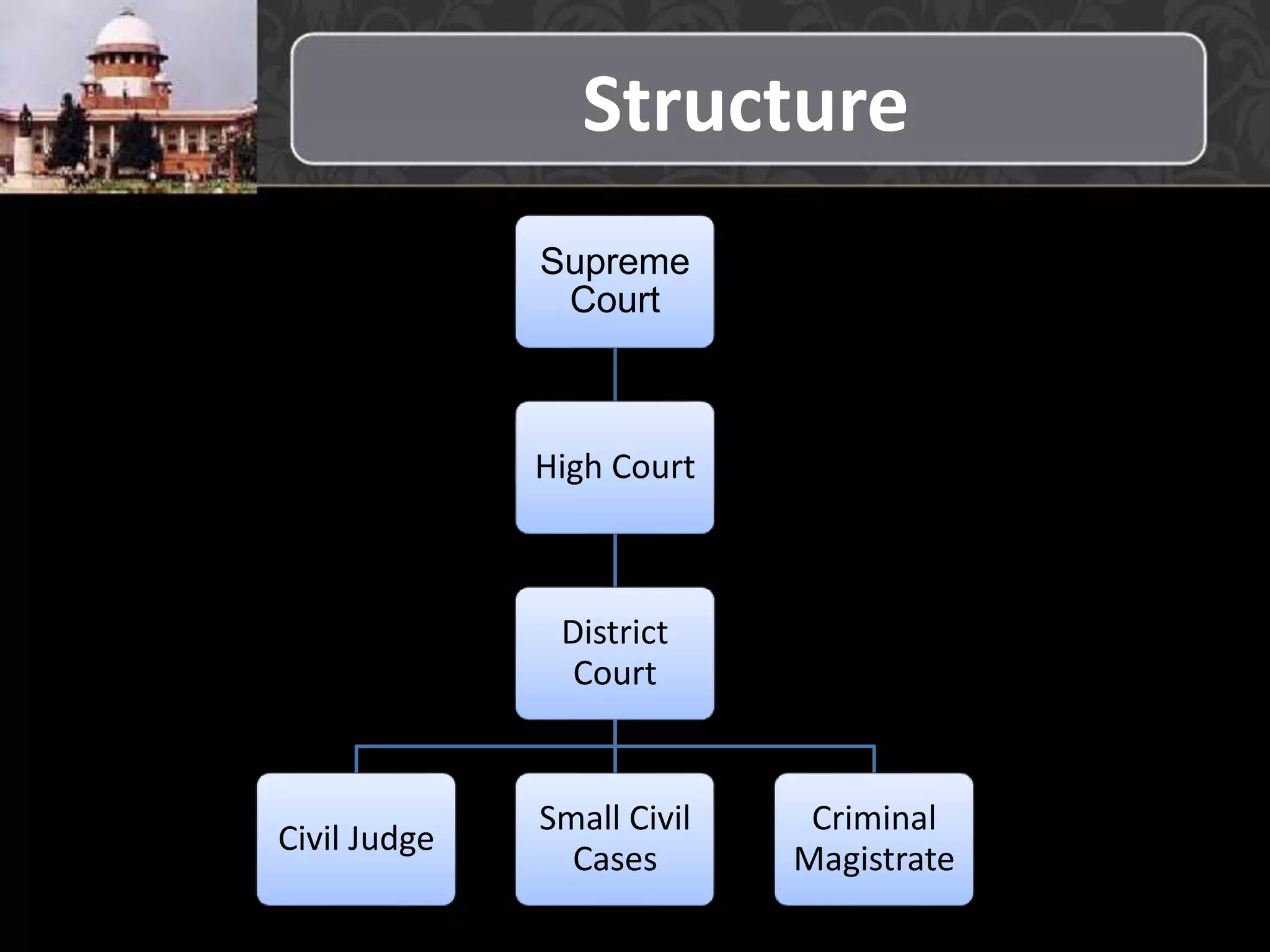
The Indian judicial system follows a three-tier structure with the Supreme Court at the top, High Courts below it, and district and lower courts at the bottom. It also includes specialized tribunals and traditional village courts. Cases can be appealed from lower to higher courts, with the Supreme Court being the final authority on interpreting the constitution and laws of India.