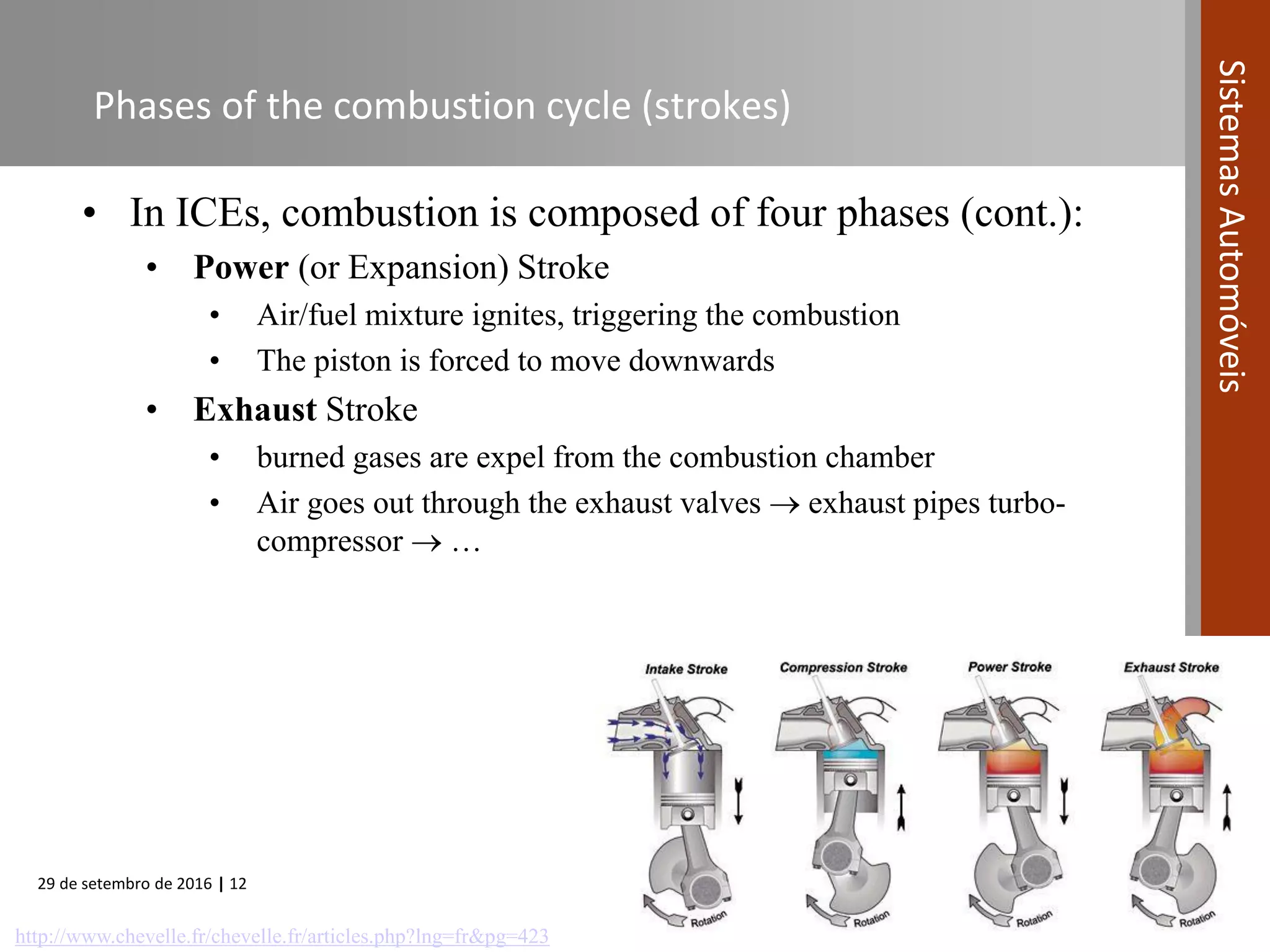
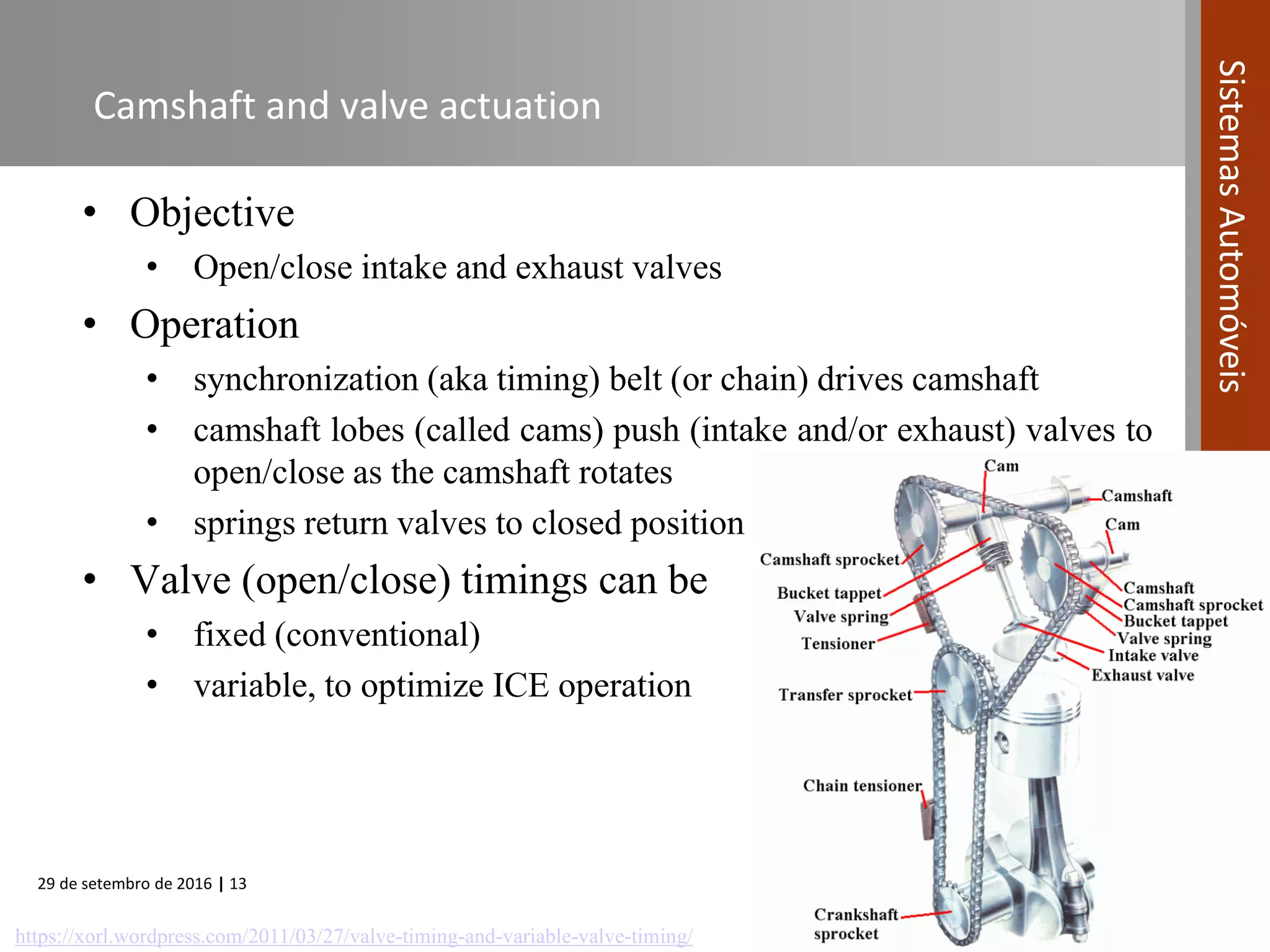
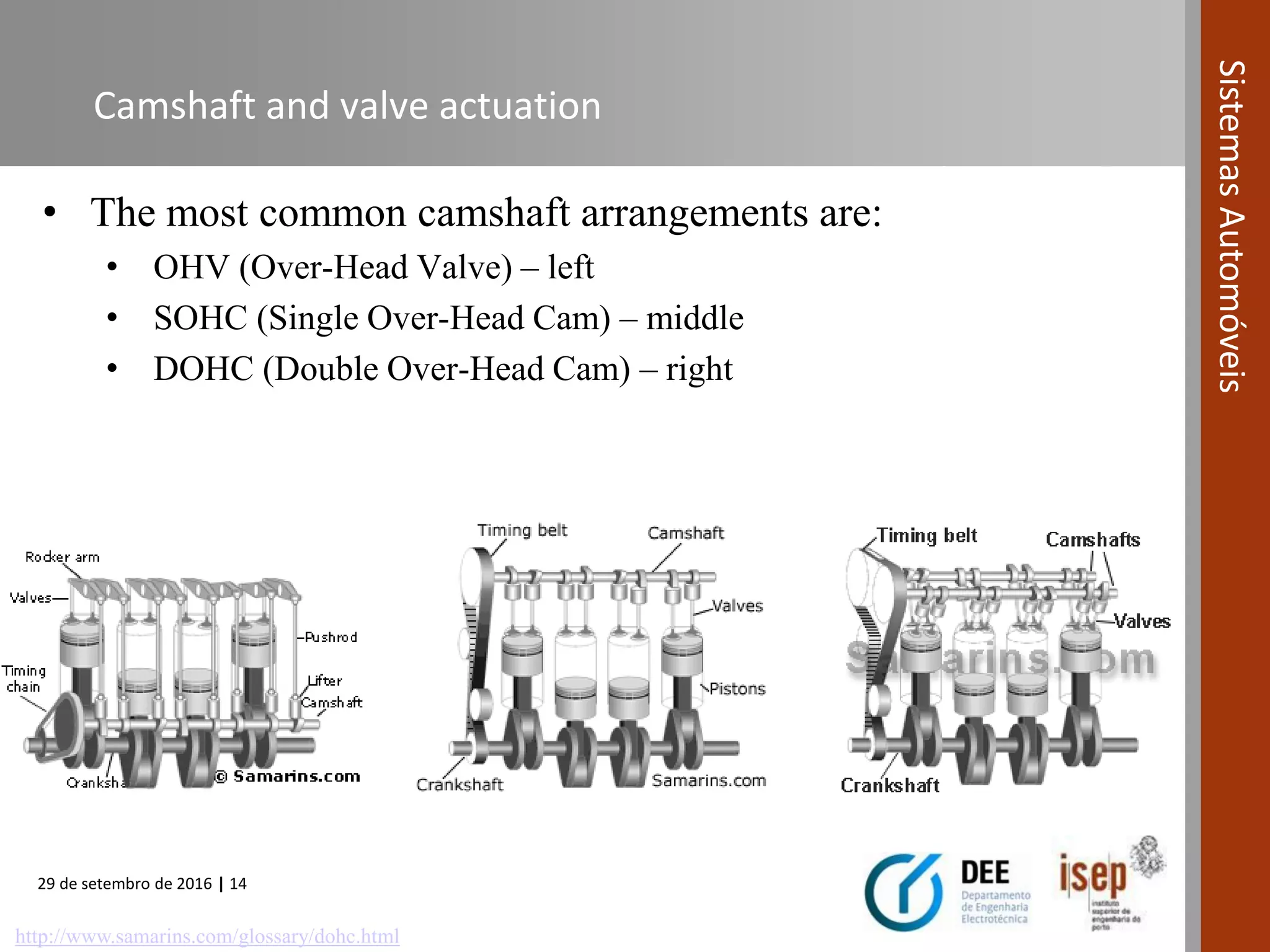
