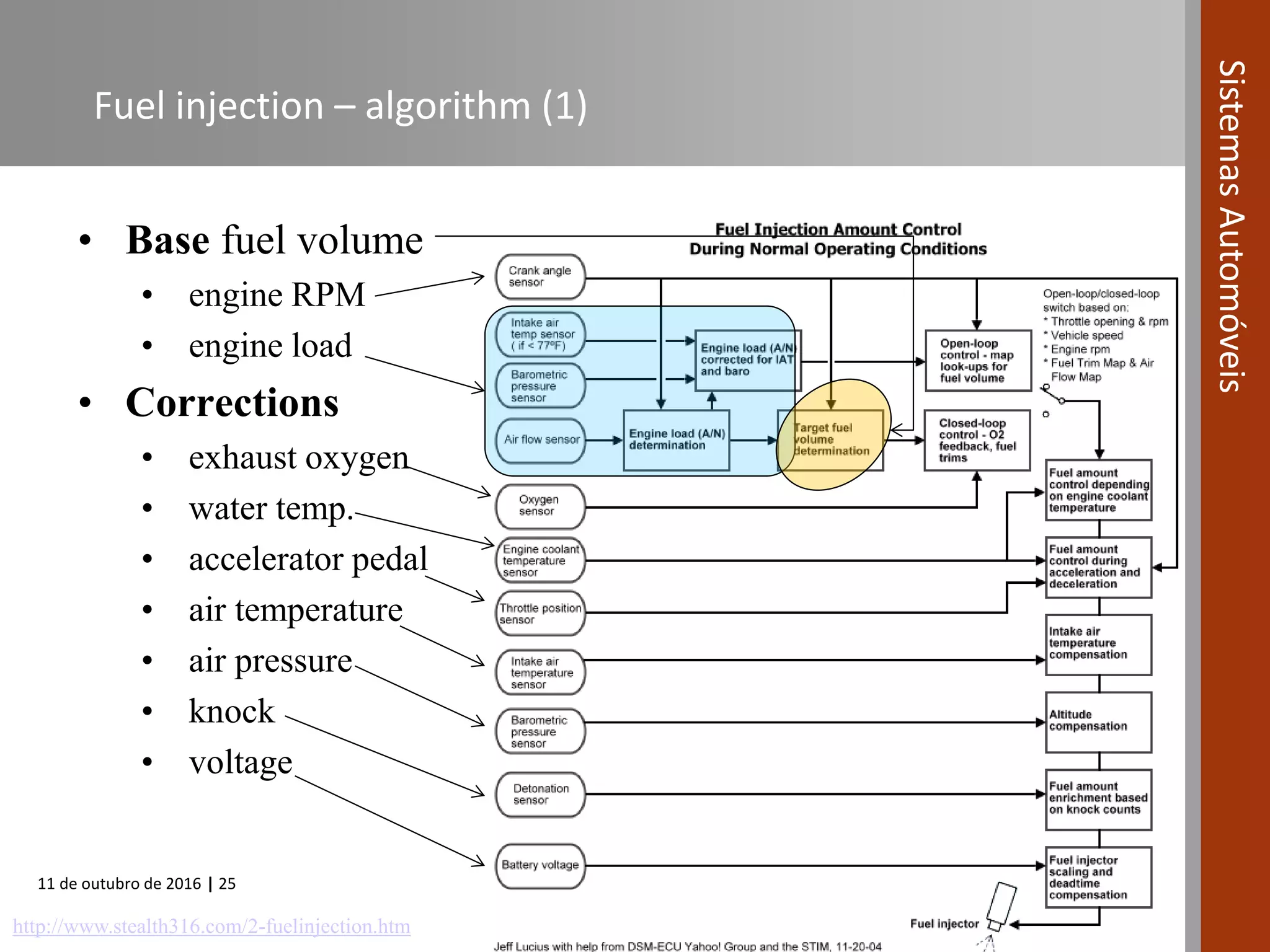
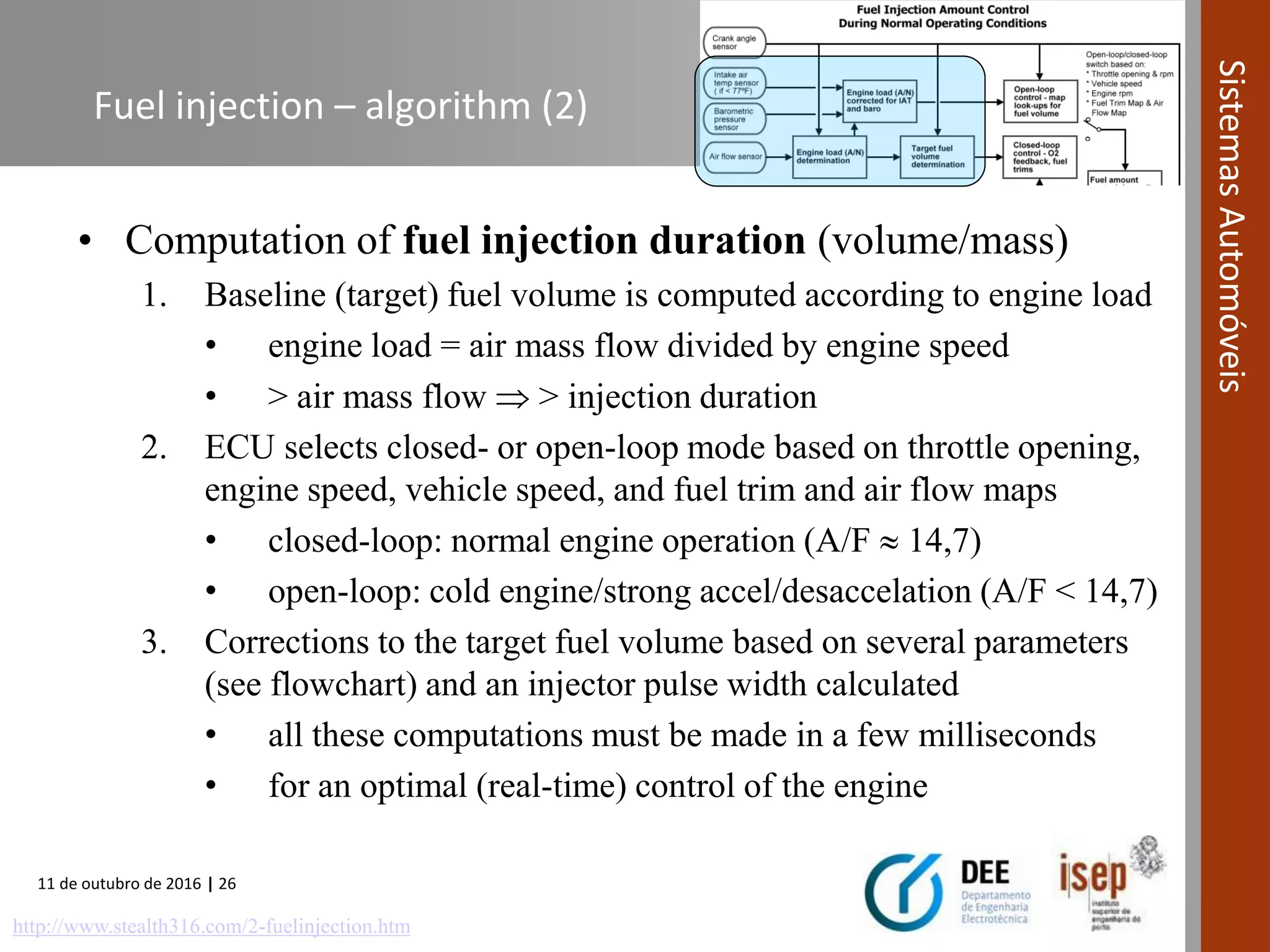
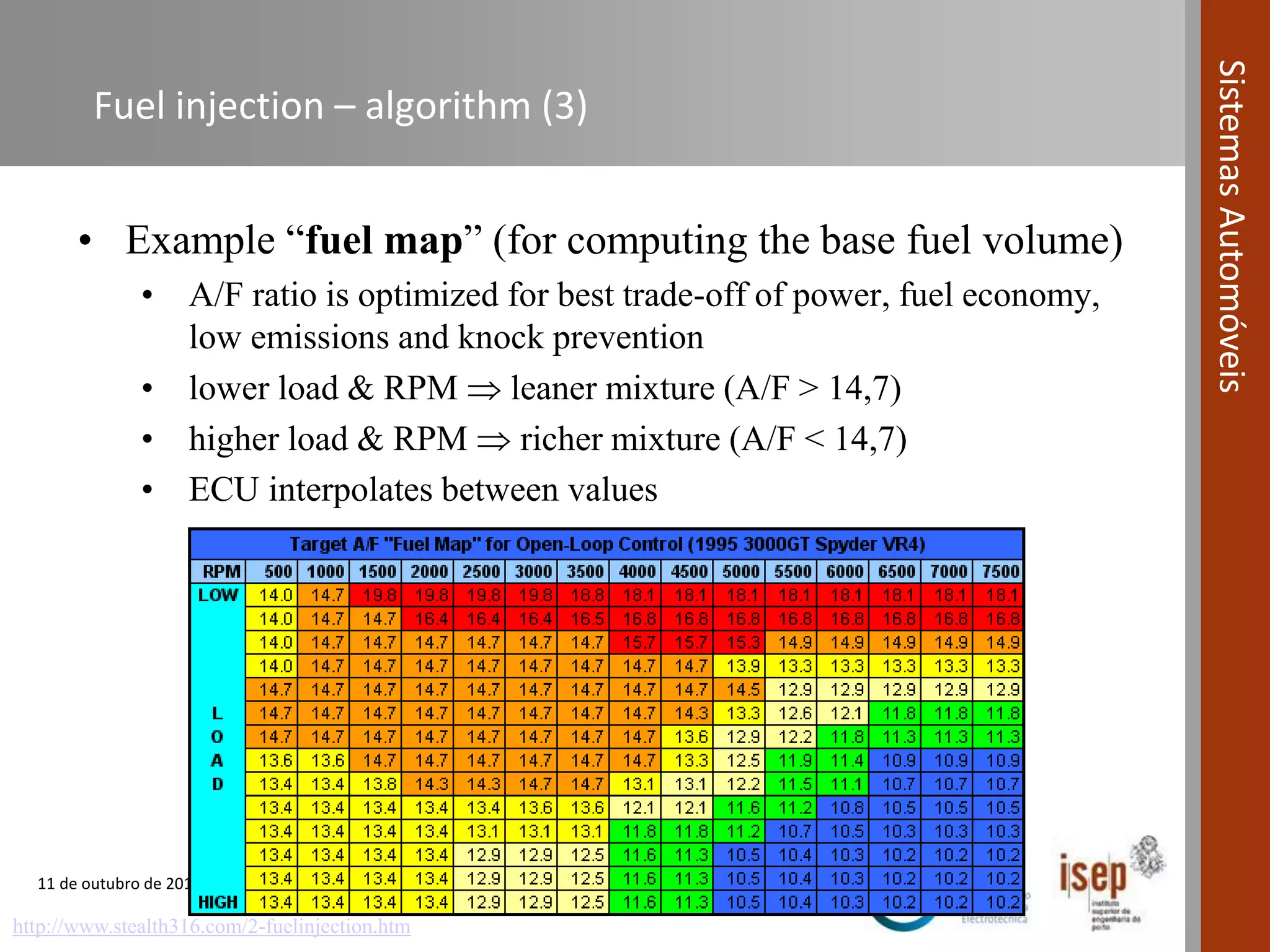
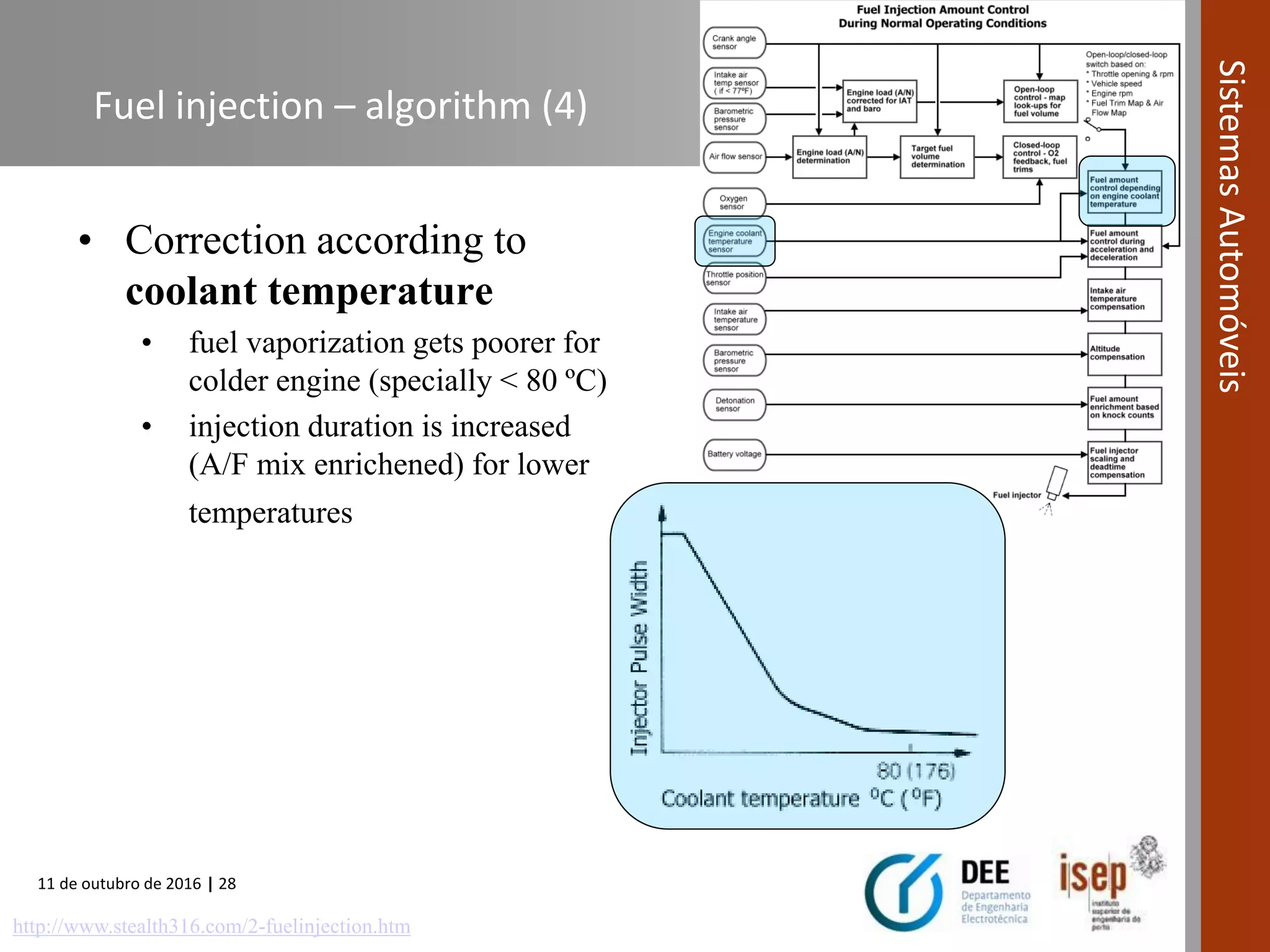
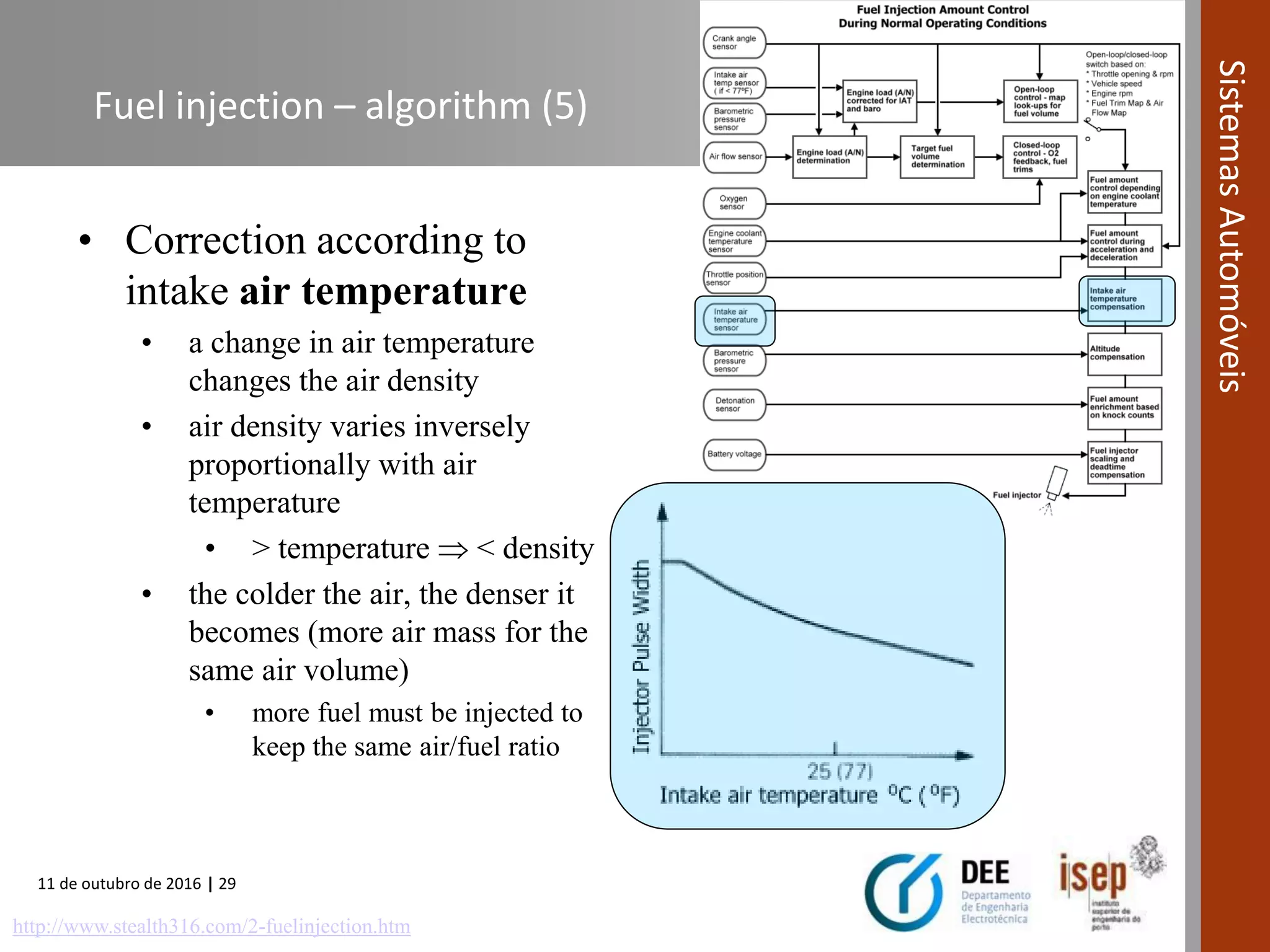
