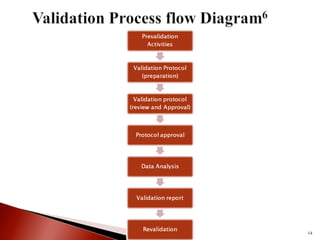
The document outlines the process of validation in various fields, detailing the structure and components of a validation protocol, which includes test parameters, critical parameters, and acceptance criteria. It emphasizes the importance of proper documentation and classification of validation procedures, such as qualification and cleaning validation. Additionally, it discusses the need for re-validation when equipment or processes change and provides references for further reading on pharmaceutical validation processes.