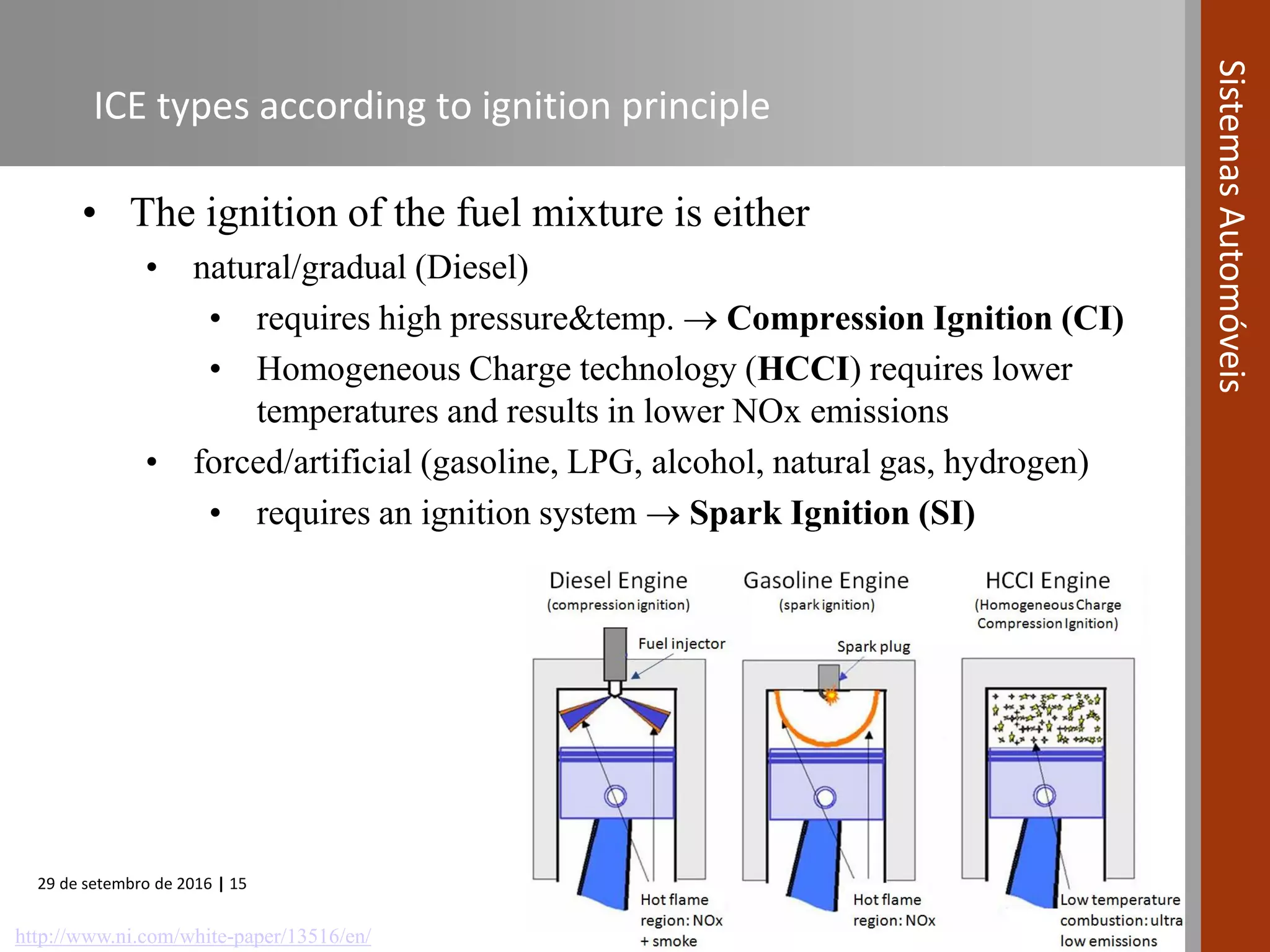
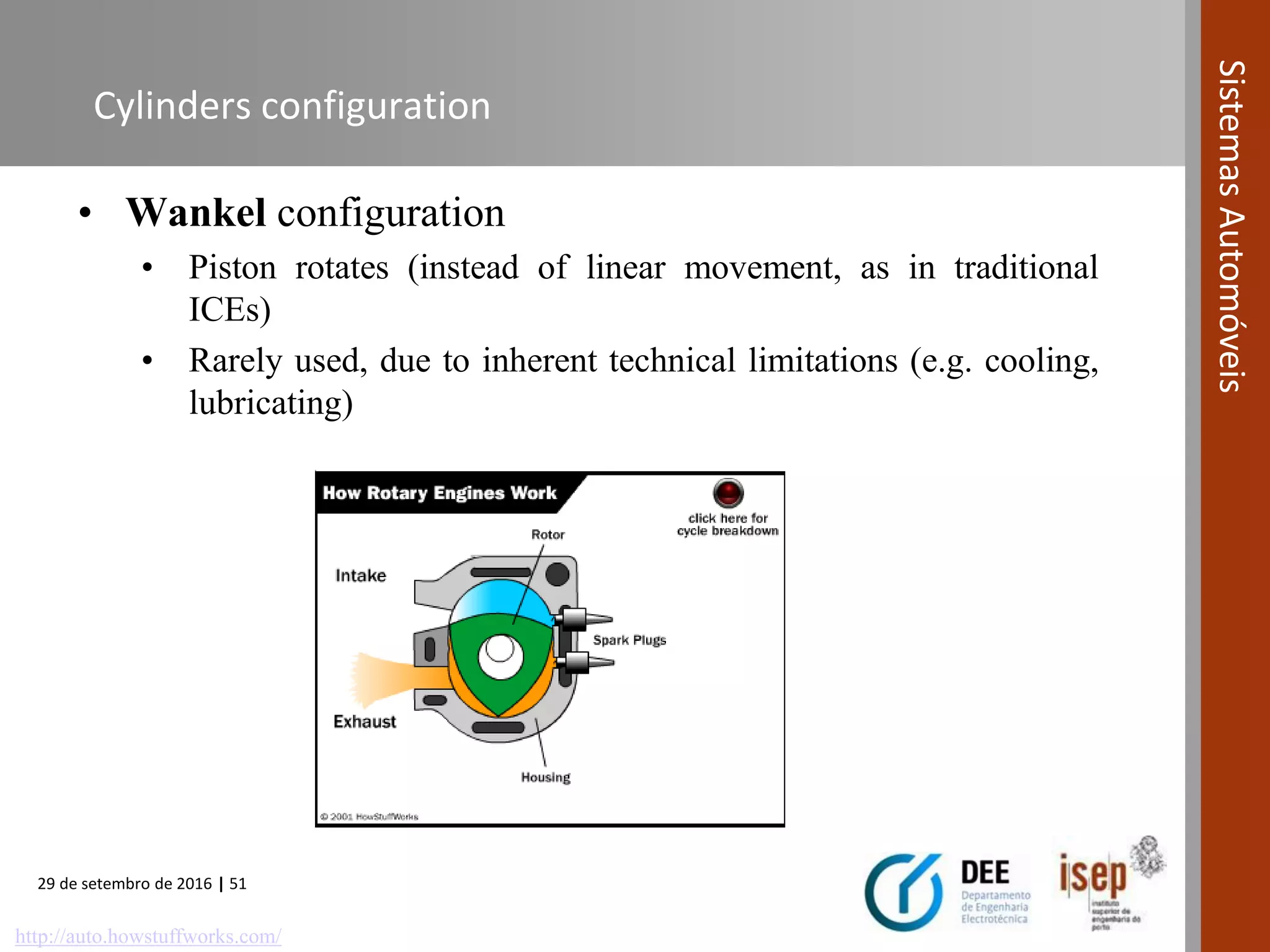
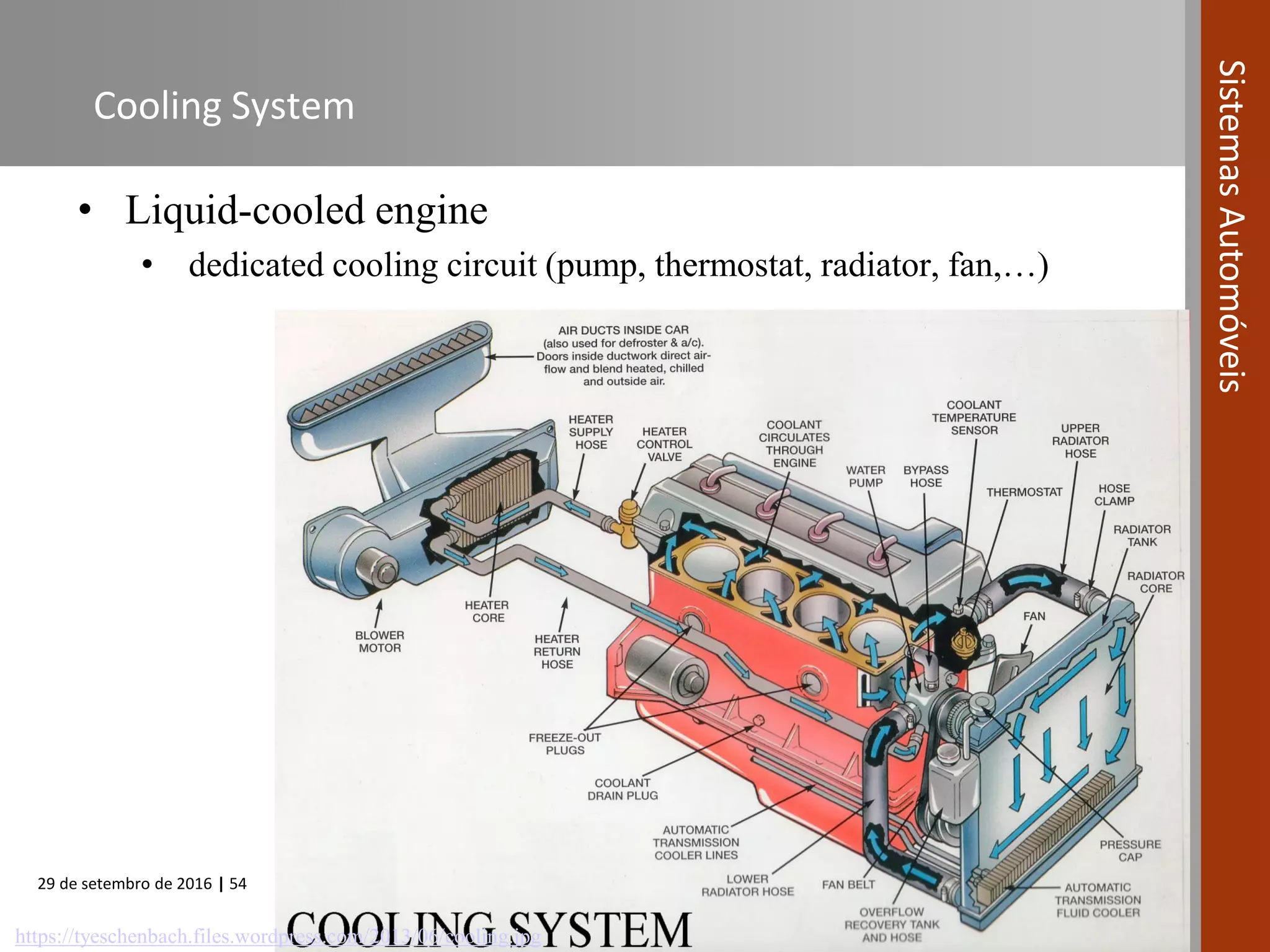
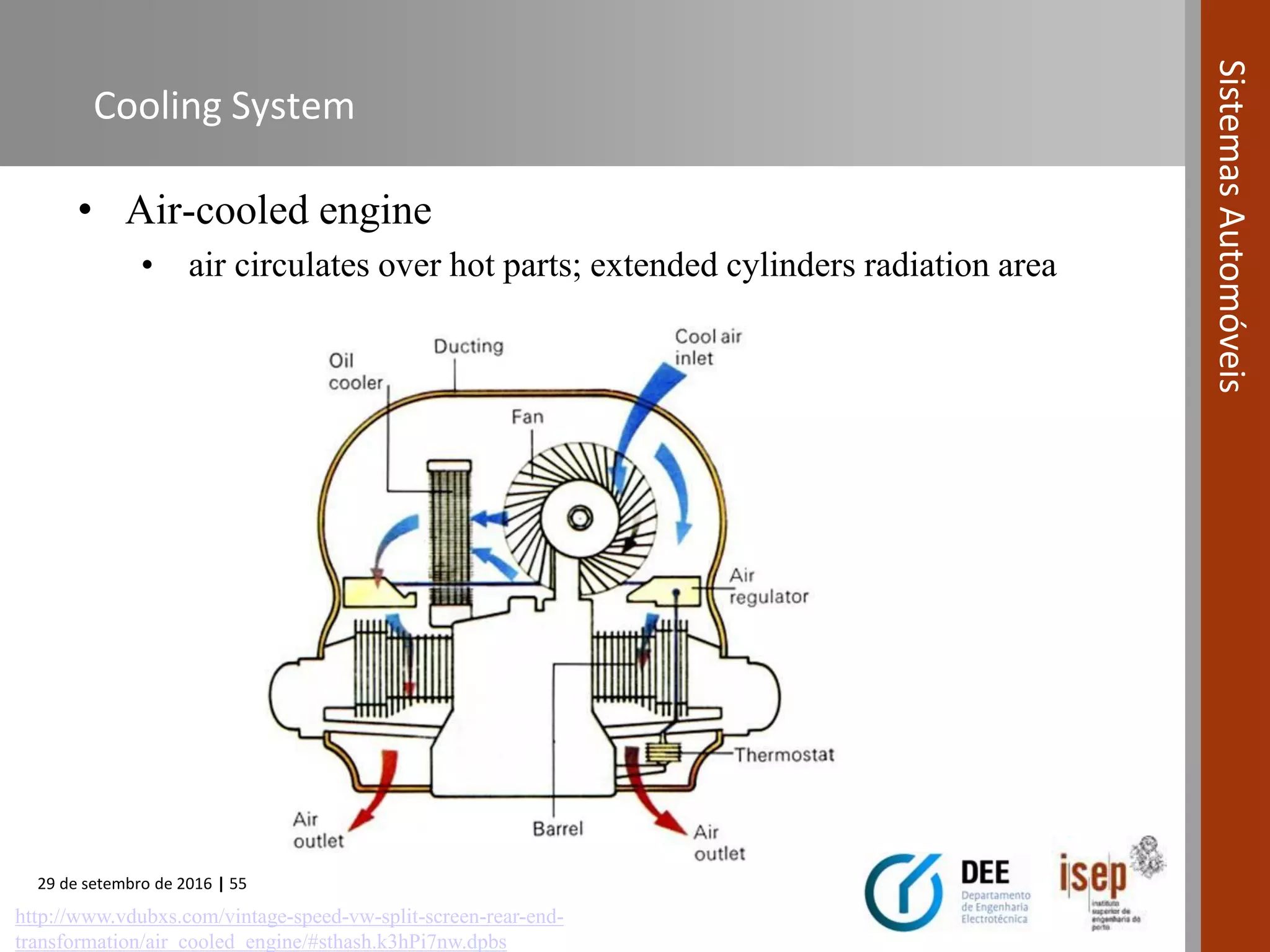