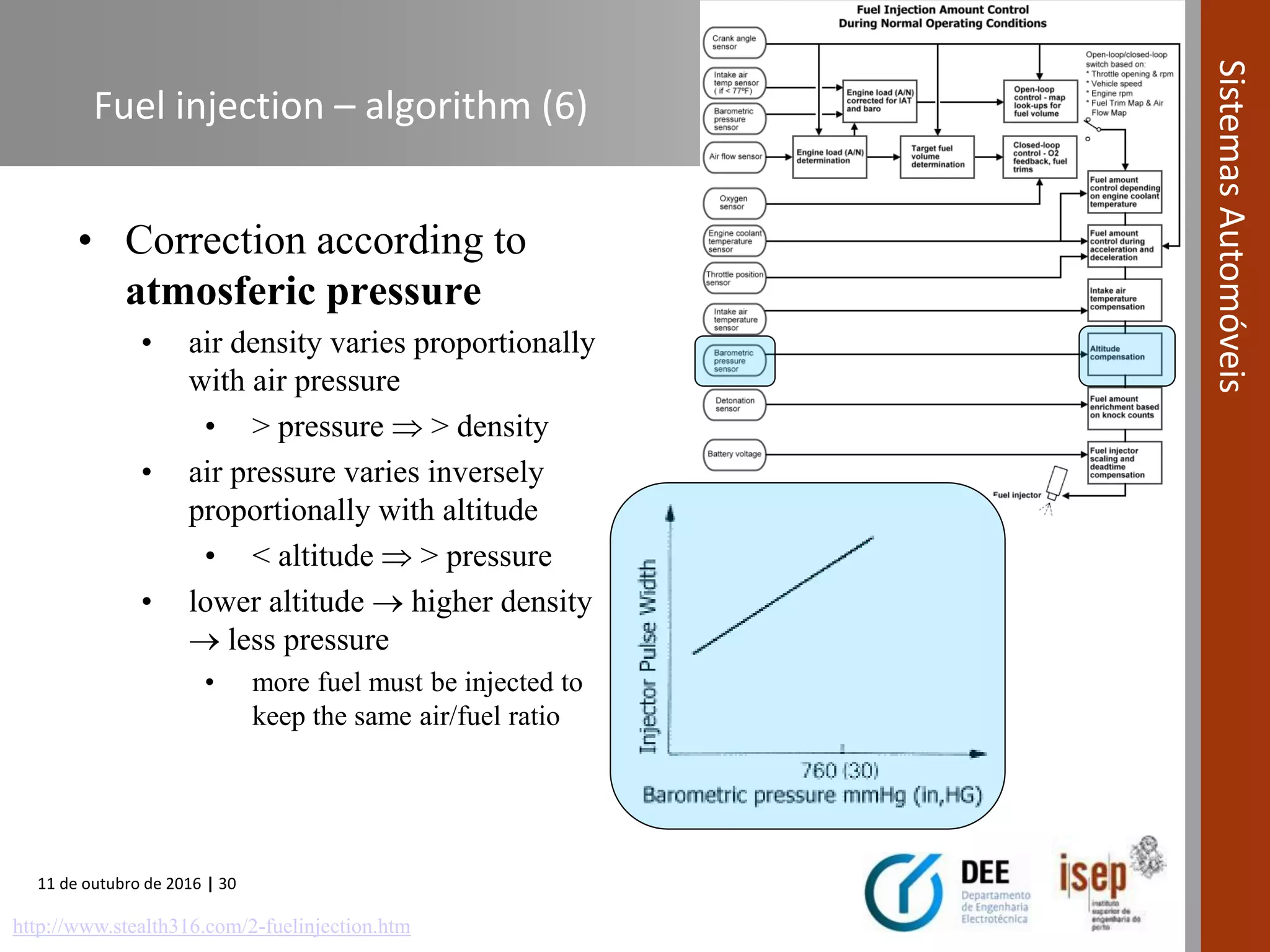
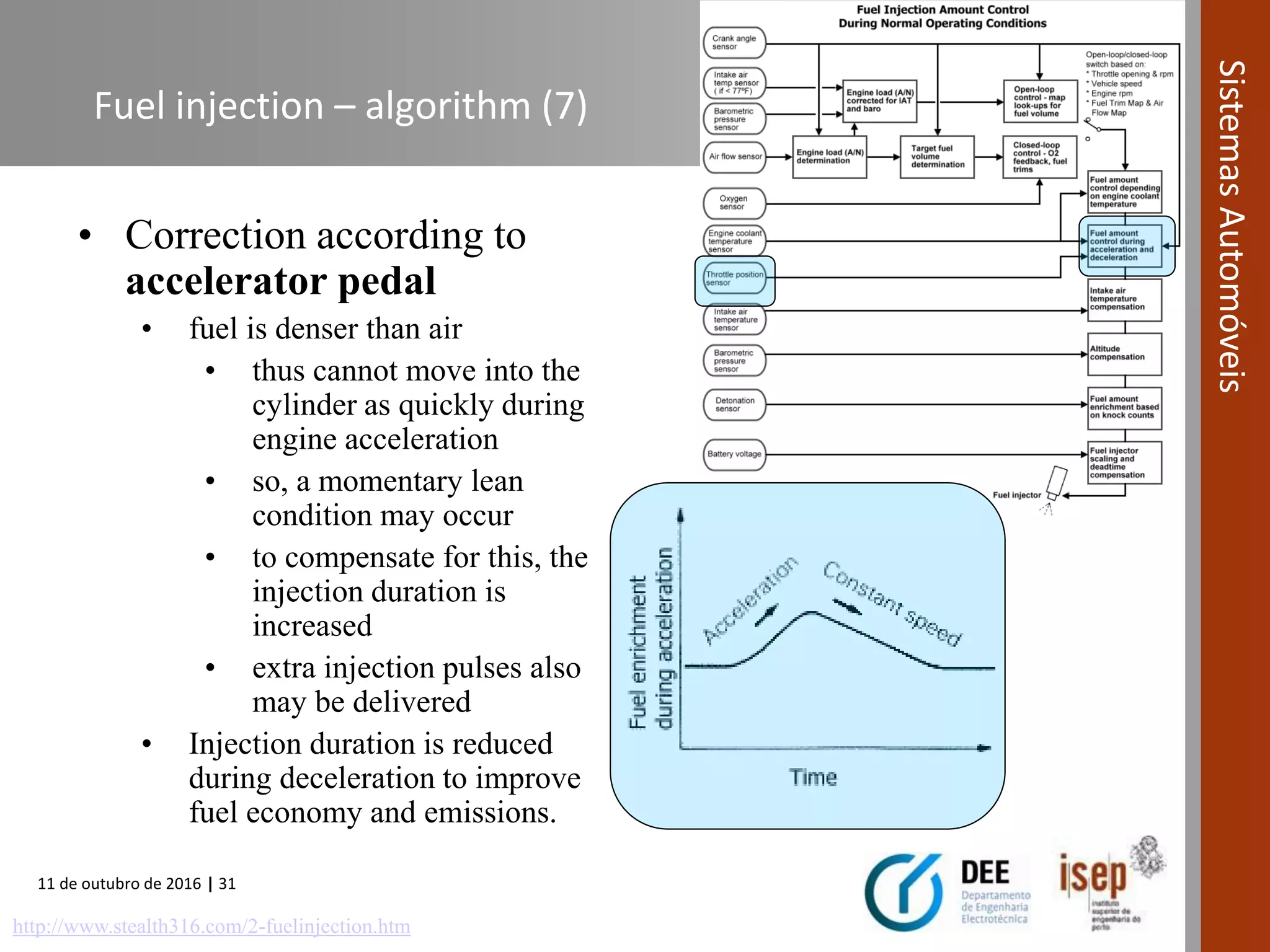
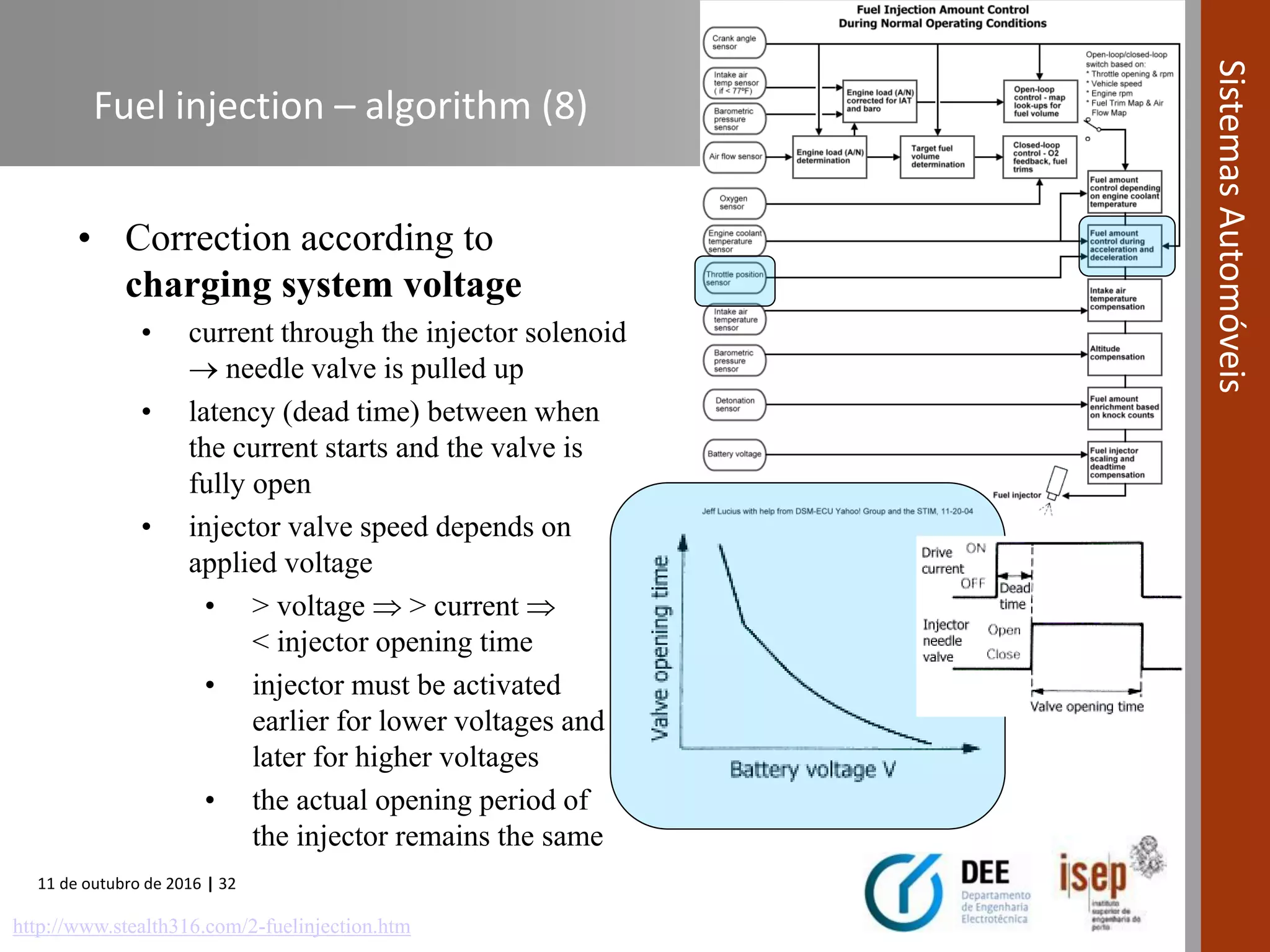
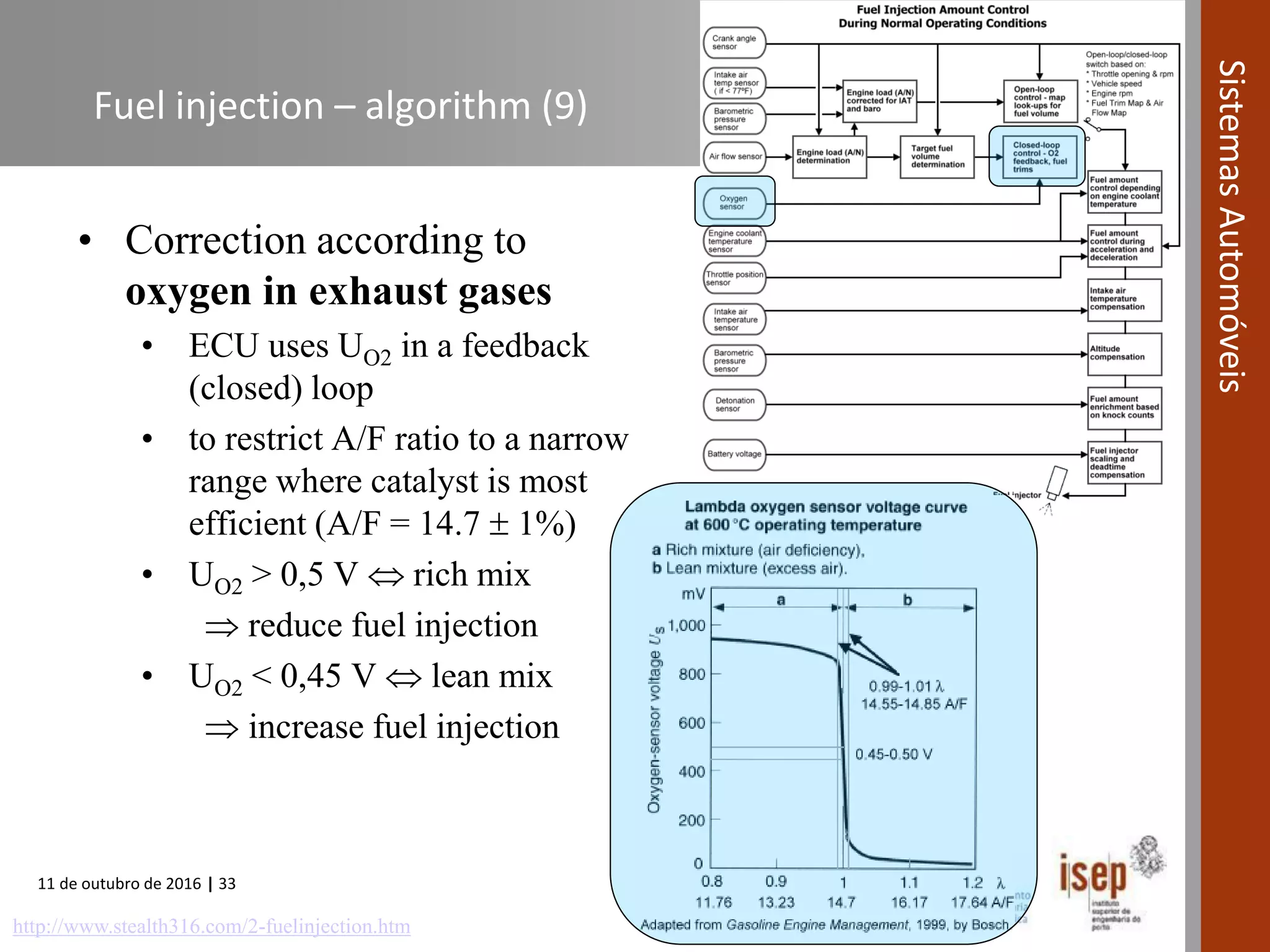
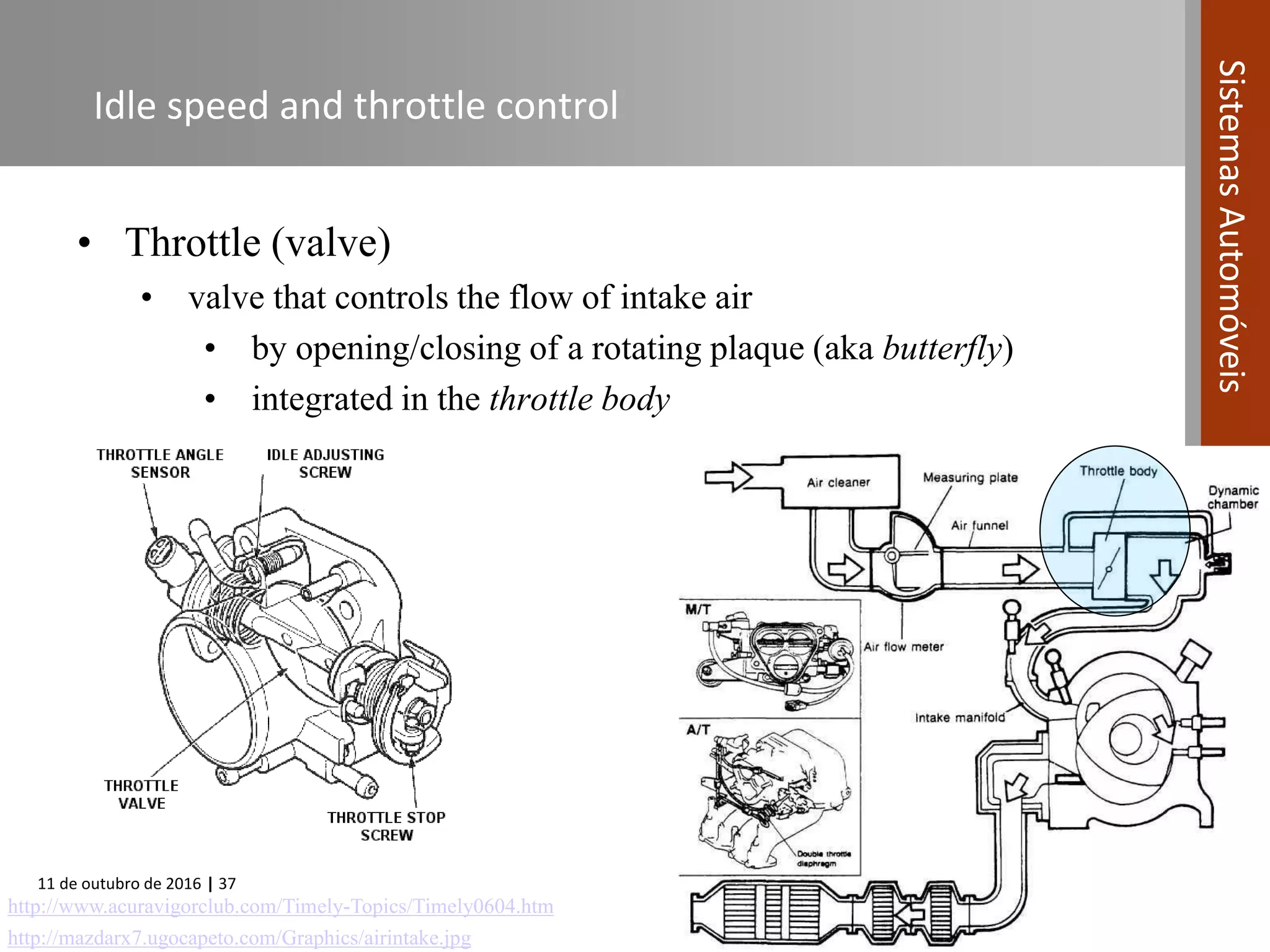
