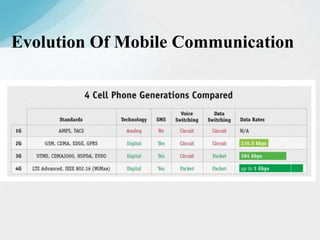
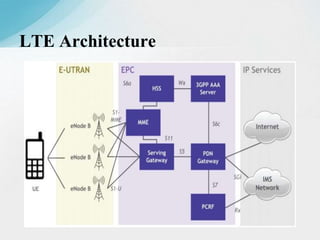
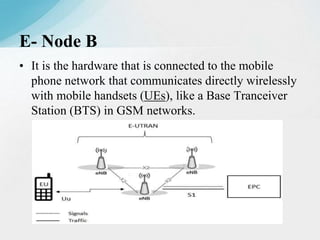
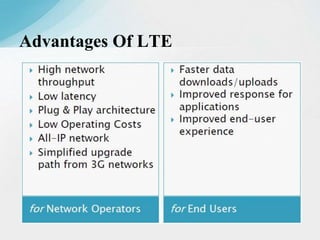
The document is a report on a two-month industrial training on LTE and VoLTE at Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited, which is India's first fully VoLTE operator providing 4G services. It discusses the technical architecture of LTE, including major components like user equipment, evolved UMTS terrestrial radio access network, and evolved packet core, along with the advantages of VoLTE over previous generations. The report emphasizes Jio's role in transforming the digital landscape in India by offering extensive 4G coverage and innovative services.