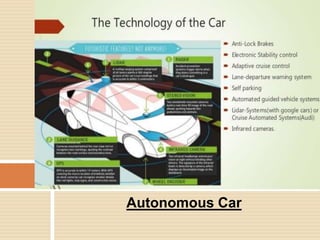
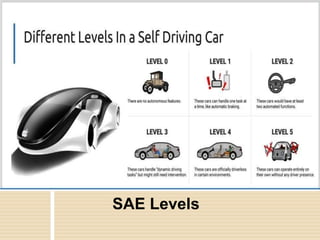
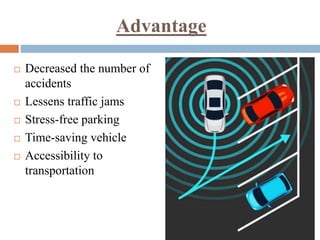
An autonomous car, also known as a self-driving car, uses sensors and computer vision to navigate and drive with little to no human input. Autonomous cars use radar, lidar, sonar, GPS and computer vision to perceive their surroundings and an advanced control system to identify navigation paths and obstacles. There are six levels of vehicle automation from fully manual to fully autonomous without human intervention. Autonomous vehicles have advantages like reducing accidents, easing traffic, and stress-free parking, but also disadvantages like high costs, safety and security concerns, and sensors being prone to failure or hacking.