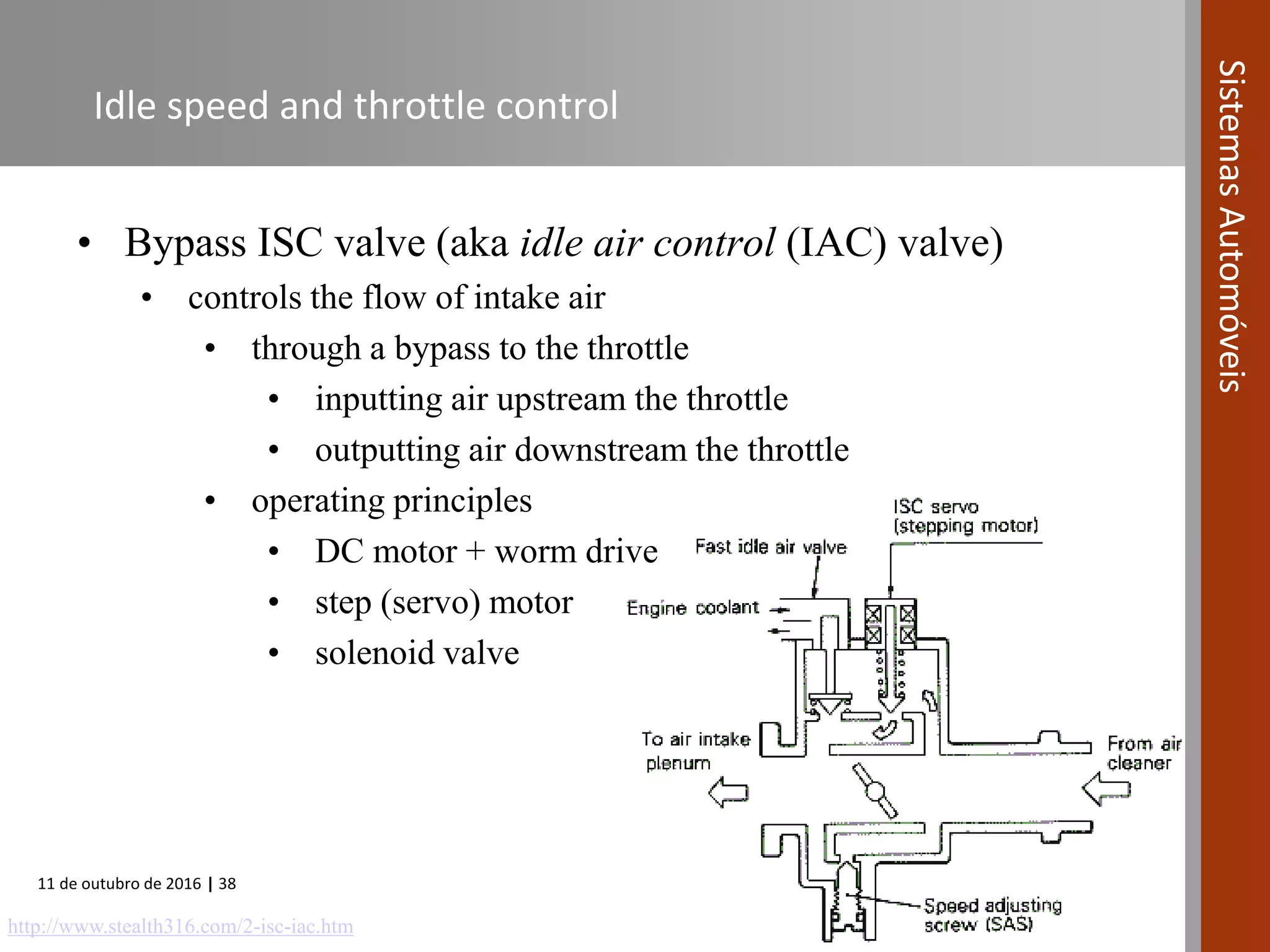
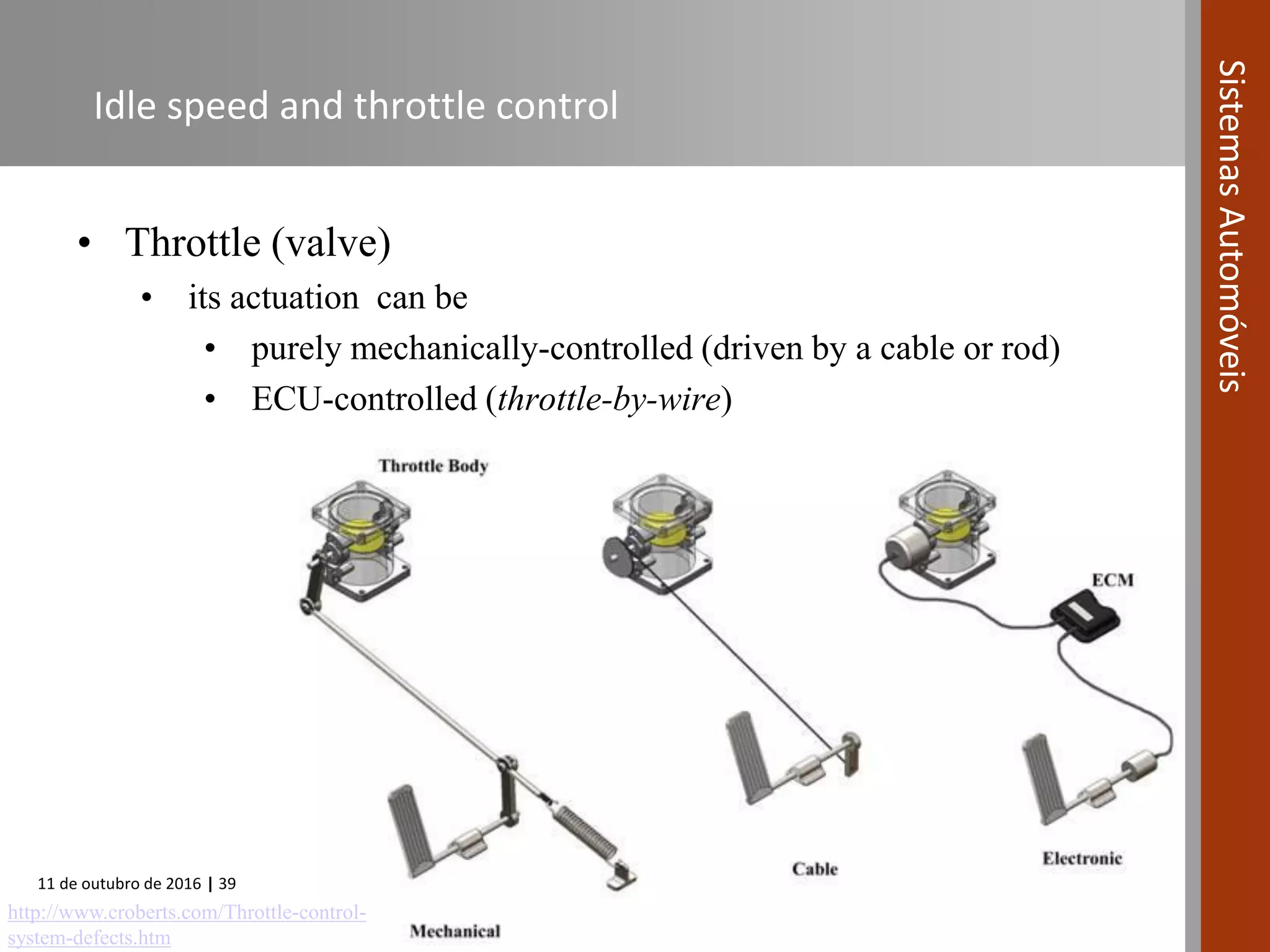
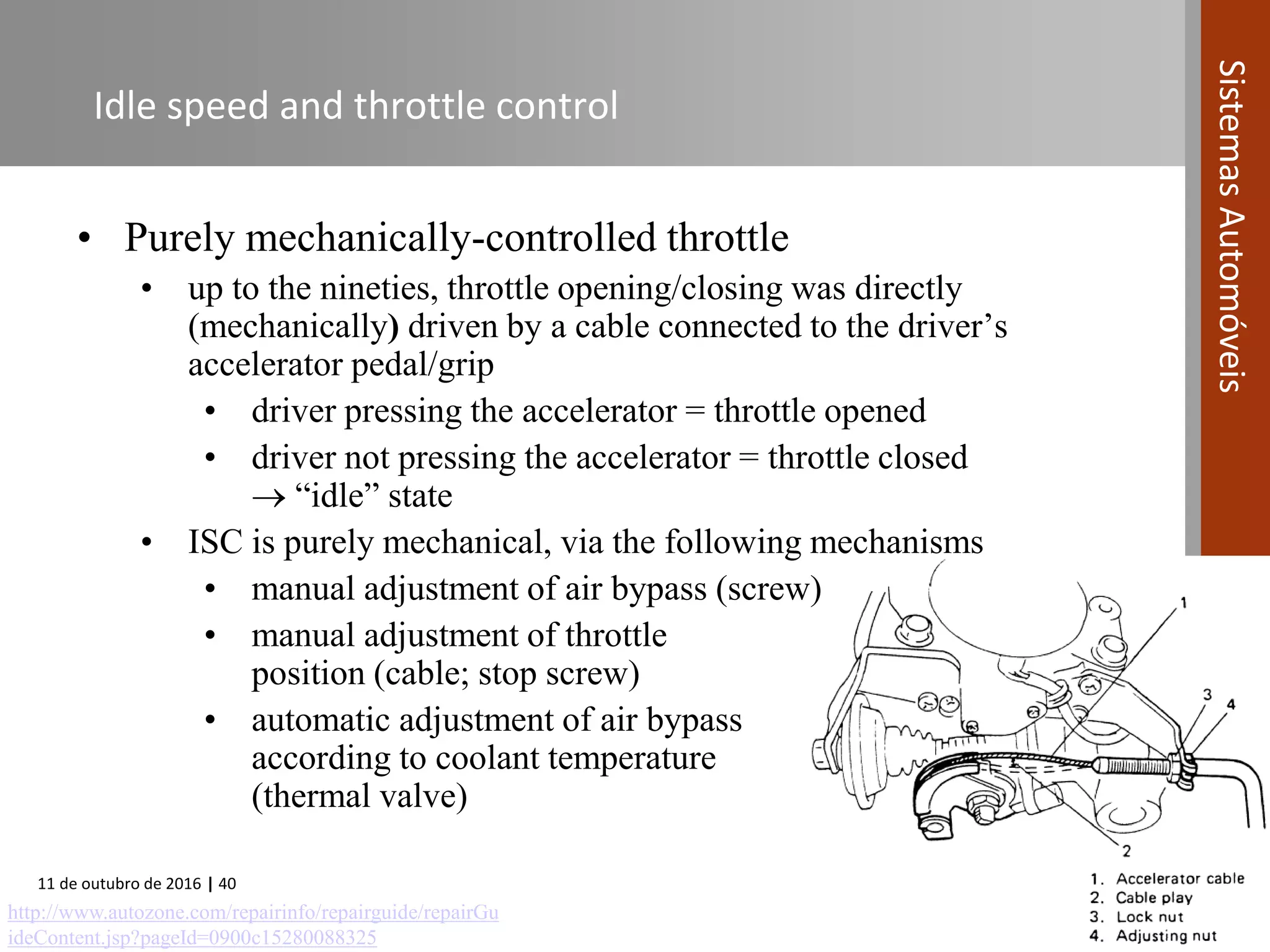
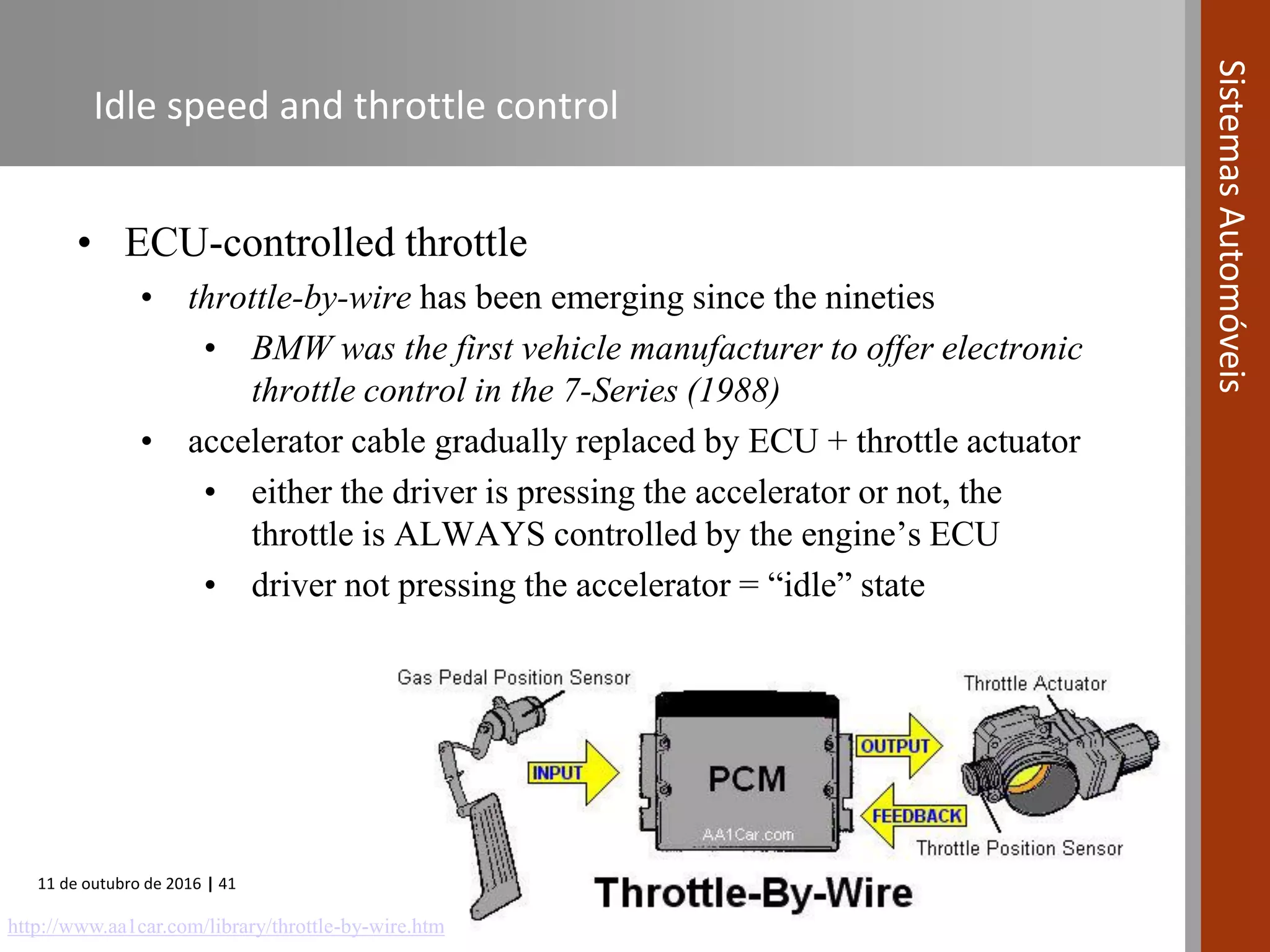
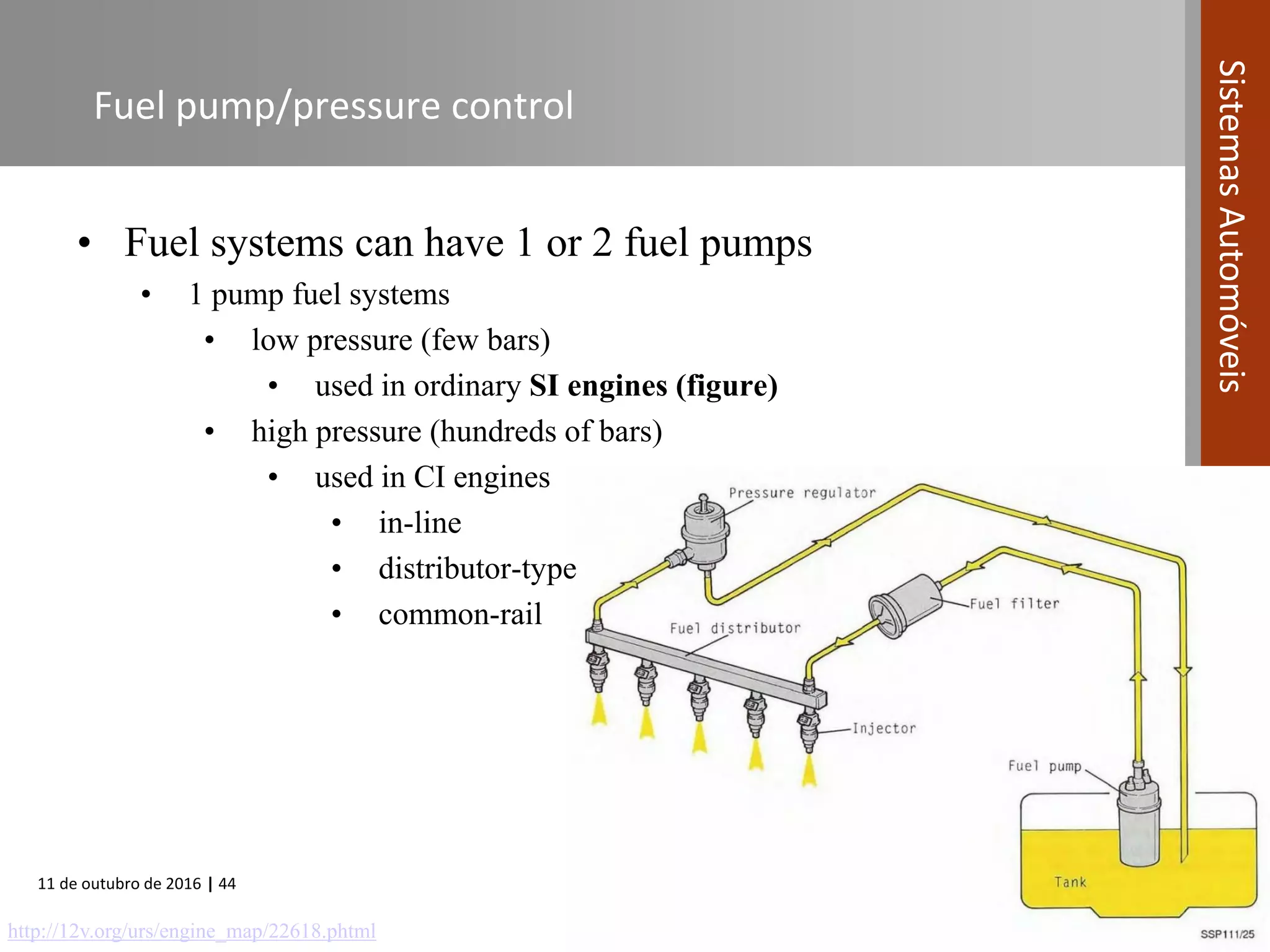
