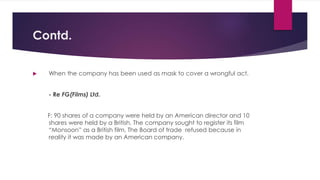
The document discusses the concept of lifting the corporate veil, which is an exception to the principle of a company having a separate legal identity from its owners. It provides examples from case law where the veil was lifted due to fraud, evasion of liability, the company being an alter ego or agent of its owners, or the company being used as a sham or mask. Statutory exceptions include misrepresentation in prospectus, failure to return application money, or investigation of ownership. The veil may also be lifted judicially when the company has been used to manipulate or evade liability based on precedents such as Gilford Motor Co. v Horne or Jones v Lipman.