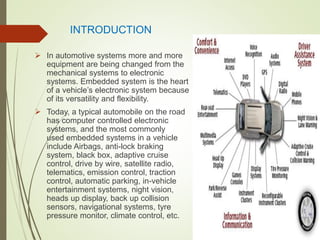
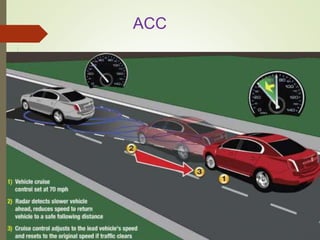
The document discusses the integration of embedded systems in modern automobiles, highlighting their transition from mechanical to electronic components. It covers various applications such as airbag systems, navigation, adaptive cruise control, automatic parking, and tire pressure monitoring, detailing their functionality and benefits. The conclusion emphasizes the significant impact of these systems on automobile design and manufacturing, marking a revolutionary change in the industry.