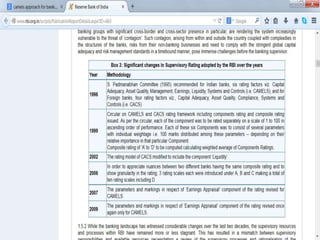
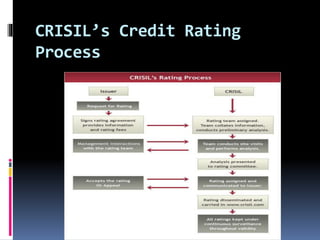
Credit ratings are assessments of creditworthiness or ability to repay loans, conducted by credit rating agencies. The top three agencies in the US are Moody's, Standard & Poor's, and Fitch Ratings, while in India they are CRISIL, CIBIL, and Fitch Ratings India. Credit ratings benefit investors by indicating risk, companies by lowering borrowing costs, and intermediaries by simplifying investment decisions. CRISIL analyzes factors like capital adequacy, asset quality, management capability, earnings, liquidity, and sensitivity to determine long-term credit ratings ranging from highest safety (AAA) to default (D).