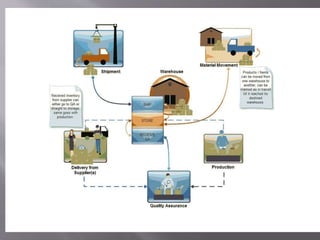
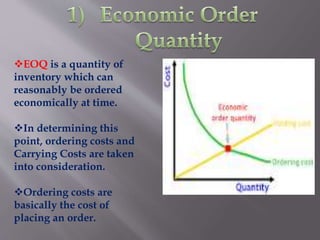
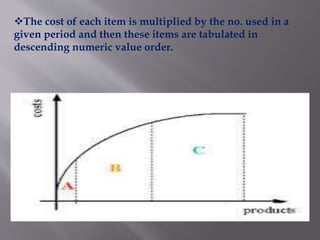
The document discusses various concepts related to inventory management. It defines inventory as stock of goods and explains that inventory includes raw materials, work in progress, and finished goods in a manufacturing context. It also discusses determining economic order quantities by balancing ordering and carrying costs. Other concepts covered include ABC analysis for classifying inventory, just-in-time manufacturing, inventory turnover ratios, and stock keeping units. The overall purpose of inventory management is to avoid overstocking or understocking.