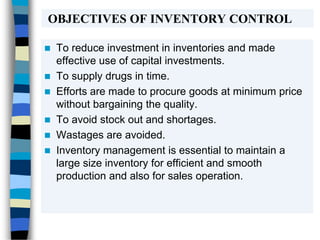
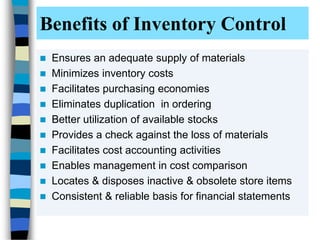
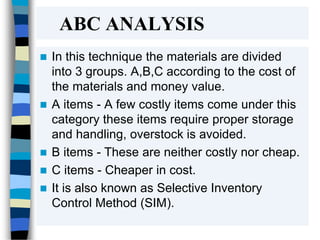
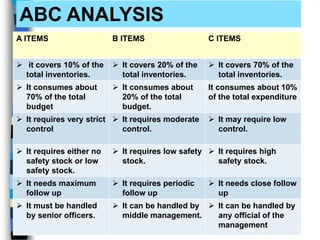
The document discusses various inventory control techniques used in pharmacy practices such as ABC analysis, VED analysis, economic order quantity, and FSN analysis to classify inventory items and maintain optimal inventory levels. The goals of inventory control are to reduce costs, ensure adequate supply of drugs, and avoid stockouts while making efficient use of capital. Proper inventory control techniques are important tools for smooth operations and effective management of business enterprises.