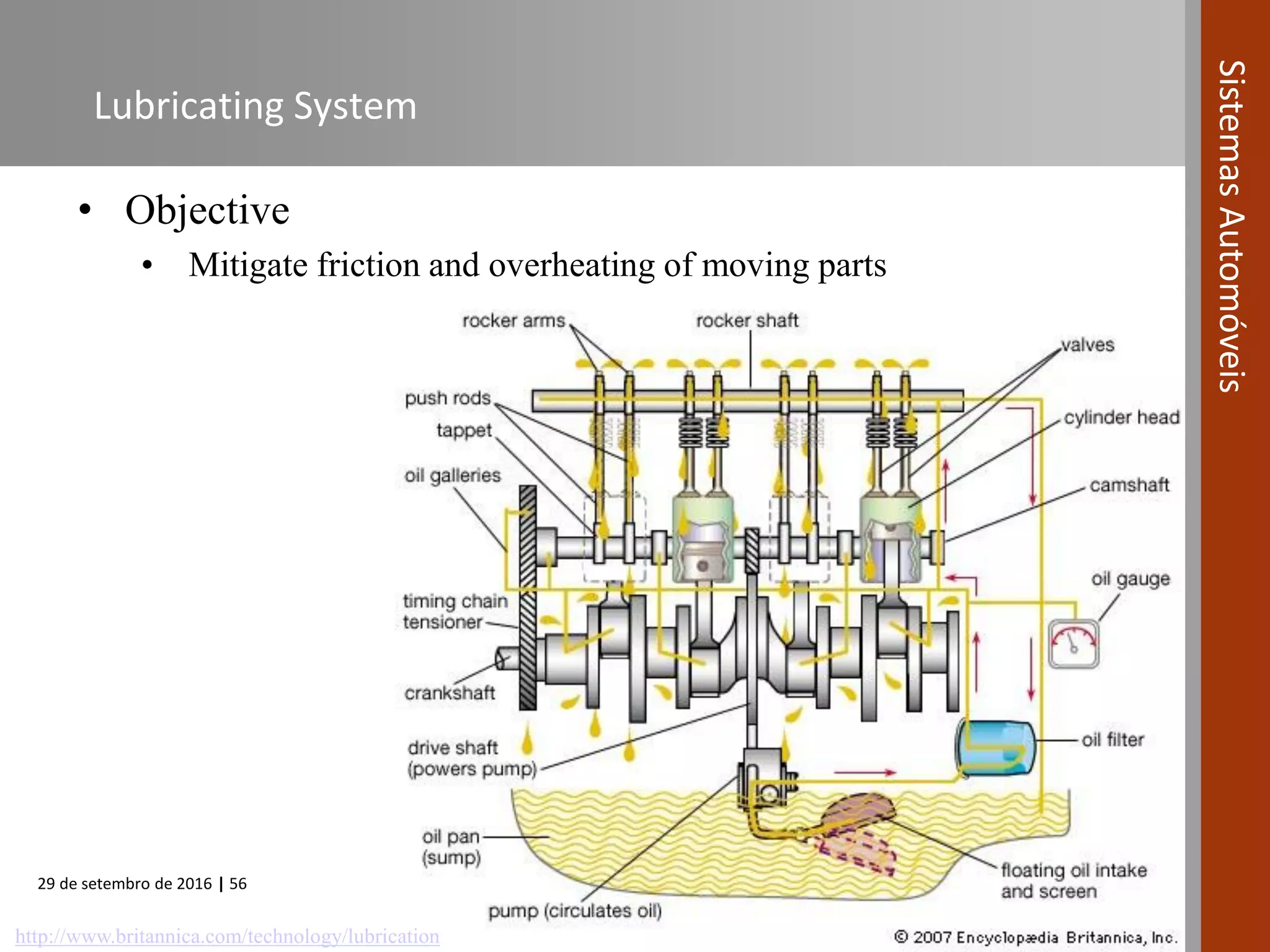
The document provides an overview of internal combustion engines (ICE), including their definition, operating principle, classification, types based on combustion and ignition methods, engine cycles, valve actuation, and fuel systems. It describes the four strokes of a 4-stroke engine as intake, compression, power, and exhaust. It also summarizes 2-stroke and rotary engine cycles. The document aims to cover basic ICE concepts.













![29 de setembro de 2016 | 58
SistemasAutomóveis
Bibliography
[1] Ricardo Marques (1030379), André Soares (1021069), class project under the
SIAUT course, ISEP, 2011.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01icebasics29set2016-161212154042/75/Automotive-Systems-course-Module-01-Internal-Combustion-Engine-ICE-basics-58-2048.jpg)