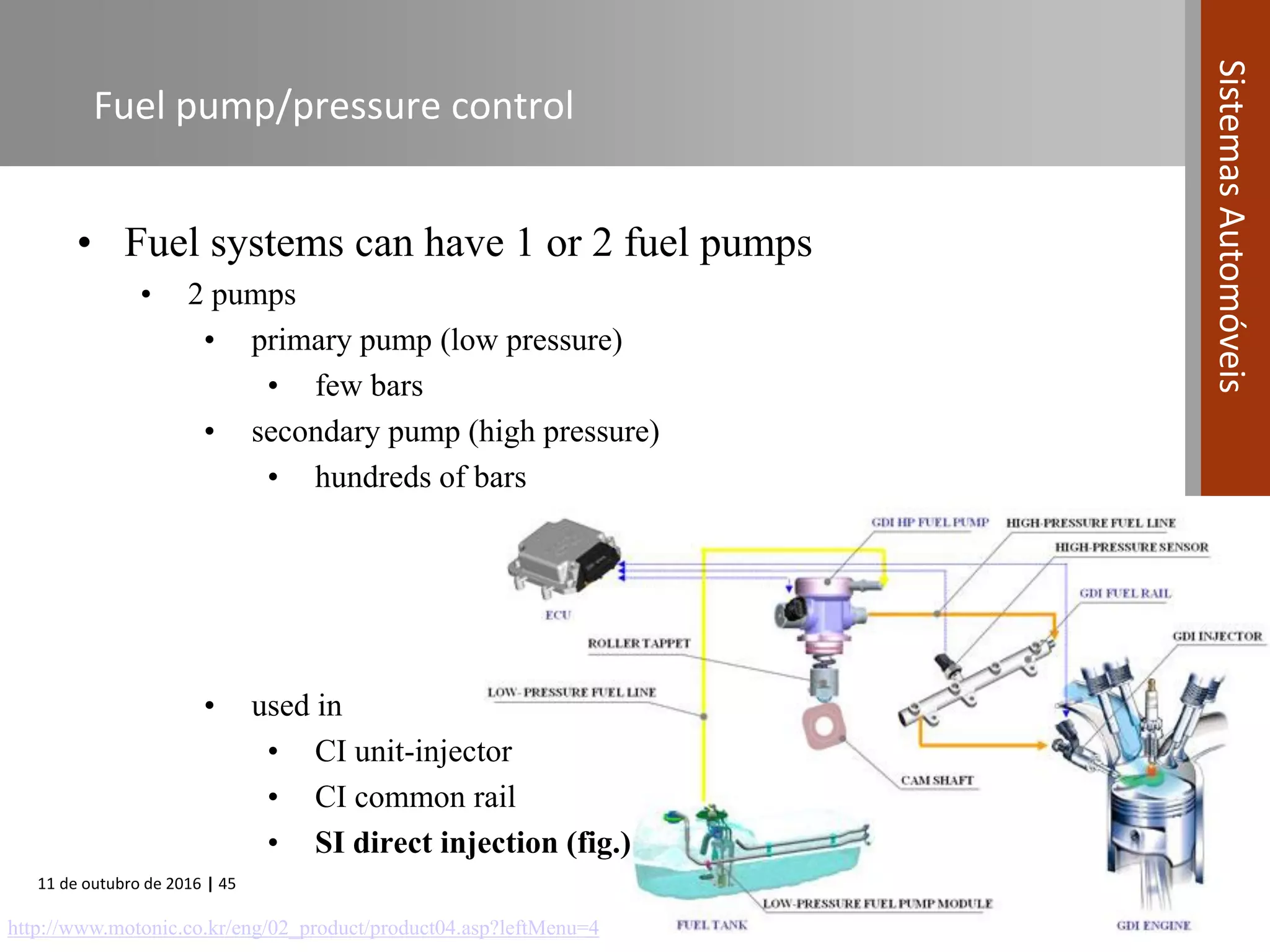
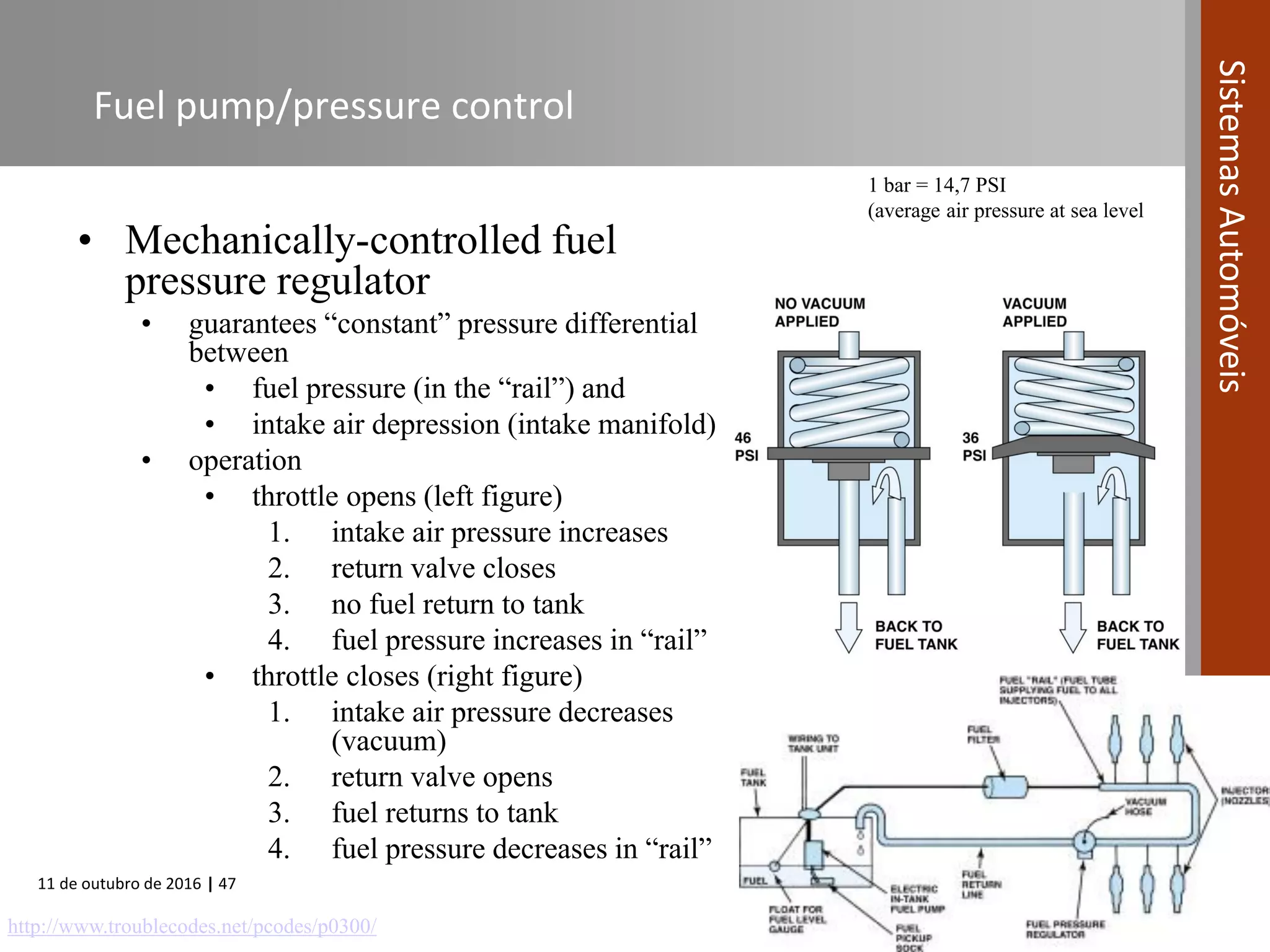
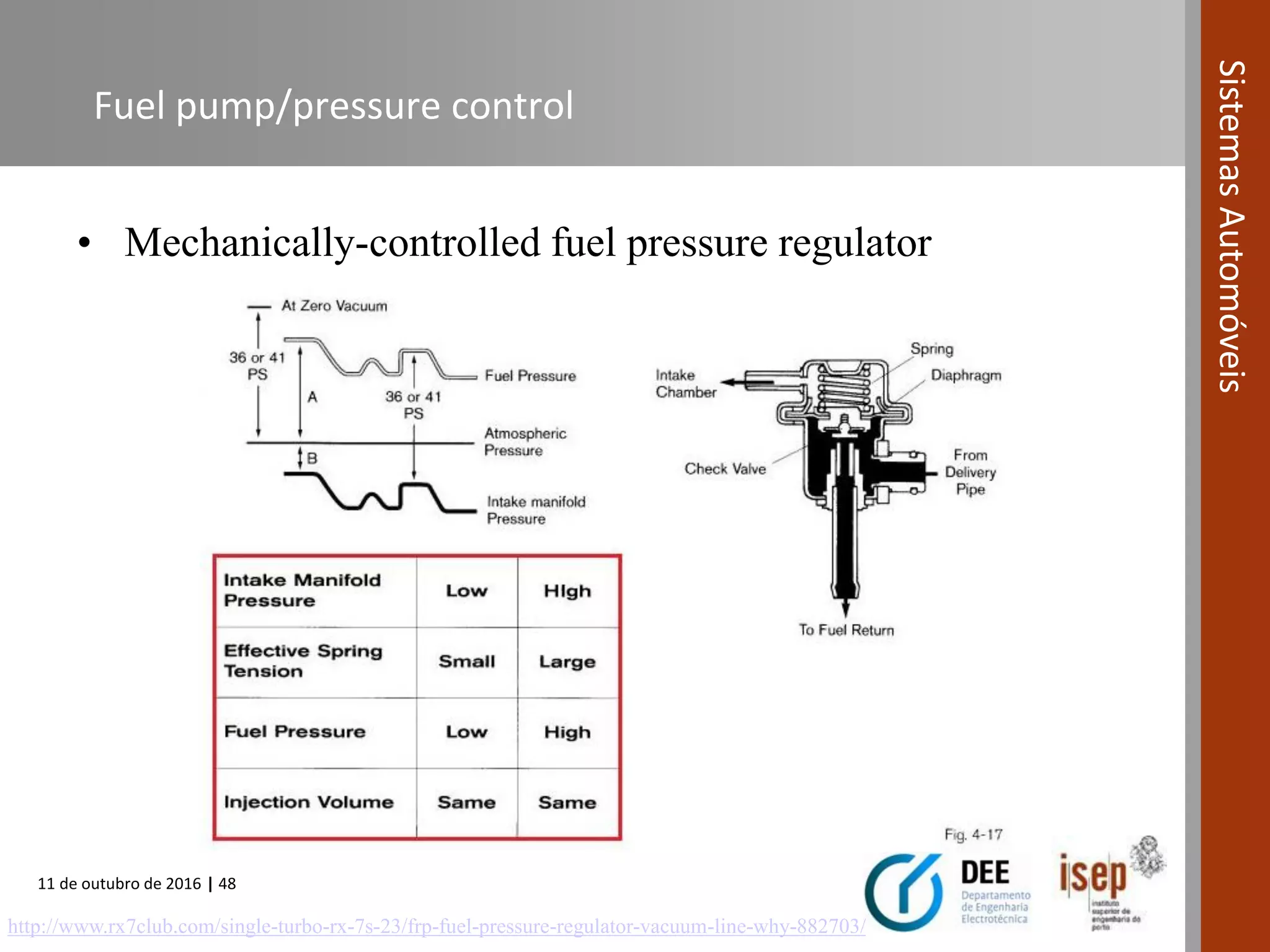
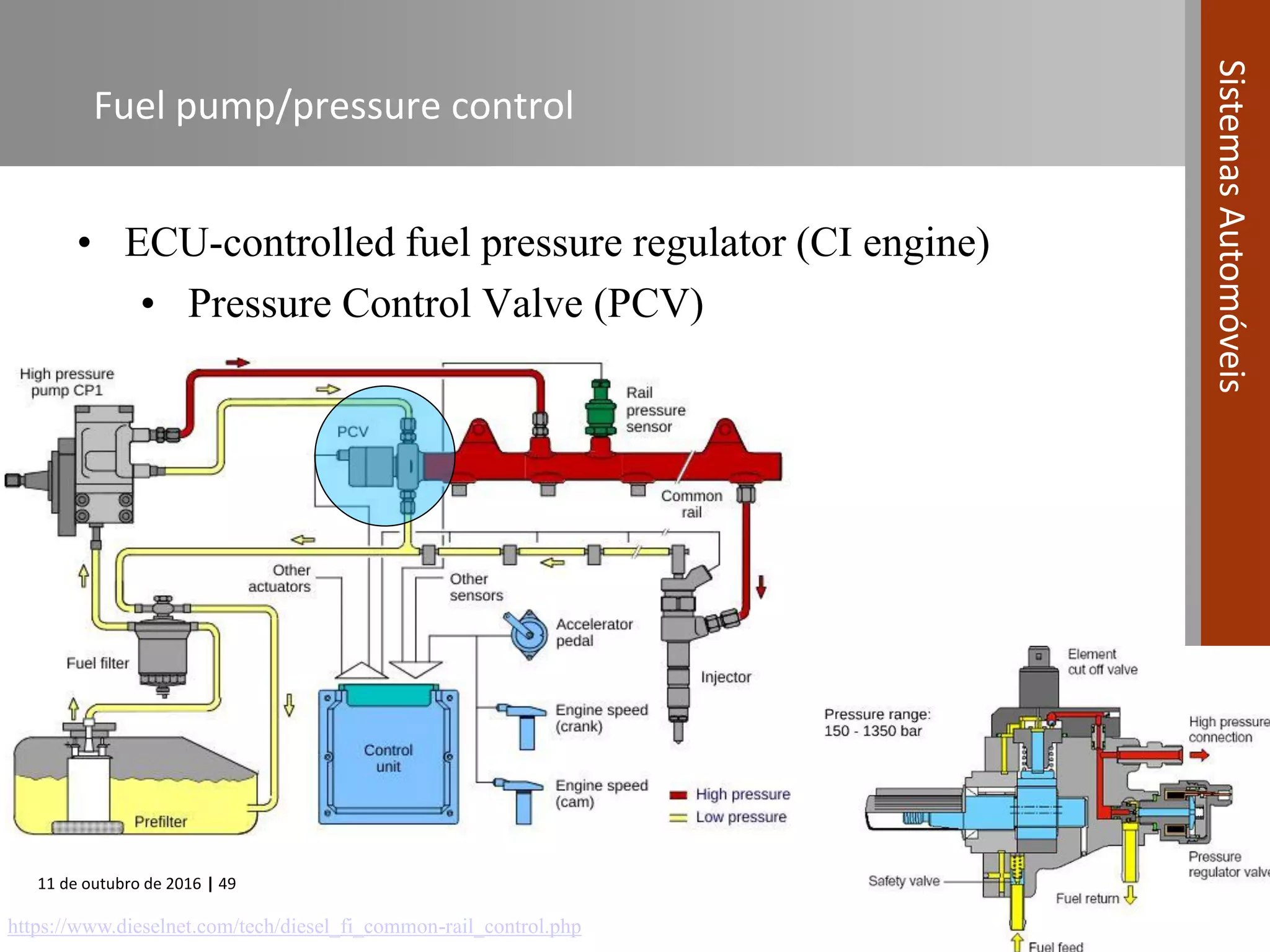
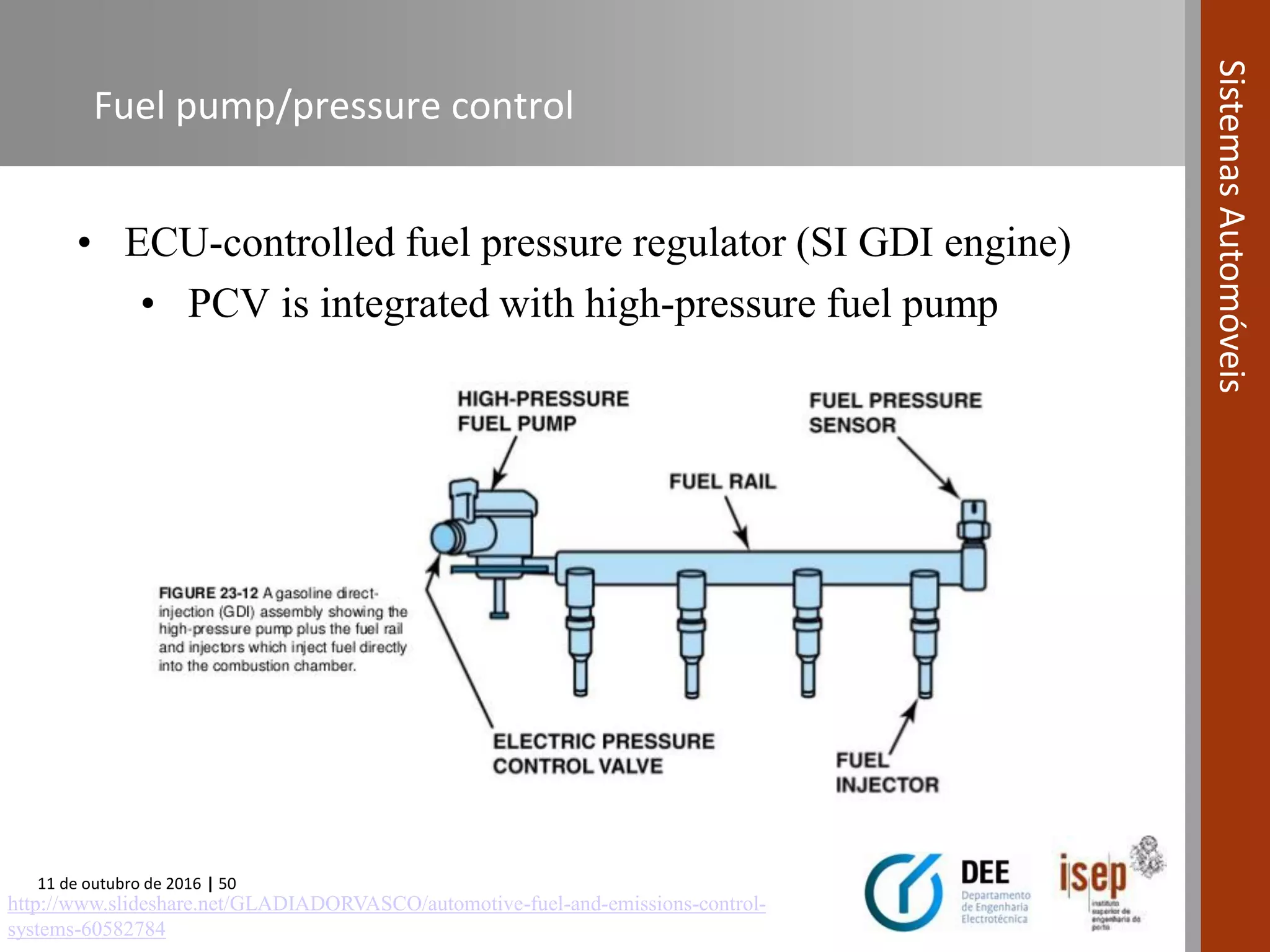
