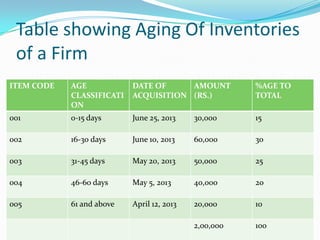
The document defines and explains economic order quantity (EOQ), which is the order size that minimizes the total costs of ordering and carrying inventory. EOQ is determined using the Wilson formula, which balances ordering costs (such as transportation and staff costs) against carrying costs (such as capital costs and storage fees). The document also provides examples of an aging schedule, which classifies inventory by age to help identify slow-moving items and better manage inventories.