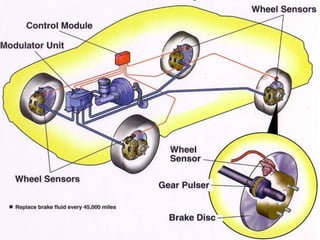
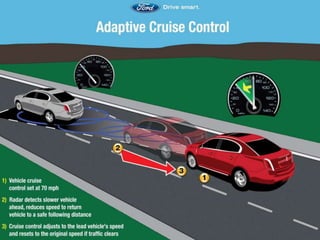
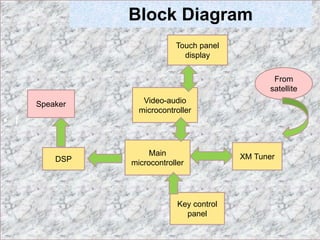
This document discusses embedded systems used in automobiles. It describes embedded systems as hardware and software designed to perform specific predefined tasks. Embedded systems allow for sophisticated functionality like operating on multiple algorithms simultaneously. The document then discusses several embedded applications used in cars, including anti-lock braking systems, adaptive cruise control, tire pressure monitoring systems, and satellite radio. It provides details on how each system works using embedded systems, microcontrollers, sensors, and other hardware. In conclusion, the document states that embedded systems have an important role in automobiles and a bright future as autonomous vehicles continue to advance.