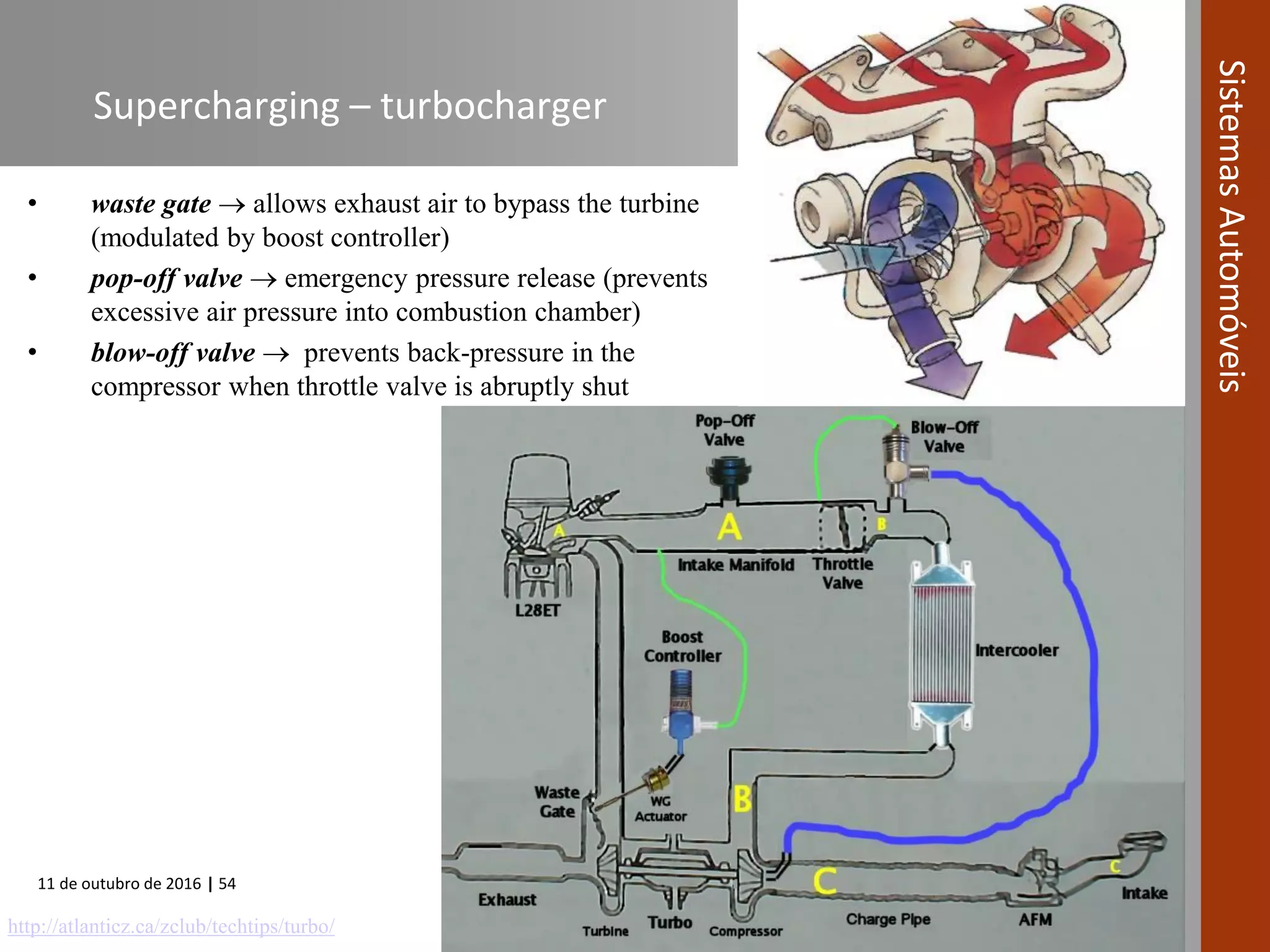
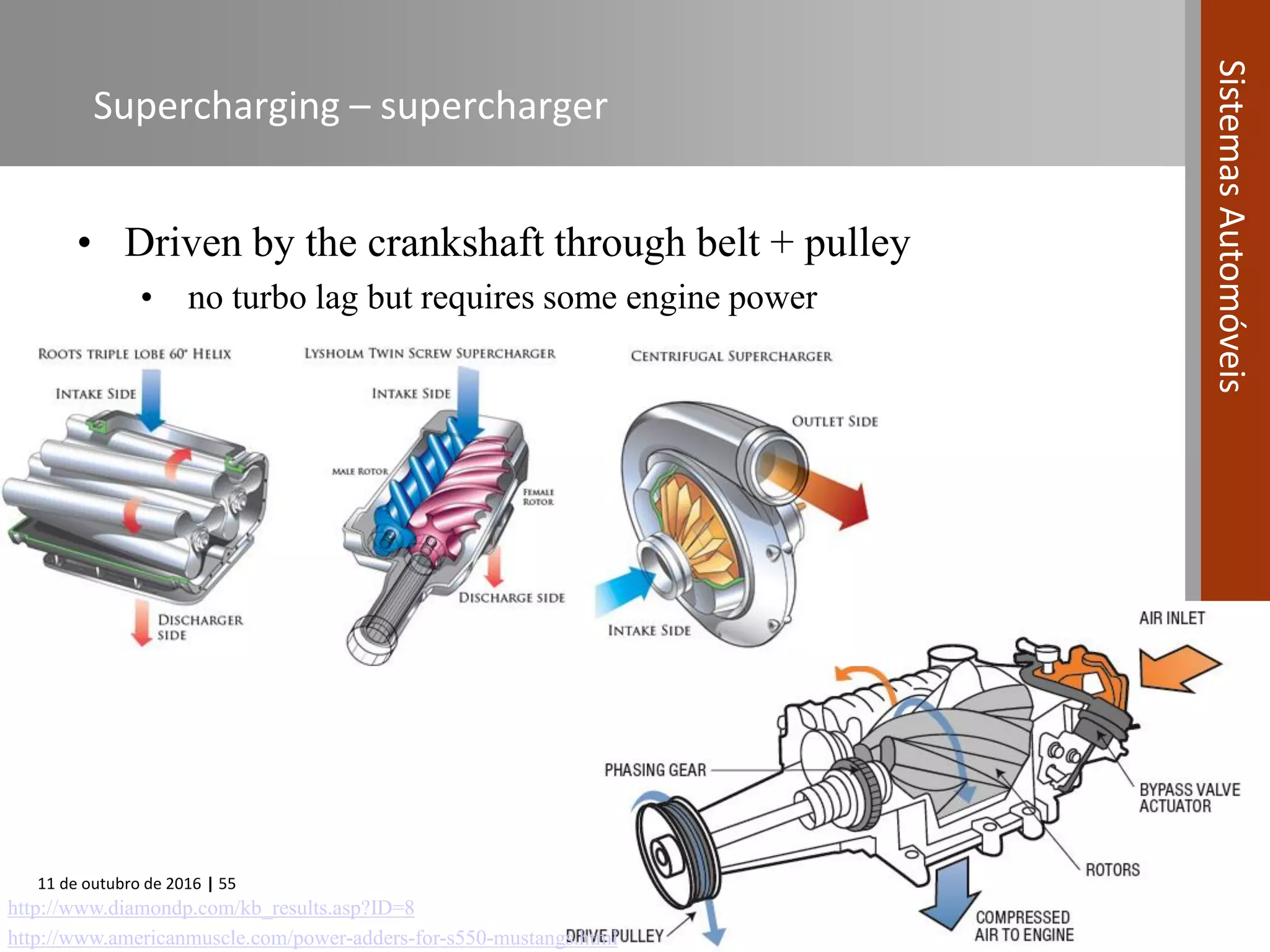
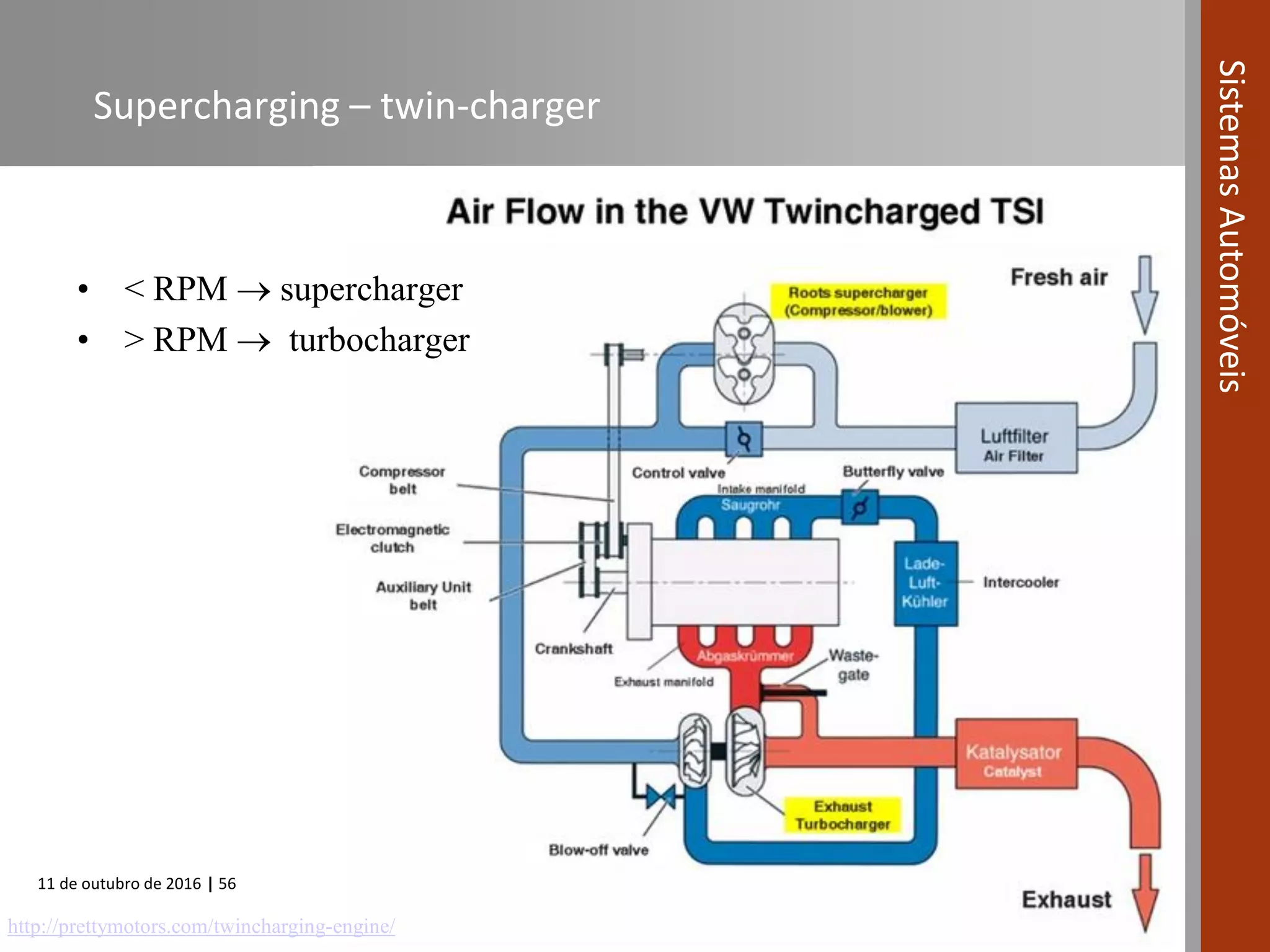
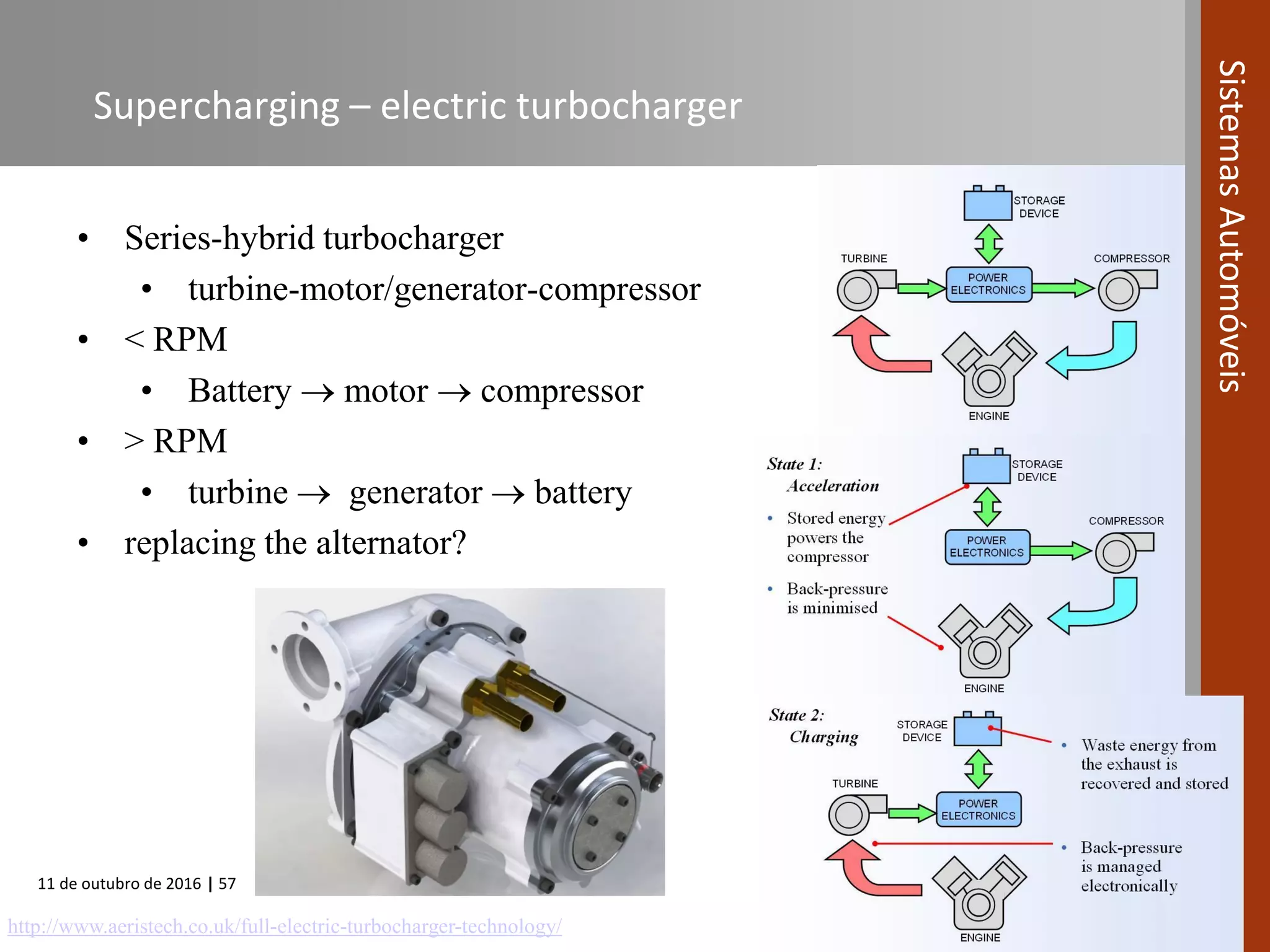
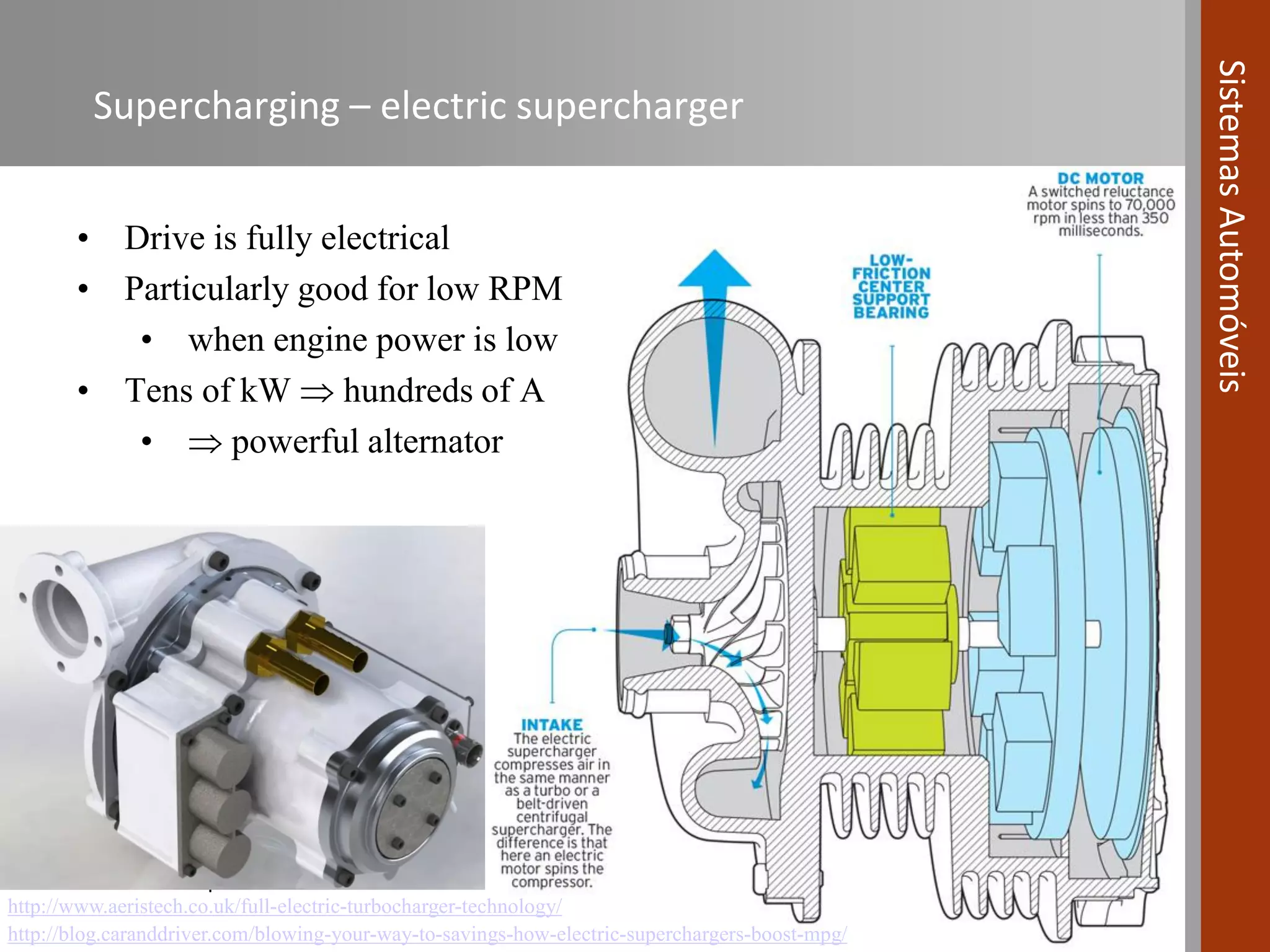
