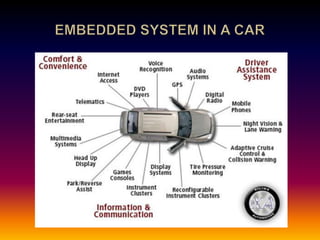
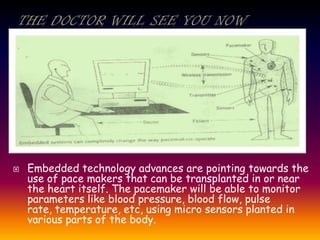
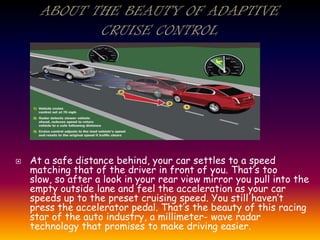
The document discusses embedded systems and their applications. It notes that embedded systems are controlled by microprocessors and use firmware. They are found in vehicles, medical devices, industrial systems, communications, and more. Adaptive cruise control is discussed as an example, using Doppler radar to maintain safe distances from other cars.