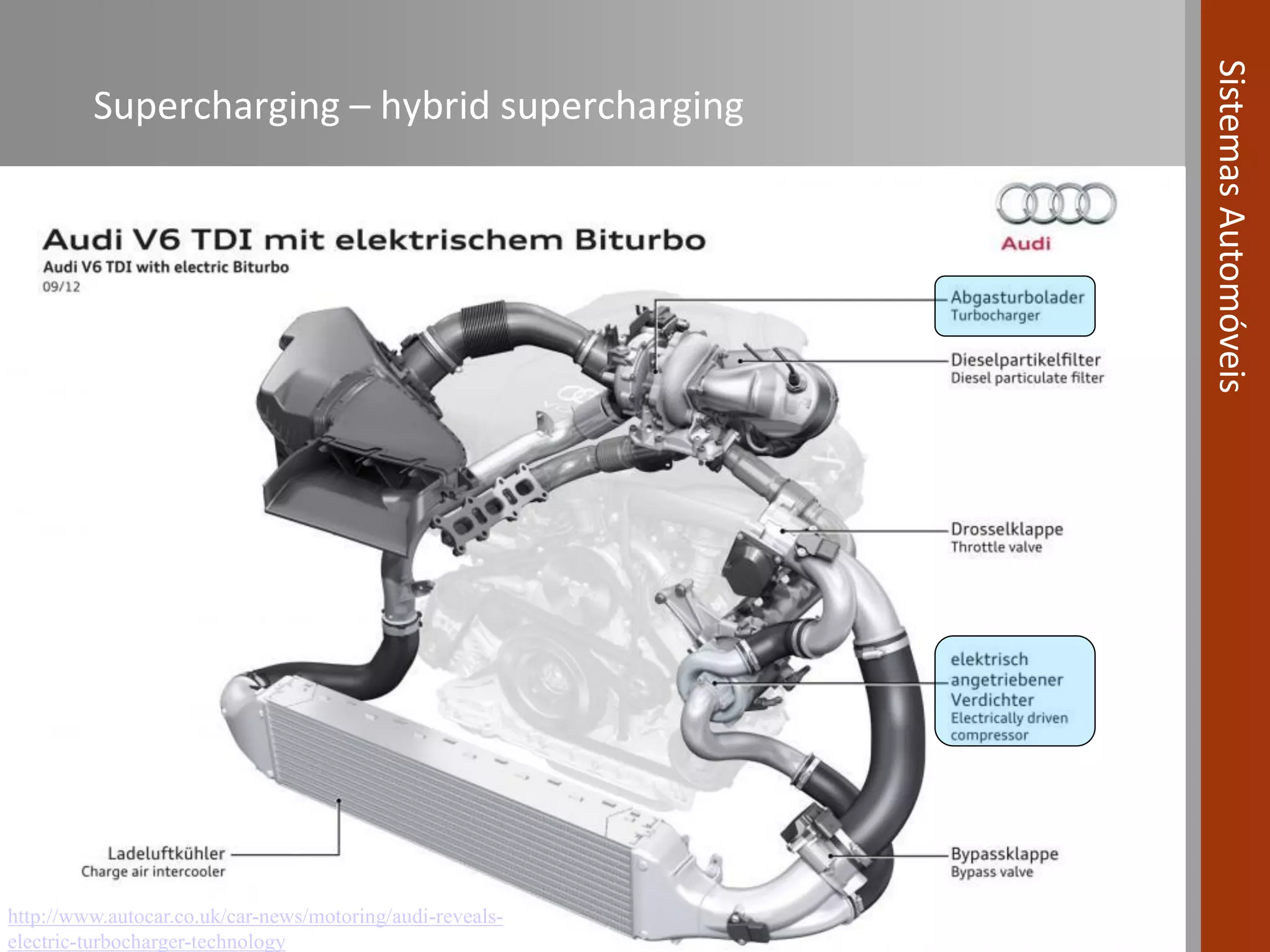
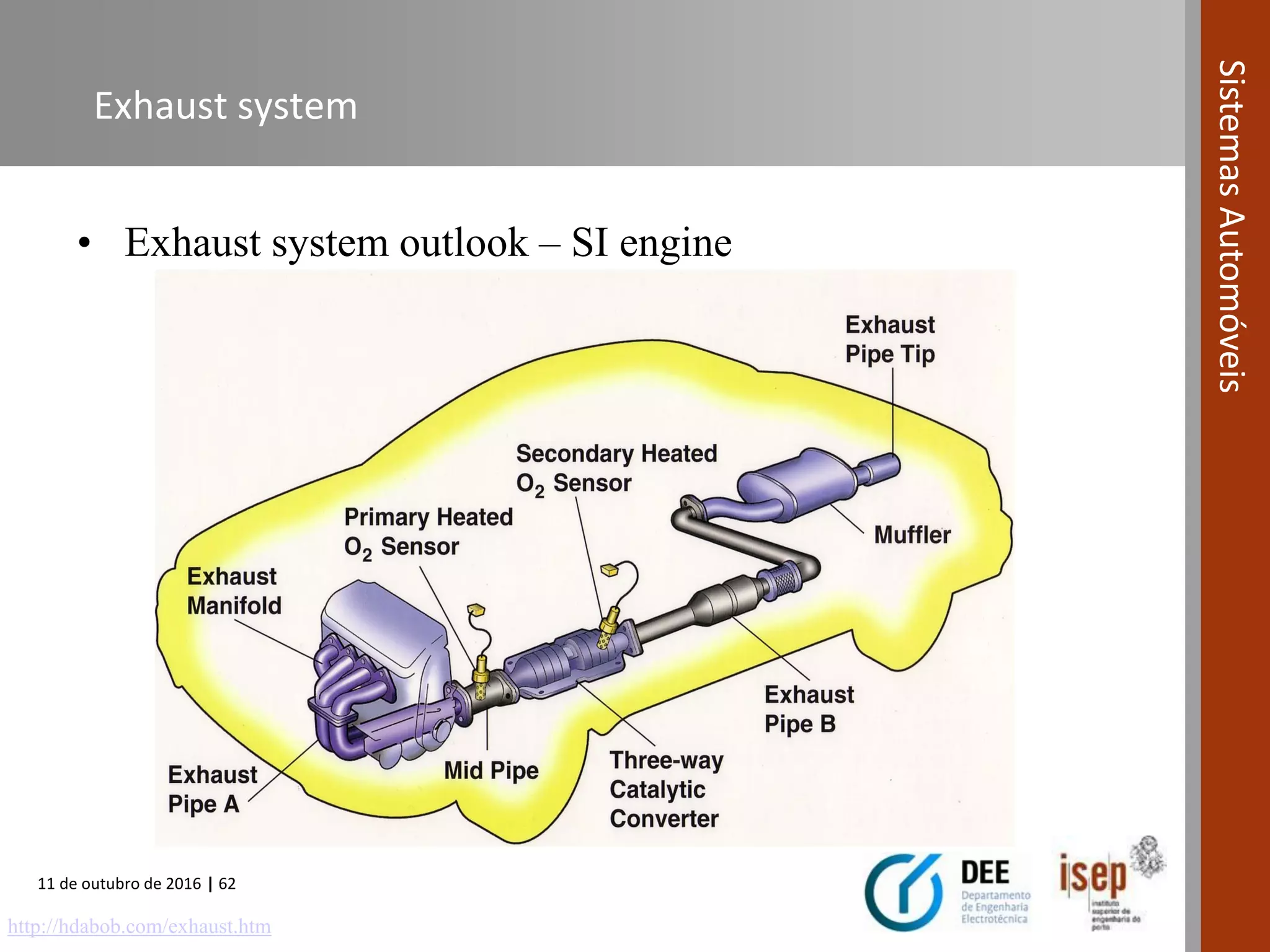
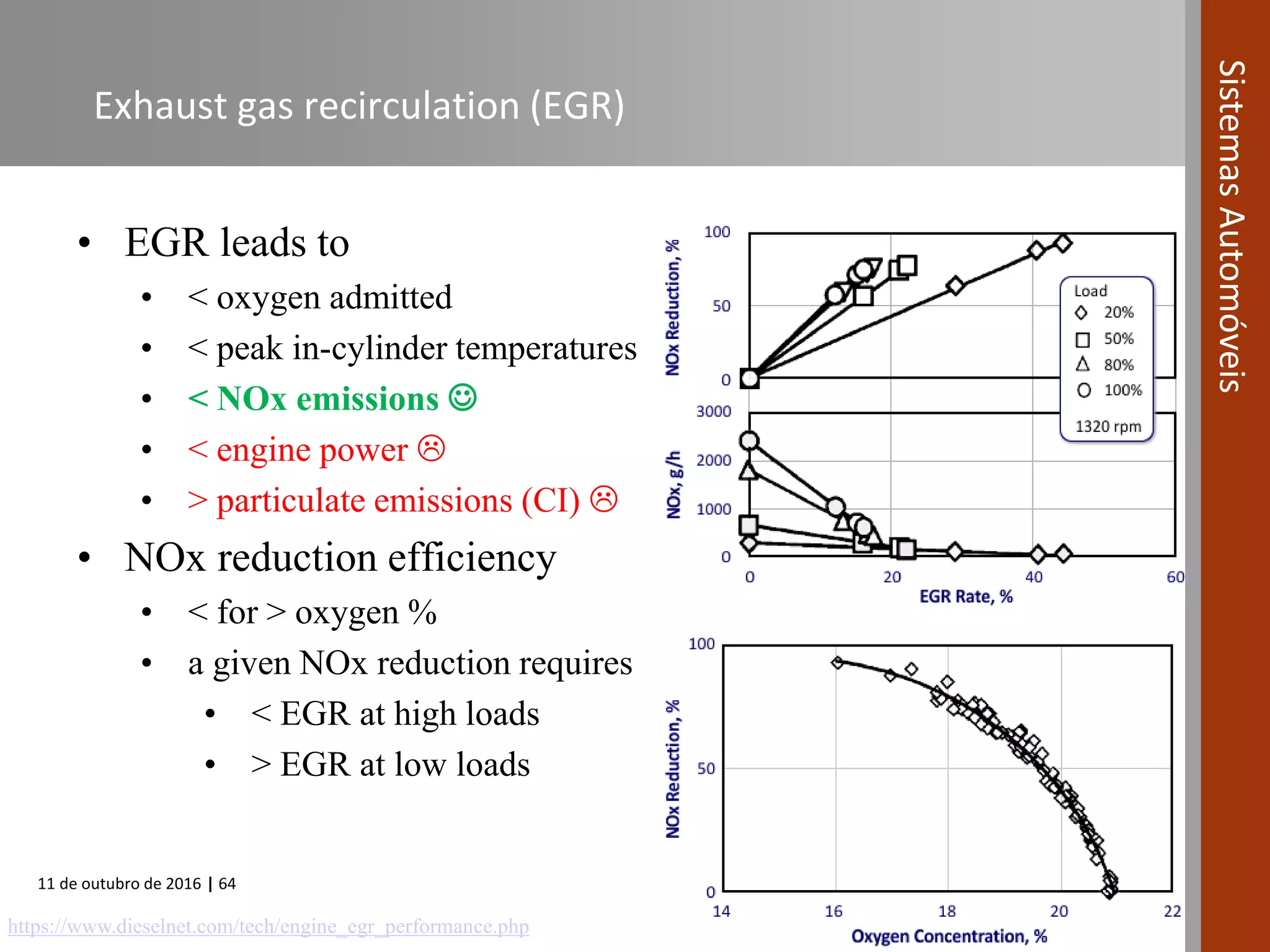
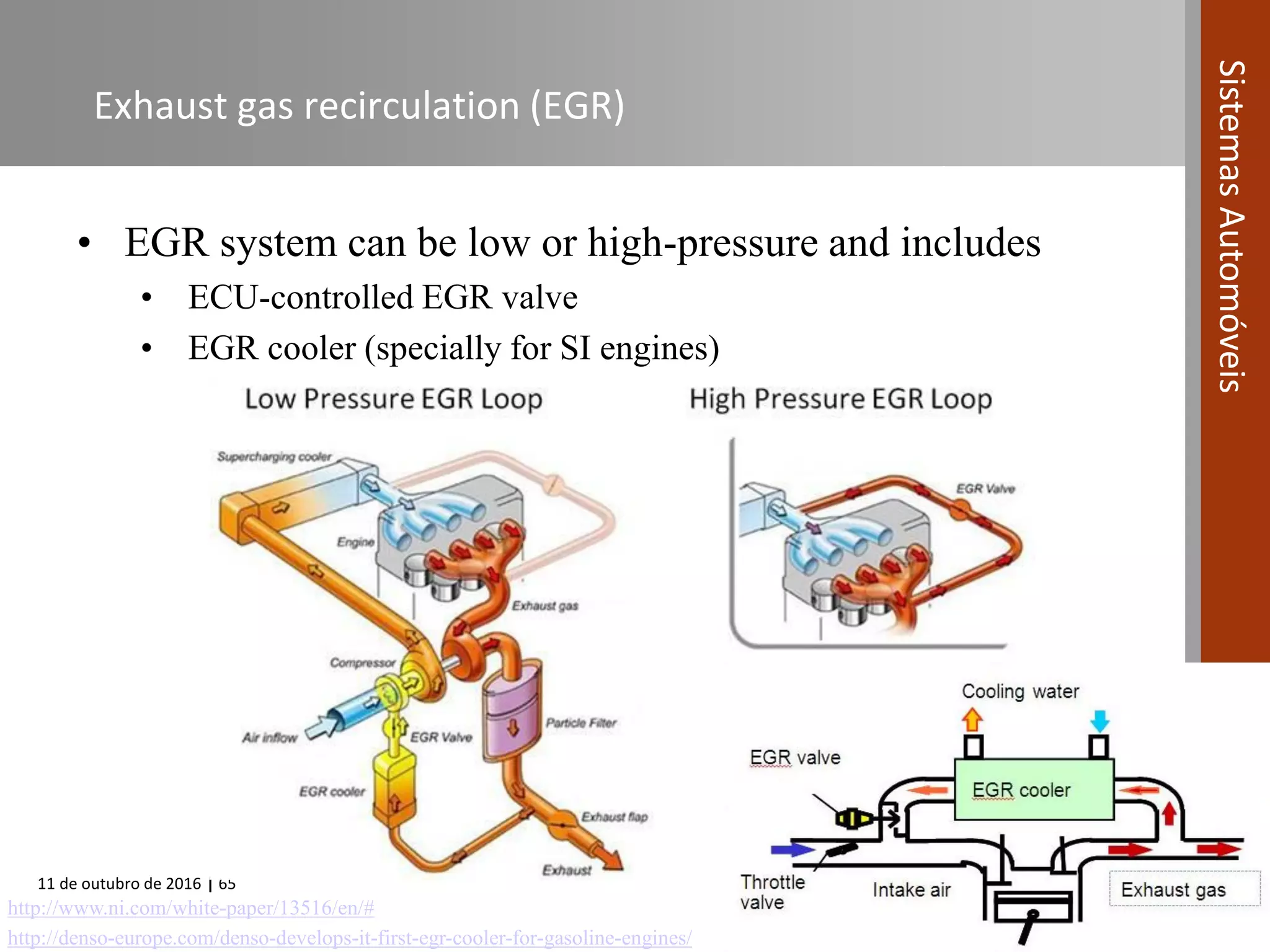
The document covers various fuel systems used in internal combustion engines, including carburetor-based and electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems. It discusses the evolution of fuel injection technologies, their classifications, and engine control fundamentals. The primary objectives outlined include optimizing fuel delivery for performance, emissions reduction, and adaptability to engine conditions.